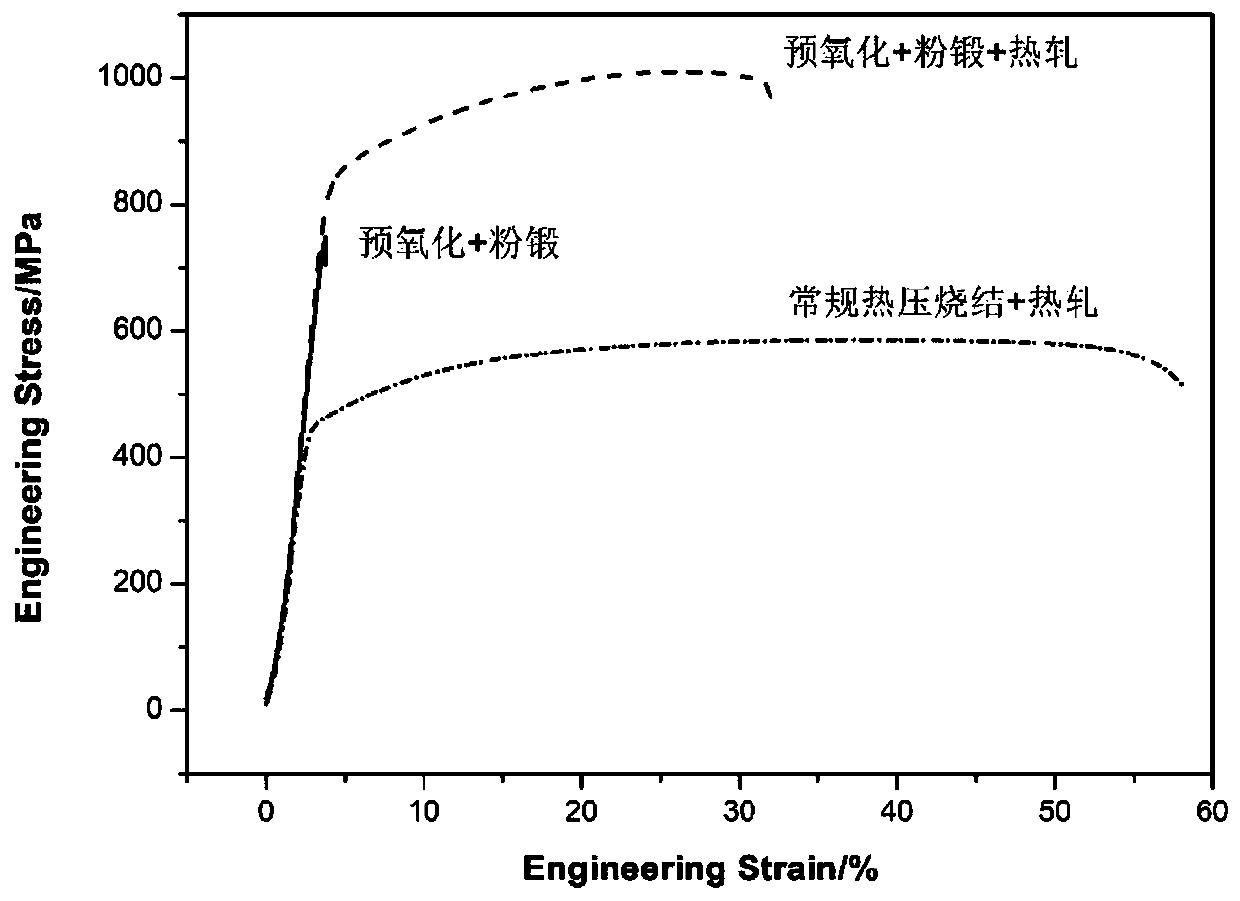
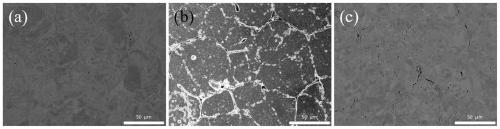
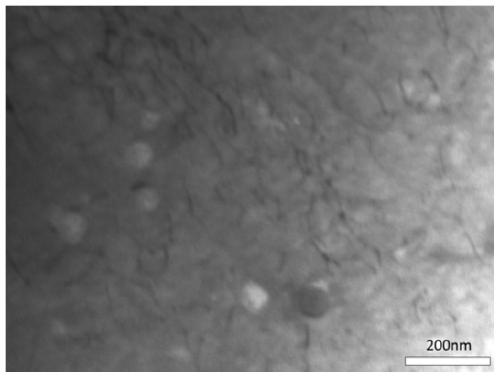
Powder metallurgy material for endophytic oxide strengthening alloy and preparation method thereof
A powder metallurgy and strengthening alloy technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy materials, can solve the problems of poor performance, limited doping amount, poor bonding and other problems of composite materials, and achieve the effect of low cost, uniform distribution and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0022] A method for preparing powder metallurgy materials of endogenous oxide-strengthened alloys, comprising the following steps:
[0023] 1) Self-made or purchased initial alloy powder with particle size between 20-100 μm;
[0024] 2) cold-pressing the alloy powder in step 1) in a cold-pressing die at a pressure of 400-700 MPa to form a preform;
[0025] 3) The preform obtained in step (2) is placed in a sintering furnace, and in N 2 +(2-5vol.%)O 2 Carry out pressureless pre-sintering in the atmosphere, determine the appropriate pre-sintering temperature and forging temperature according to the "MPIF Standard 35-2012" standard, sinter under vacuum conditions for 20-480 minutes, and then put the pre-sintered parts into the hot forging die Hot forging is performed at the hot forging temperature in the cavity. After forging, the surface oxide layer is removed by shot peening, and the structural allowance is removed by machining and finishing to obtain powder forgings;
[002...
Embodiment 1
[0029] This embodiment 1 provides a kind of Fe 40 Mn 40 Co 10 Cr 10 Powder metallurgy material, self-made Fe 40 Mn 40 Co 10 Cr 10 Alloy powder, its particle size is 40 μm; the above alloy powder is placed in a cold pressing mold for cold pressing, and the pressure is 700 MPa to form a preform; the obtained preform is placed in a sintering furnace, in N 2 +2vol.%O 2 Pressureless pre-sintering is carried out in the atmosphere, that is, sintered at 1150 °C for 240 minutes under vacuum conditions and pre-oxidized, and then the pre-sintered parts are placed in the hot forging die cavity for hot forging at 1100 °C, and shot blasting is removed after forging. The surface oxide layer is machined and finished to remove the structural allowance to obtain powder forgings; the powder forgings are hot-rolled at 1000 ℃ to obtain Fe 40 Mn 40 Co 10 Cr 10 Powder metallurgy materials.
Embodiment 2
[0031] This embodiment 2 provides a kind of Fe 40 Mn 40 Co 10 Cr 10 Powder metallurgy materials, purchase Fe 40 Mn 40 Co 10 Cr 10 Alloy powder, its particle size is 100μm; the above alloy powder is placed in a cold pressing mold for cold pressing, and the pressure is 400MPa to form a preform; the obtained preform is placed in a sintering furnace, in N 2 +5vol.%O 2 Pressureless pre-sintering is carried out in the atmosphere, that is, sintered at 1150 °C for 20 minutes under vacuum conditions and pre-oxidized, and then the pre-sintered parts are placed in the hot forging die cavity for hot forging at 1100 °C, and shot blasting is removed after forging. The surface oxide layer is machined and trimmed to remove the structural allowance to obtain powder forgings; the powder forgings are forged at 1000 ℃ to obtain Fe 40 Mn 40 Co 10 Cr 10 Powder metallurgy materials.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com