Method for detecting NSPs residues in foot-and-mouth disease inactivated antigens or inactivated vaccines
A technology of inactivated vaccines and inactivated antigens, applied in the field of immunology, can solve the problems of expensive, time-consuming, inability to determine which kinds of NSPs antigens or vaccines have, and achieve the effects of strong specificity, high sensitivity and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Reactivity of 3B monoclonal antibody with FMDV O / NC / CHA / 2010 infected cells
[0040] 1. Preparation of 3B monoclonal antibody
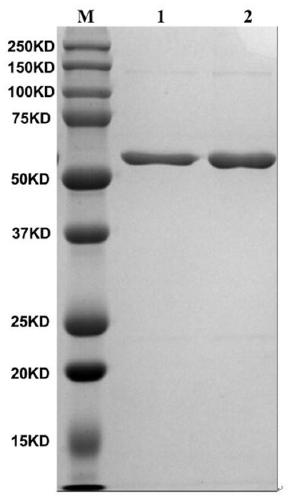
[0041] The foot-and-mouth disease NSP 3ABC of prokaryotic expression is purified ( figure 1 ), and after gradient dialysis and renaturation, the mice were immunized to prepare monoclonal antibodies, the positive hybridoma cells were subcloned three times by the limiting dilution method, and the highly reactive monoclonal cells were screened out, and then the screened cells were injected into small The ascites fluid was prepared from the peritoneal cavity of the rat and purified, and the purified monoclonal antibody was coupled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (9E2-HRP). Verification by Western blot showed that the monoclonal antibody recognized 3B protein ( figure 2 ).
[0042] 2. Expression of NSPs in BHK-21 infected with O-type FMDV at different times
[0043] Inoculation: Resuspend the BHK-21 digested with trypsin and add it ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2 detects NSPs in the foot-and-mouth disease inactivated antigen
[0050] Take 60 μl of FMD antigen and add 20 μl of 4× loading buffer, then place it in boiling water for 10 min. Add the boiled samples and markers into protein gel wells, electrophoresis, transfer to membrane, block, react with 9E2-HRP, expose or scan the membrane (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
[0051] Depend on Figure 4 It can be known that when detecting NSPs residues in unpurified antigen (0#), once-purified antigen (1#) and twice-purified antigen (2#), the unpurified and once-purified antigens were both 3ABB, 3ABBB and 3ABC degradation products (3ABC-) were detected, while the antigen purified twice was not detected. Compared with unpurified antigens, NSPs residues in antigens purified once have been greatly reduced. When detecting concentrated antigens (1-10), it can be observed that 3ABB, 3ABBB and 3ABC- are detected for all antigens 1-10, while there are no band...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3 detects NSPs in the finished product vaccine of foot-and-mouth disease
[0054] Take 1.5 mL of the vaccine and place it in a 2 mL centrifuge tube, then add 75 μL of n-pentanol to vortex for 30 s, and then stand at 4°C for 1 h. After complete demulsification, centrifuge at 8,000 g for 10 min, absorb the lower aqueous phase, centrifuge at 8,000 g for 10 min, take 60 μl, then add 20 μl of 4× loading buffer, and boil it in boiling water for 10 min. Add the cooked samples and markers to the protein gel wells, perform electrophoresis, transfer to membrane, block, react with 9E2-HRP, expose or scan the membrane (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
[0055] Depend on Image 6 It can be seen that when testing the finished vaccines A-L, NSPs 3ABBB and 3ABC- were only detected in C, F and K, and the amount detected in K was large, and NSPs 3ABB was also detected.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com