A method for improving the coercive force of sintered NdFeB magnets
A neodymium iron boron and coercivity technology is applied in the field of improving the coercivity of sintered neodymium iron boron magnets, which can solve the problems of restricting the production efficiency of continuous coating equipment, affecting the production efficiency, affecting the diffusion effect, etc., and shortening the pre-evacuation. time, improve production efficiency, and simplify the effect of furnace charging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
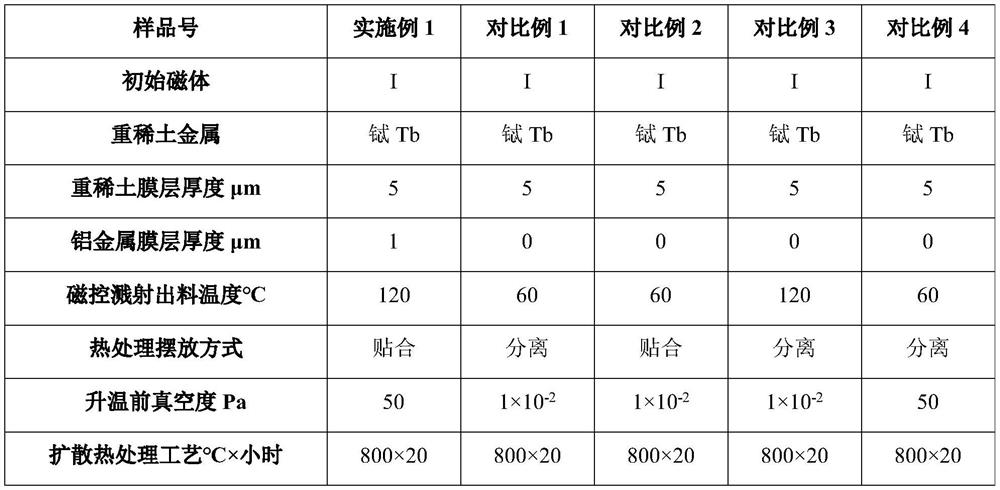
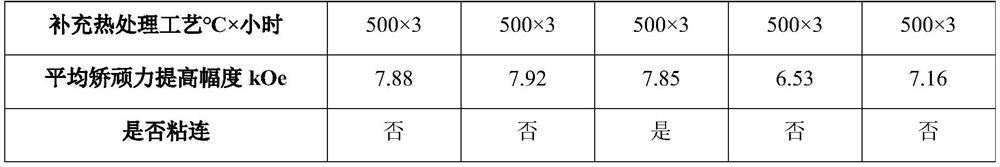
[0040] Using the 3-target continuous magnetron sputtering equipment, the magnet I with the specification of 40mm×30mm×3mm (the brand is N52, the main component is Nd 30 Fe 69 B 1 , wt.%) on two 40mm×30mm surfaces from the inside to the outside were deposited 5μm terbium metal film layer and 1μm aluminum metal film layer, when the magnet temperature was 120 ℃, it was taken out of the magnetron sputtering equipment, and the two magnets The surface coated with the film layer is put into a high-vacuum sintering furnace for high-temperature heat treatment after bonding. Before the heat treatment, the temperature in the furnace is 35°C, the vacuum degree is 50Pa, the heating rate is 10°C / min, and the temperature is kept at 800°C for 20 hours. Afterwards, high-purity argon gas was introduced to start cooling, and the magnet was taken out when cooled to 75°C, and the magnet was heat-treated at 500°C for 3 hours to obtain the magnet of Example 1.
Embodiment 2
[0055] Using 4-target continuous magnetron sputtering equipment, in the magnet II with a specification of 35mm×30mm×4mm (the grade is 50M, the main component is Nd 30 Dy 1 Fe 68 B 1 , wt.%) on two 35mm×30mm surfaces, deposit 10μm dysprosium metal film layer and 1.5μm aluminum metal film layer respectively from the inside to the outside, and take it out of the magnetron sputtering equipment when the magnet temperature is 160°C, two magnets The film layer on the surface is directly bonded and placed in a high-vacuum sintering furnace for high-temperature heat treatment. Before heat treatment, the temperature in the furnace is 35°C, the vacuum degree is 80Pa, and the heating rate is 10°C / min. After holding at 850°C for 30 hours, Introduce high-purity argon gas to start cooling. When the magnet is cooled to 75° C., the magnet is taken out, and the magnet is heat-treated at 460° C. for 5 hours to obtain the magnet of Example 2.
Embodiment 3
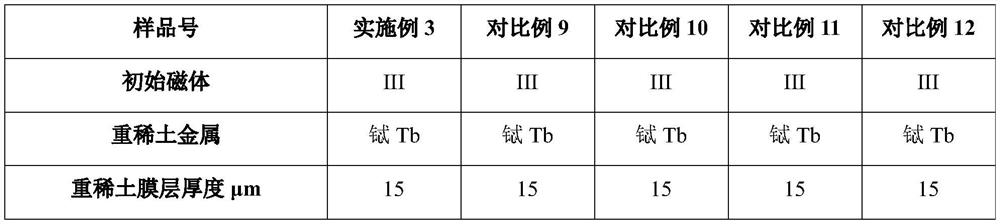
[0069] Using 5-target continuous magnetron sputtering equipment, in the magnet III with a specification of 30mm×25mm×6mm (the grade is 50H, the main component is Nd 30 Tb 1 Fe 68 B 1 , wt.%) two 30mm×25mm surfaces were deposited from the inside to the outside 15μm terbium metal film layer and 2μm aluminum metal film layer, when the magnet temperature was 200 ℃, it was taken out of the magnetron sputtering equipment, the two magnet surfaces After the film layer is directly bonded, it is placed in a high-vacuum sintering furnace for high-temperature heat treatment. Before the heat treatment, the temperature in the furnace is 35°C, the vacuum degree is 100Pa, and the heating rate is 10°C / min. After holding at 880°C for 40 hours, pass Enter high-purity argon gas to start cooling, take out the magnet when cooling to 75°C, and obtain the magnet of Example 3 after the magnet is heat-treated at 550°C for 6 hours.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com