A kind of starch hemostatic sponge and its preparation method and application
A technology of hemostatic sponge and starch, which is applied in the field of starch hemostatic sponge and its preparation, which can solve the problems of unsatisfactory water absorption and complex components, and achieve the effect of facilitating skin or organ surface bonding, no cracks and ice, and convenient curling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0052] The preparation method of the present invention will be further described in detail in conjunction with specific examples below. It should be understood that the following examples are only for illustrating and explaining the present invention, and should not be construed as limiting the protection scope of the present invention. All technologies realized based on the above contents of the present invention are covered within the scope of protection intended by the present invention.
[0053] The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified; the reagents and materials used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
[0054] The starches used in the following examples were purchased from commercial sources.
Embodiment 1
[0056] Put 5g of cornstarch, 150mL of water, and 1mL of glycerin into a reaction vessel, heat and stir to 100°C, and continue to stir for 3 hours to gelatinize the starch; inject the gelatinized starch into the mold, and place it in a freeze-dryer at a temperature of minus 20°C. Pre-freeze in the freezer for 4 hours; then raise the temperature of the freezer to 0°C and keep it for 4 hours; then lower the temperature of the freezer to minus 20°C for a second pre-freeze and keep it for 4 hours; Turn on the vacuum pump at minus 60°C. When the vacuum degree drops below 20Pa, raise the temperature of the freezer to minus 5°C to start the first stage of drying and keep it for 12 hours; then raise the temperature to 30°C to start the second stage of drying and keep it 5h; the hemostatic sponge finished product 1 was obtained.
Embodiment 2-36 and comparative example 1-4
[0058] The other process steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the ratio of raw materials and process parameters are different. The selection, consumption and key process parameters of each material in the reaction are shown in Table 1 below.
[0059] Table 1
[0060]
[0061]
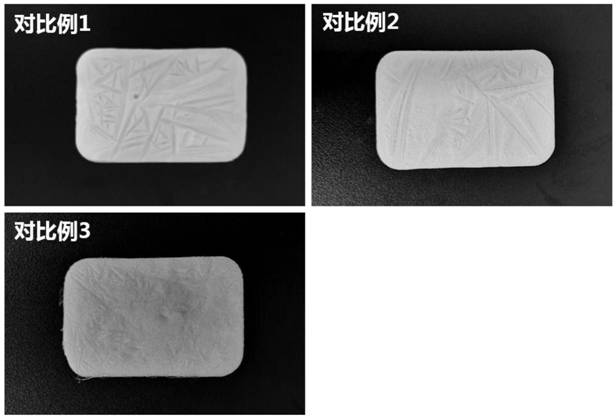
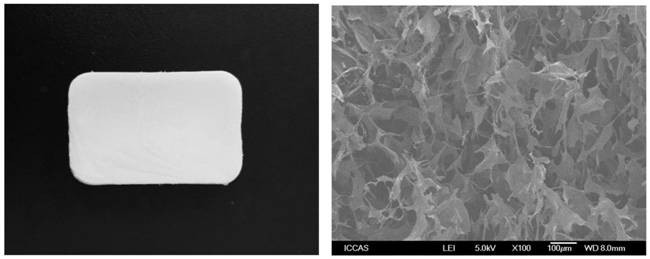
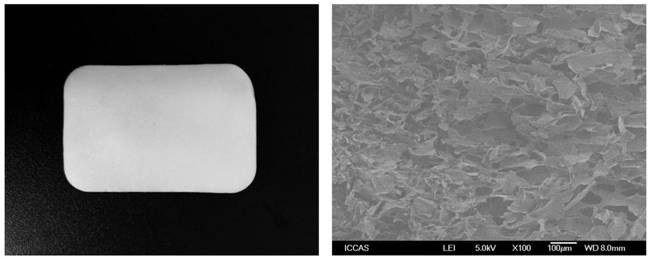
[0062] The hemostatic sponge 1-36 obtained in the present application has a smooth and fine surface, no cracks and ice flakes, and is soft and easy to curl. And the surface of the sponge prepared by Comparative Documents 1-4 is uneven, has cracks and ice flakes, and is not soft. For example, digital photos of hemostatic sponges 4 and 9 and scanning electron micrographs of sections, and digital photos of hemostatic sponges of comparative examples 1-3 can be found in Figure 1-Figure 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com