Label quality control method and device
A labeling and quality control technology, applied in the field of high-throughput sequencing, can solve the problems of difficult and accurate quality control of labels, and achieve the effect of low detection cost and simplified workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
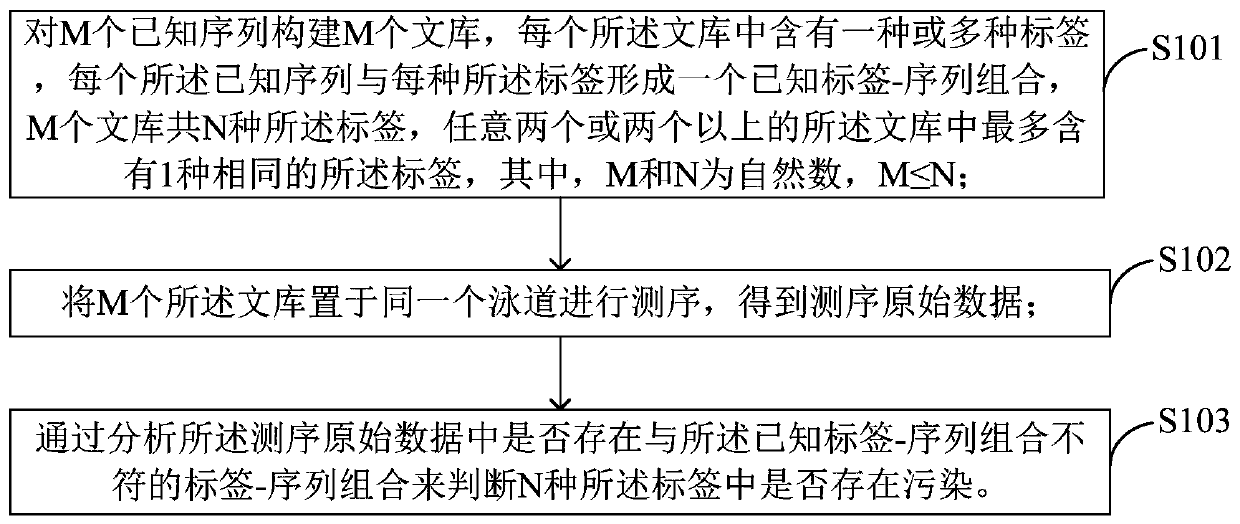
[0048] As mentioned in the background art, the existing method is difficult to perform quality control on the contamination of the index used in the mixed sample sequencing of the library. In order to improve this situation, the applicant of the present application improved the existing method. In a preferred embodiment, a method for label quality control is provided, such as image 3 As shown, the method includes:
[0049] Step S101, construct M libraries for M known sequences, each library contains one or more tags, each known sequence and each tag form a known tag-sequence combination, and there are N types of M libraries Tags, any two or more libraries contain at most one same tag, where M and N are natural numbers, M≤N;
[0050] Step S102, putting the M libraries in the same lane for sequencing to obtain the original sequencing data;
[0051] Step S103, by analyzing whether there is a tag-sequence combination inconsistent with known tag-sequence combinations in the raw ...
Embodiment 2
[0094] This embodiment also provides a device for label quality control, such as Figure 4 As shown, the device includes: a preset combination module 20, a sequencing module 40 and a pollution judgment module 60, wherein the preset combination module 20 is used to construct M libraries for M known sequences, and each library contains a or multiple tags, each known sequence and each tag form a known tag-sequence combination, there are N tags in M libraries, and any two or more libraries contain at most 1 identical tag, where , M and N are natural numbers, M≤N; the sequencing module 40 is used to place M libraries in the same lane for sequencing to obtain the original sequencing data; the pollution judgment module 60 is used to analyze whether there is a The known tag-sequence combinations do not match the tag-sequence combinations to determine whether there is contamination in the N tags.
[0095] The device for quality control of the above-mentioned tags performs quality in...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Oligo sequence: artificially synthesized nucleic acid sequence. The specific design method is: randomly generate sequences, each 150bp, and then compare it with the human reference genome sequence. The sequence that cannot be compared is used as the Oligo sequence here. The sequences selected in this example are 23 non-repetitive sequences selected from the sequences that meet the above design conditions (see the sequence listing for specific sequences), and were synthesized at Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
[0106] It should be noted that these Oligo sequences cannot be compared (mapped) with the human genome, so they can be used for library quality inspection of human genome sequencing. When it is used for co-sequencing with other species, it needs to be used after targeted analysis.
[0107] The 96 indexes mentioned in the examples of this application are derived from 96 of the 128 indexes in the MGI Easy DNAAdapters-96 (plate format) kit manufactured by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com