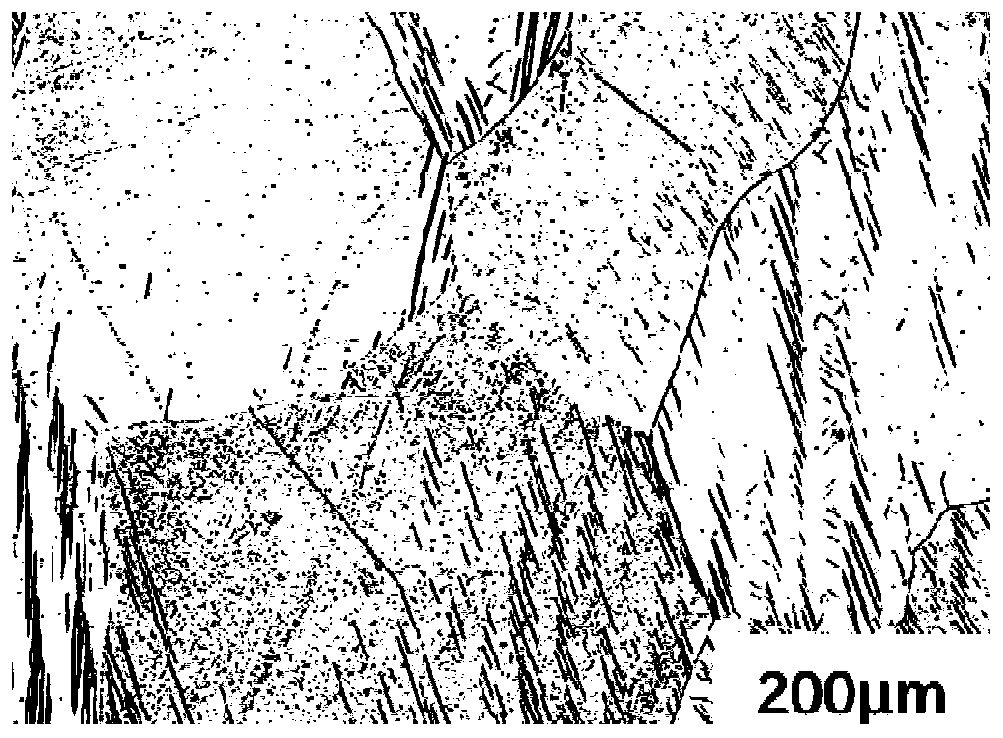
Medical zinc alloy stent and production method thereof
A production method and zinc alloy technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve problems such as reducing the structural strength of the stent, and achieve the effects of avoiding movement disorders, improving tensile strength and excellent plasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
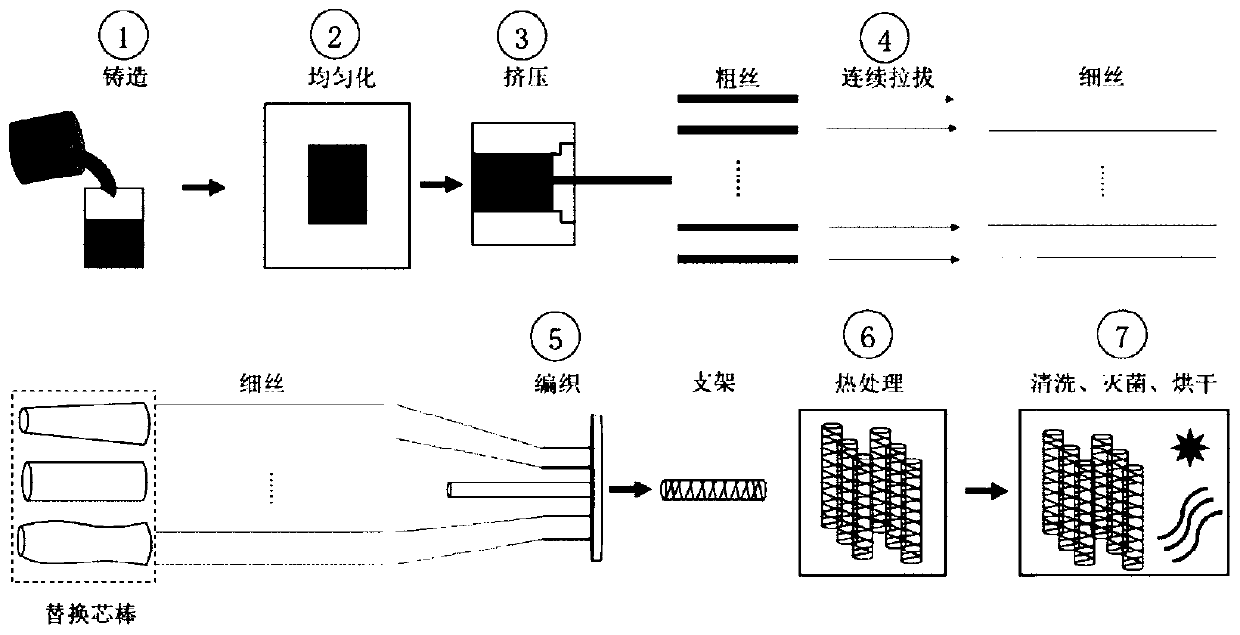
[0043] Example 1: The design content of alloy elements copper and magnesium is 0.2wt.% and 0.1wt.%, respectively, and it needs to be added appropriately during smelting. The preparation process is as follows:
[0044] (1) Mix and smelt high-purity zinc, high-purity copper and high-purity magnesium, pour them into a water-cooled mold, and obtain alloy ingots;
[0045] (2) Homogenize the ingot obtained in step (1), the treatment temperature is 390°C, and the time is 48h;
[0046] (3) extruding the alloy ingot obtained in step (2) into a thick wire with a diameter of 2.5mm, the extrusion ratio is 16:1, the extrusion temperature is 240°C, and the extrusion speed is 5mm / s;
[0047] (4) the thick wire gained in the step (3) is produced in parallel at room temperature in multiple lines, continuously drawn into thin wires with a diameter of 0.3mm, the amount of deformation in a single pass is 15%, and the initial drawing speed is 8mm / s;
[0048] (5) The multi-strand zinc alloy wire...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: The design content of alloy elements copper and magnesium is 0.1wt.% and 0.05wt.%, respectively, and it needs to be added appropriately during smelting. The preparation process is as follows:
[0053] (1) Mix and smelt high-purity zinc, high-purity copper and high-purity magnesium, pour them into a water-cooled mold, and obtain alloy ingots;
[0054] (2) homogenize the ingot obtained in step (1), the treatment temperature is 380°C, and the time is 48h;
[0055] (3) Extruding the alloy ingot obtained in the step (2) into a thick wire with a diameter of 2.5mm, the extrusion ratio is 16:1 and the extrusion temperature is 230°C, and the extrusion speed is 5mm / s;
[0056] (4) the thick wire gained in the step (3) is produced in parallel at room temperature in multiple lines, continuously drawn into thin wires with a diameter of 0.3mm, the amount of deformation in a single pass of drawing is 20%, and the initial drawing speed is 10mm / s;
[0057] (5) The multi-st...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3: The design content of alloying elements copper and magnesium is 0.3wt% and 0.15wt%, respectively, and it needs to be added appropriately during smelting. The preparation process is as follows:
[0062] (1) Mix and smelt high-purity zinc, high-purity copper and high-purity magnesium, pour them into a water-cooled mold, and obtain alloy ingots;
[0063] (2) Homogenizing the ingot obtained in step (1), the treatment temperature is 400°C, and the time is 48h;
[0064] (3) extruding the alloy ingot obtained in step (2) into a thick wire with a diameter of 2.5mm, the extrusion ratio is 16:1, the extrusion temperature is 250°C, and the extrusion speed is 5mm / s;
[0065] (4) the thick wire gained in the step (3) is produced in parallel at room temperature in multiple lines, continuously drawn into thin wires with a diameter of 0.3mm, the amount of deformation in a single pass is 10%, and the initial drawing speed is 5mm / s;
[0066] (5) The multi-strand zinc alloy ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com