Method for purifying AgCd alloy from AgCd waste and recycling AgCd alloy
A waste and alloy technology, which is applied in the field of purification and recycling of AgCd alloys, can solve the problems of low utilization rate, poor product processing performance, and comparison, and achieve the effects of fast material turnover, no industrial three waste pollution, and significant economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1) Set the density of the equal area to 0.32g / cm 3 , 64% porosity, 35nm-950um pore size, 0.8 mm thick SiC foam ceramic sheet is placed at the bottom of the crucible, and then 25Kg AgCd10.5 scraps are placed, and the melting and refining is carried out in three stages: the first stage: heating up to 500°C Constant temperature for 0.5h; second stage: heating up to 900°C and constant temperature for 0.5h; third stage: 800°C, cooling at a constant speed, and controlling the cooling time for 0.5h;
[0021] 2) taking out the ceramic foam sheets floating on the surface of the melt to obtain a high-purity AgCd alloy melt;
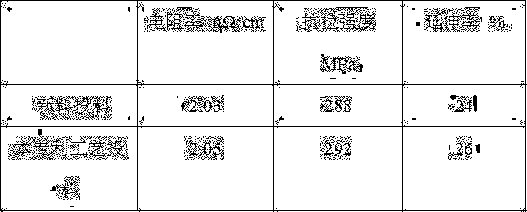
[0022] 3) The AgCd alloy is used to feed AgCdO (10), and the product performance comparison is shown in the following table:
[0023]
Embodiment 2
[0025] 1) Set the density of the equal area to 0.42g / cm 3 Al with a porosity of 78%, a pore size of 45nm-865um, and a thickness of 0.6 mm 2 o 3 The foam ceramic sheet is placed at the bottom of the crucible, and then 22Kg of AgCd13.13 trimmings are put in, and the melting and refining is carried out in three stages: the first stage: the temperature is raised to 600°C for 1 hour; the second stage: the temperature is raised to 1000°C and the temperature is held for 1 hour; the third stage Stage: 900°C, cooling at a constant speed, and controlling the cooling time for 0.5h;
[0026] 2) taking out the ceramic foam sheets floating on the surface of the melt to obtain a high-purity AgCd alloy melt;
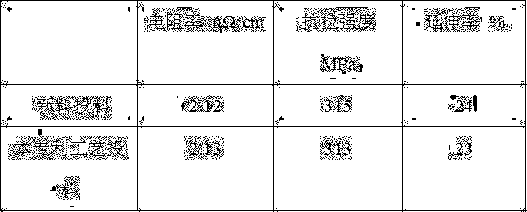
[0027] 3) Using the AgCd alloy to feed AgCdO (12), the product performance comparison is shown in the following table:
[0028]
Embodiment 3
[0030] 1) ZrO with an equal area density of 1.27g / cm3, a porosity of 86%, a pore diameter of 68nm-730um, and a thickness of 1.2mm 2 The ceramic foam piece is placed at the bottom of the crucible, and then 20Kg of AgCd8.75 corner material is put in, and the melting and refining is carried out in three stages: the first stage: the temperature is raised to 600°C and kept at a constant temperature for 0.5h; the second stage: the temperature is raised to 1000°C and held at a constant temperature for 0.5h; The third stage: 800°C, cooling at a constant speed, and the controlled cooling time is 1h;
[0031] 2) taking out the ceramic foam sheets floating on the surface of the melt to obtain a high-purity AgCd alloy melt;
[0032] 3) Using the AgCd alloy to feed AgCdO (15), the product performance comparison is shown in the following table:
[0033] Resistivity μΩ·cm Tensile strength MPa Elongation % New material feeding 2.21 330 22 Feeding of this patented ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com