Fluorescently-labeled polyacrylamide, and preparation method and application thereof as visual soil structure improver
A polyacrylamide and fluorescent labeling technology, applied in the fields of application, soil conditioning materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem that polyacrylamide solution does not achieve the effect visible to the naked eye, and can control the decomposition reaction, increase the content, low temperature effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
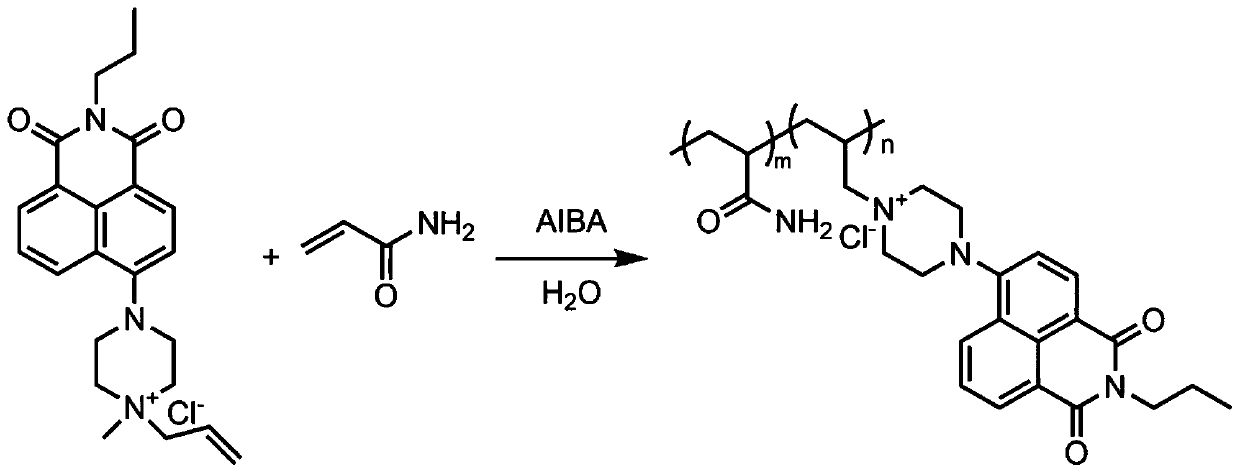
[0045] The preparation of the polyacrylamide (FL-PAM) of fluorescent mark comprises the following steps (chemical reaction scheme can refer to figure 1 shown):
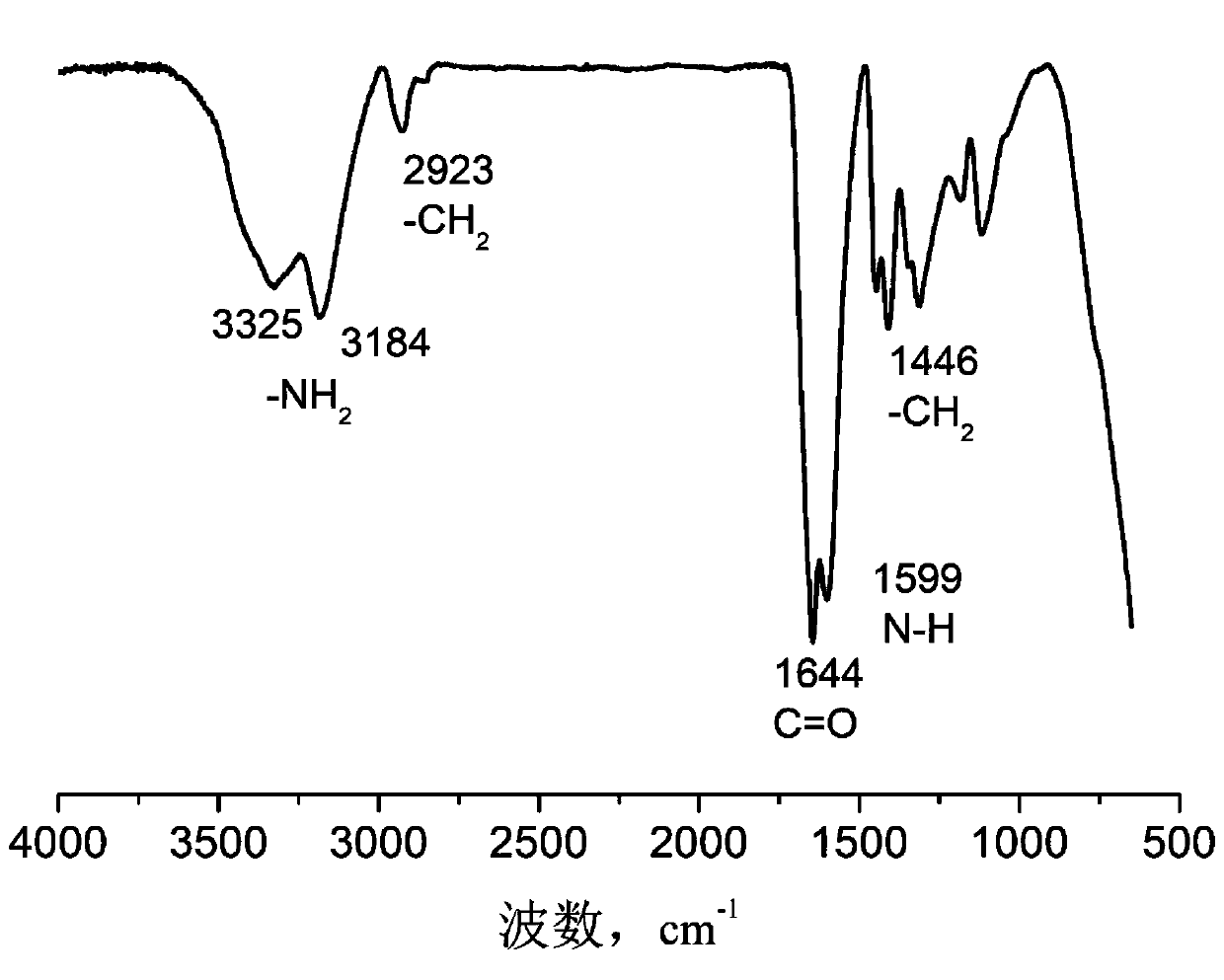
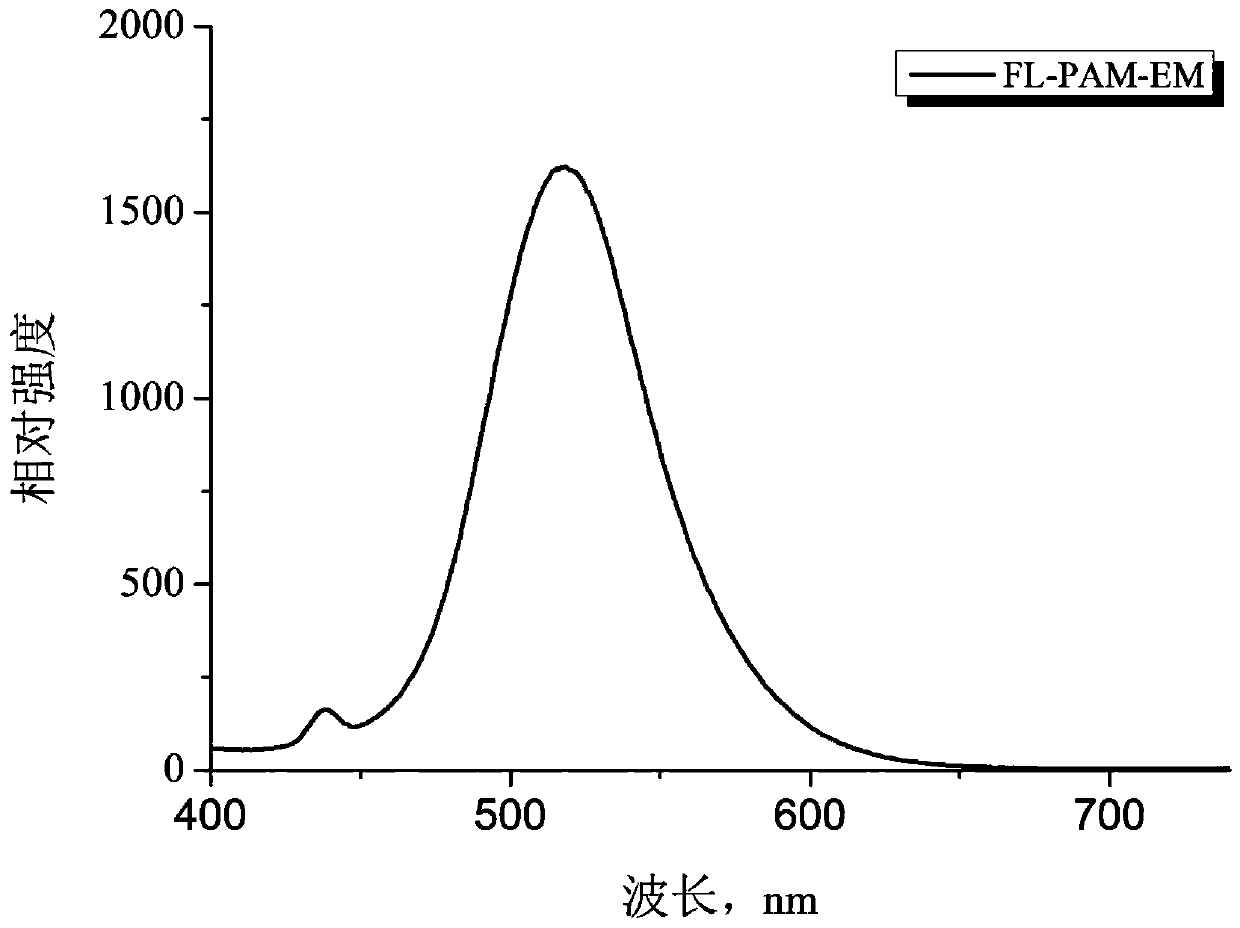
[0046] Add 7.1g of acrylamide, 0.0071g of FL, and 0.0071g of urea to a three-neck flask equipped with mechanical stirring, reflux condenser, and nitrogen gas, add 100mL of water to dissolve, mechanically stir at a speed of 250 r / min, and heat to After 56°C, add 0.0036 g of initiator azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride (AIBA) and react for 6 hours. Pour the reacted product into a beaker with ethanol. After washing for five times, put it into an oven at 80° C. for drying, and grind it into uniform small particles after drying to obtain the fluorescently labeled polyacrylamide. The reference standard "GB / T 12005.10-1989 Polyacrylamide Intrinsic Viscosity Determination Method", "GB / T 12005.10-1992 Polyacrylamide Molecular Weight Determination" measures its viscosity average molecular weight to be about 5×10 6 . The flu...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The preparation of the polyacrylamide (FL-PAM) of fluorescent mark comprises the following steps (chemical reaction scheme can refer to figure 1 shown):
[0049] In a three-neck flask equipped with mechanical stirring, reflux condenser, and nitrogen gas, add 7.1g of acrylamide, FL0.0071g, without urea, add 100mL of water to dissolve, mechanically stir at a speed of 230r / min, and heat to 60 ℃, then add initiator azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride (AIBA) 0.0071g to react for 6h, pour the reacted product into a beaker filled with ethanol, separate out and cut into pieces, replace with new ethanol and wash under mechanical stirring Five times, and then placed in an oven at 80° C. for drying, and then ground into uniform small particles to obtain the fluorescently labeled polyacrylamide. The viscosity-average molecular weight of the reference standard "GB / T 12005.10-1989 Polyacrylamide Intrinsic Viscosity Determination Method" and "GB / T 12005.10-1992 Polyacrylamide Molecul...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The preparation of the polyacrylamide (FL-PAM) of fluorescent mark comprises the following steps (chemical reaction scheme can refer to figure 1 shown):
[0052] In a three-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, a reflux condenser, and nitrogen gas, add 7.1g of acrylamide, FL 0.0213g, without urea, add 100mL of water to dissolve, mechanically stir at a speed of 210r / min, and heat to 56°C, then add 0.1065g of initiator azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride (AIBA) to react for 6 hours, pour the reacted product into a beaker with ethanol, separate out and cut it into pieces, replace with new ethanol and stir it under mechanical stirring After washing five times, put it into an oven at 80° C. for drying, and grind it into uniform small particles after drying to obtain the fluorescently labeled polyacrylamide. The viscosity-average molecular weight of the reference standard "GB / T 12005.10-1989 Polyacrylamide Intrinsic Viscosity Determination Method" and "GB / T 12005.10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com