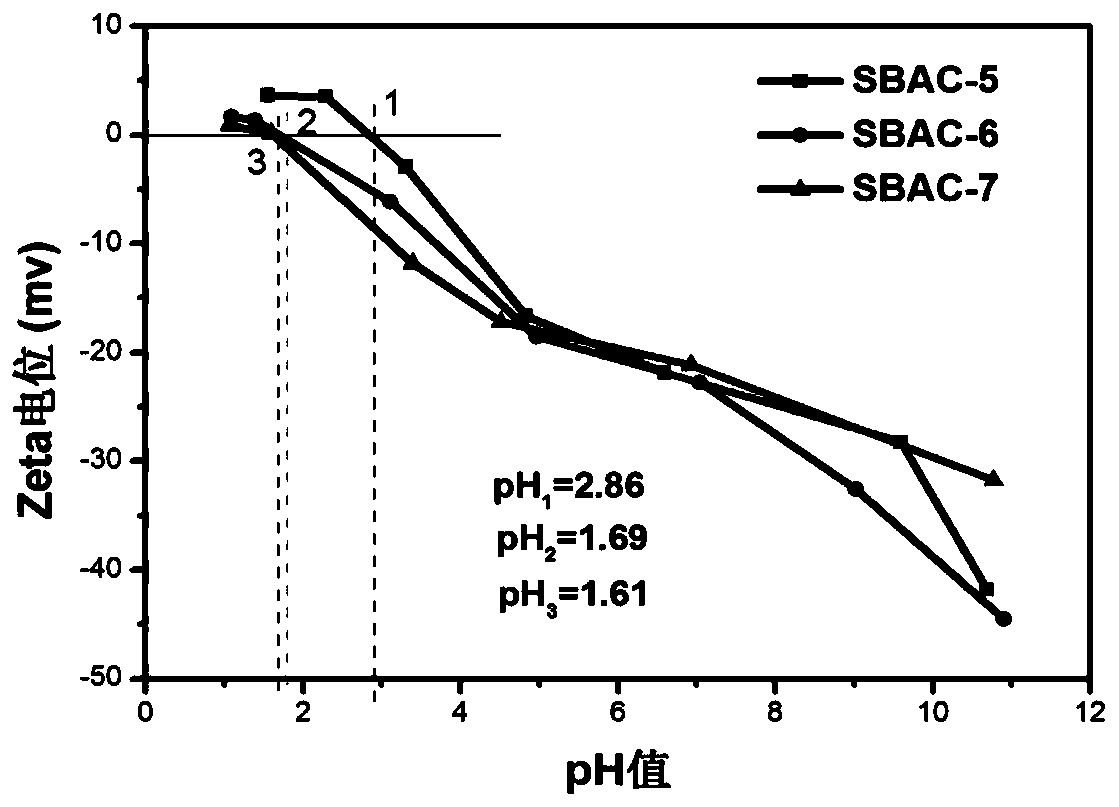
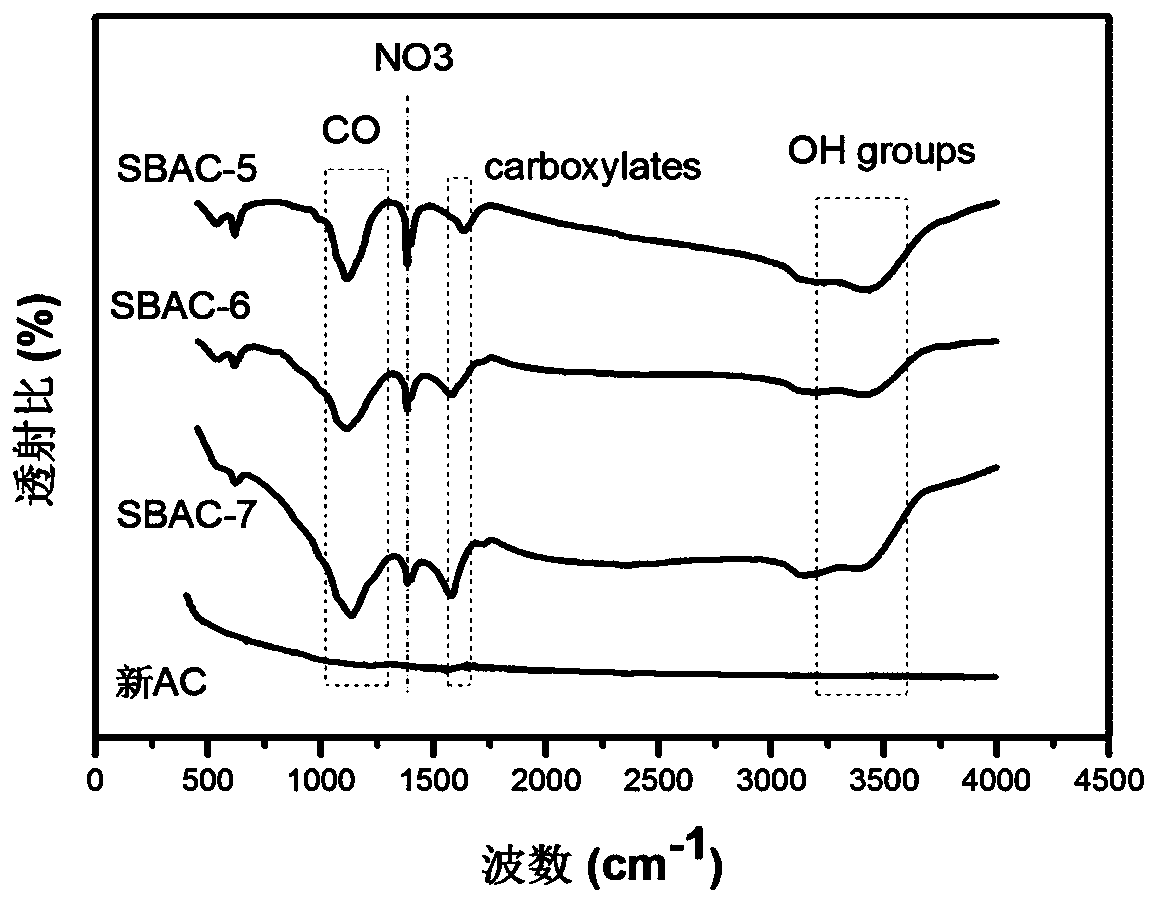
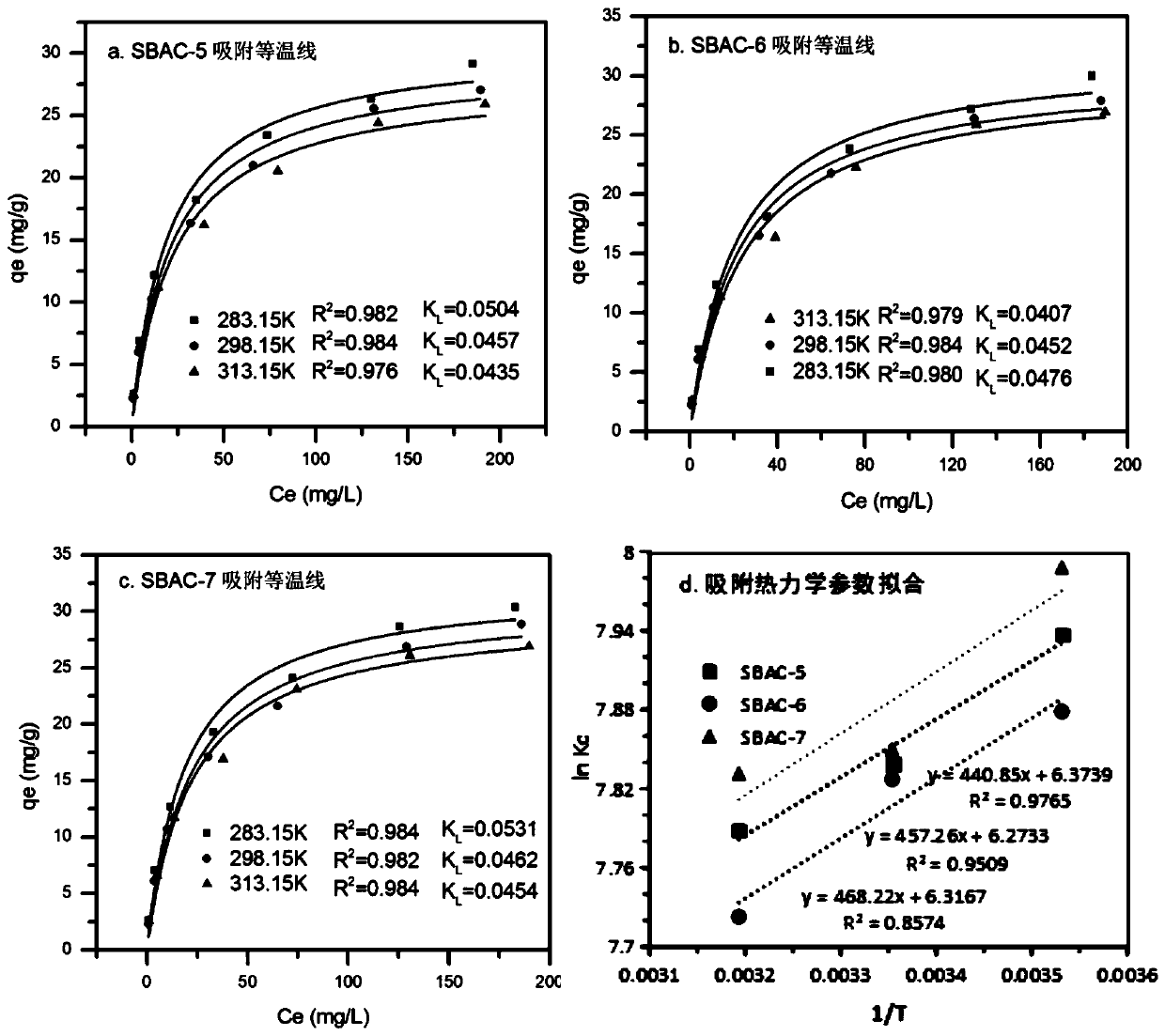
Method for removing radionuclide strontium in water
A radionuclide and water removal technology, applied in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering and other directions, can solve the problem of unsatisfactory removal of radioactive strontium in water, and achieve the effects of low cost, economic benefit, resource saving, and avoidance of secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1: The two-stage BAC process has been in operation for 5 years, and the first-stage adsorption pool has failed to meet the requirements of the internal control indicators of the water plant, so it is set as the second-stage adsorption pool. The plant uses coagulation, sedimentation, two-stage BAC(O 3 / GAC) and filtration combined water treatment process, its production capacity is (200,000m 3 / d), the empty bed contact time EBCT of the AC bed is 14 minutes, the height of the AC bed is 2.0 meters, the ozone dose is 2.0-2.5mg / L, and the contact time is 24 minutes. The water source of the water plant comes from the HP River, and the average effluent quality of the water plant is better than the Chinese drinking water quality standard.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: The two-stage BAC process has been in operation for 6 years, and the first-stage adsorption pool has failed to meet the requirements of the internal control indicators of the water plant, so it is set as the second-stage adsorption pool. The plant used coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and two-stage BAC(O 3 / GAC) combined water treatment process with a production capacity of (260,000m 3 / d), the empty bed contact time EBCT of the AC bed is 14 minutes, the height of the AC bed is 1.8 meters, the ozone dose is 1.8-2.0 mg / L, and the contact time is 20 minutes. The water source of the water plant comes from the CJ River, and the average effluent quality of the water plant is better than the Chinese drinking water quality standard.
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3: The two-stage BAC process has been in operation for 7 years, and the first-stage adsorption pool has failed to meet the requirements of the internal control indicators of the water plant, so it is set as the second-stage adsorption pool. The plant used coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and two-stage BAC(O 3 / GAC) combined water treatment process, its production capacity is (100,000m 3 / d), the empty bed contact time EBCT of the AC bed is 14 minutes, the height of the AC bed is 2.0 meters, the ozone dose is 2.0-2.5mg / L, and the contact time is 22 minutes. The water source of the water plant comes from the HP River, and the average effluent quality of the water plant is better than the Chinese drinking water quality standard.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com