Methods for large tissue labeling, clearing and imaging
A labeling and labeling agent technology, which is applied in the preparation of test samples, instruments, and analysis materials, etc., can solve the problems of imaging without single-cell resolution in adult mice, making tissues transparent, and analyzing the body, so as to reduce time and effort. Cost, Quantity Reduction, Conversion Boosting Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
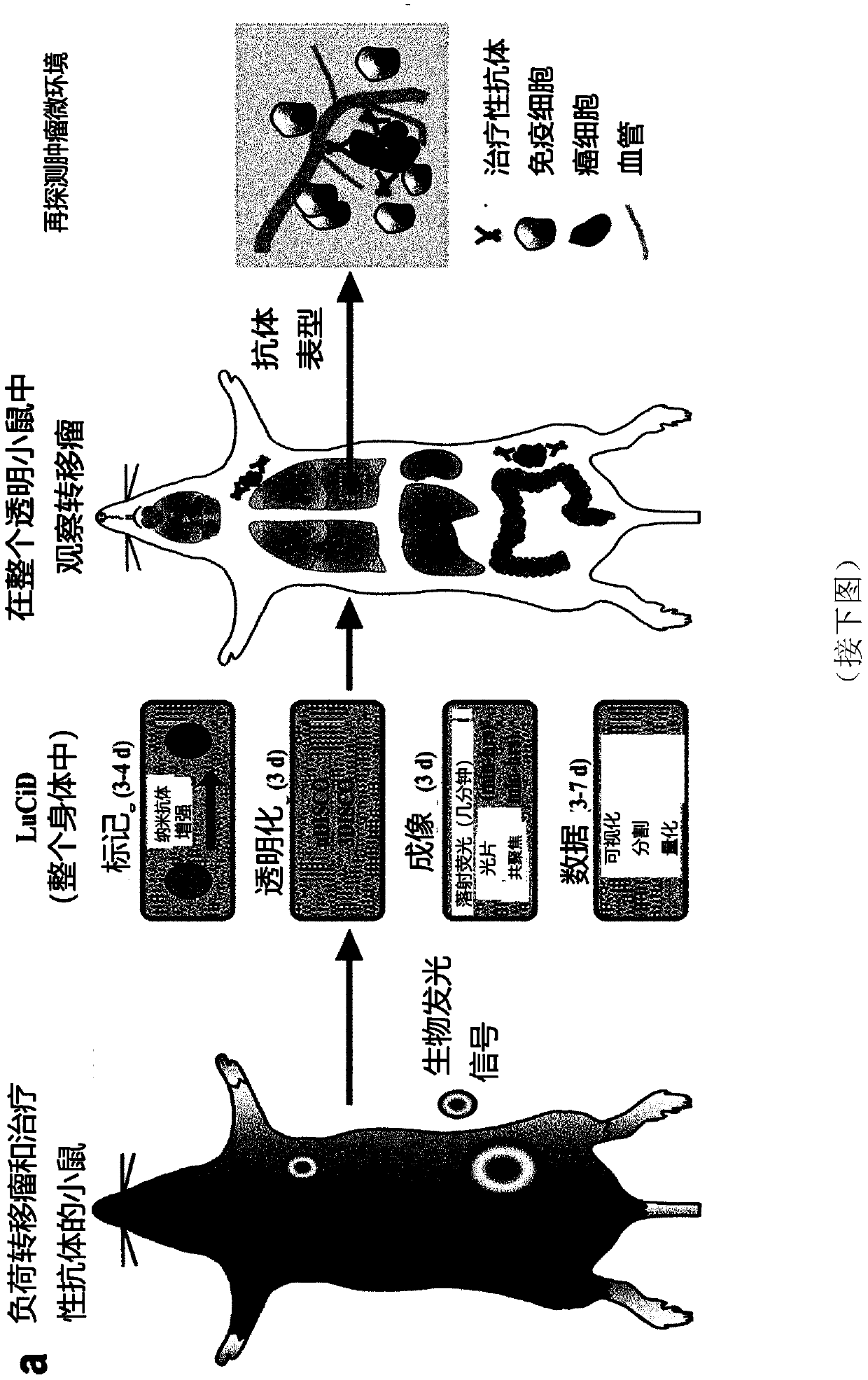
[0259] Example 1: Whole body immunolabeling of adult mice
[0260] The inventors set out to develop an immunostaining method for using fluorescent proteins to label cancer cells expressed throughout adult mice. The inventors reasoned that nanobodies are best suited to achieve immunolabelling of whole adult mice due to their small size (12-15 kDa compared to ~150 kDa for conventional antibodies) (Muyldermans, 2013; Yang et al., 2014). To deliver nanobodies conjugated to brightly colored Atto dyes (called nanoenhancers) throughout the body, the inventors developed a permeabilization solution containing Triton X-100, methyl-β-cyclodextrin (with for extracting cholesterol from biofilms) and trans-1-acetyl-4-hydroxy-L-proline (for loosening collagen networks) (Hama et al., 2015). The inventors circulated this permeabilization solution in mice (Gage et al., 2012; Ghanavati et al., 2014) via a high-pressure peristaltic pump (230mmHg, compared to 80-150mmHg for standard mouse heart...
example 2
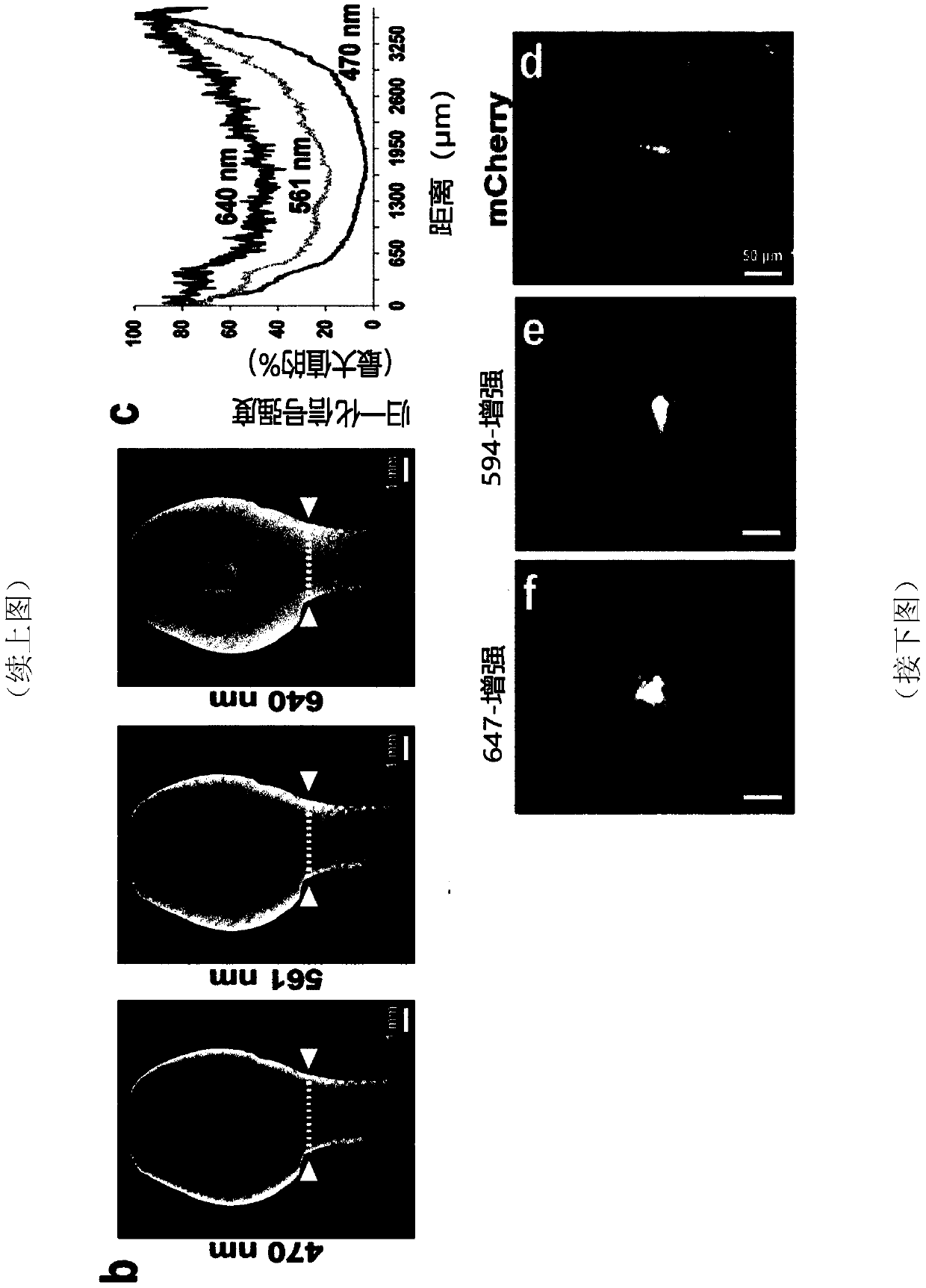
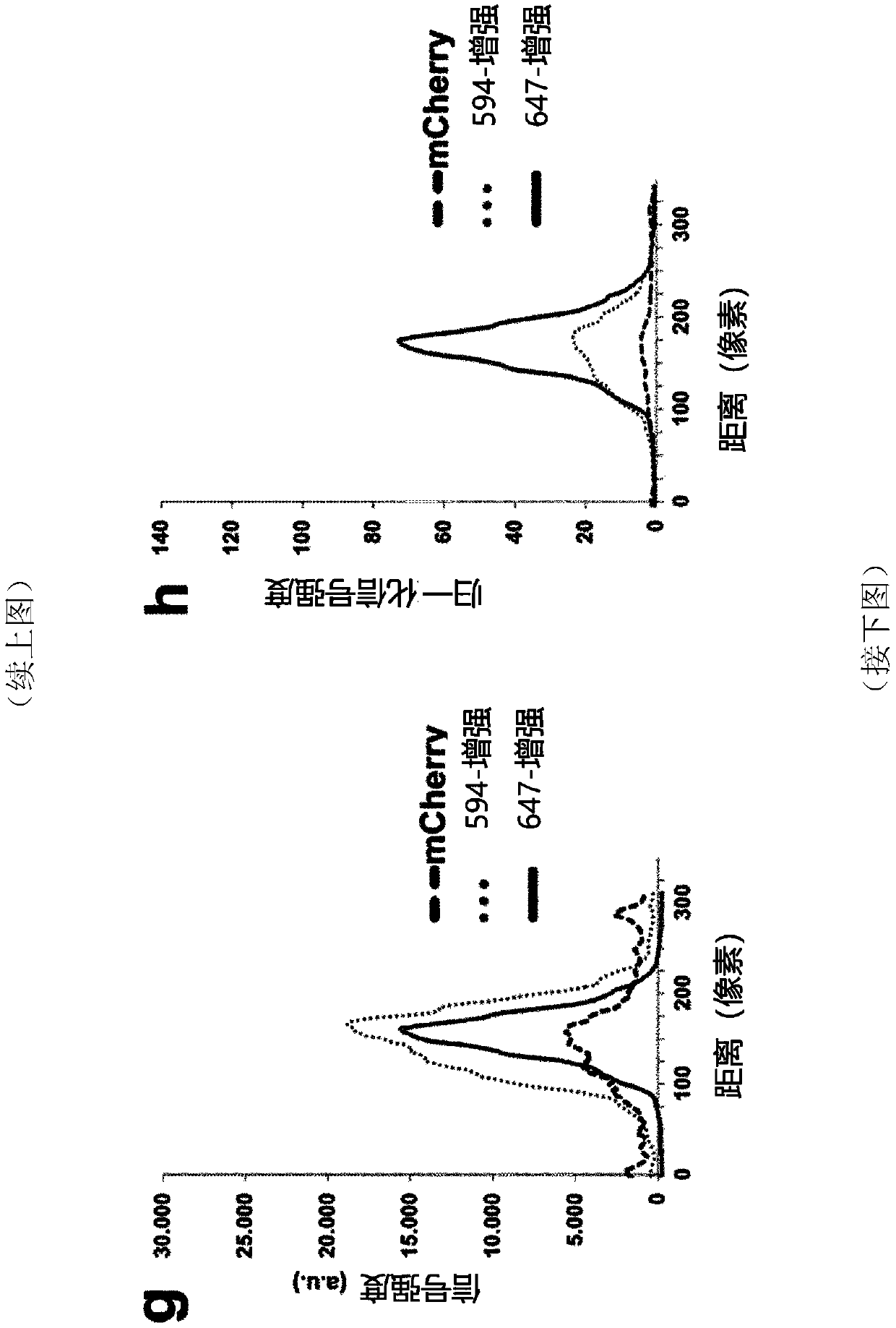
[0262] Example 2: Detection of tumor metastasis at single cell level in transparent mice
[0263] Many preclinical studies of cancer metastasis use mouse models using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), or ultrasound and bioluminescent imaging (Condeelis and Weissleder, 2010; Massoud and Gambhir, 2003, 2007; Ntziachristos, 2010; Pichler et al., 2008; Timpson et al., 2011) and other methods to observe cancer cells at the primary site and in the distant body Regional growth. Although these methods provide important longitudinal information on the size of primary tumors and large metastases, they can usually only resolve structures larger than 50 μm (approximately 75 cells), so they are not capable of detecting smaller cells composed of fewer cells. The resolution of micrometastases. Because it is critical to detect smaller-sized clusters of tumor cells that may rep...
example 3
[0265] Example 3: Assessing therapeutic antibodies using LuCiD
[0266] Monoclonal antibodies targeting key tumor cell antigens are one of the most promising cancer treatments to emerge in the past two decades. A number of tumor-targeting monoclonal antibodies have become part of the standard of care for a variety of solid and hematologic malignancies, and many are in early or late stages of clinical development (Pandey and Mahadevan, 2014). Typically, therapeutic antibodies are raised against tumor-associated antigens overexpressed by cancer cells. Once these antibodies are injected, they are distributed throughout the body to target cancer cells. However, to date, there is no method for determining the distribution of therapeutic antibodies throughout the body at cellular resolution. Here, the inventors used LuCiD to assess the biodistribution of the therapeutic monoclonal antibody 6A10 against human CA12 (Battke et al., 2011). CA12 is overexpressed in various types of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com