Method and kit for constructing sequencing library for simultaneously realizing genome copy number variation detection and gene mutation detection
A copy number variation and genome technology, which can be used in biochemical equipment and methods, chemical libraries, and microbial determination/inspection. It can solve the problems of high sequencing cost, inability to detect three variants, and limited sample size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1. Construction of a DNA sequencing library according to the method of the present invention
[0048] Step 1: Lyse white blood cells (blood samples from healthy people) and extract DNA. Reaction mixtures as shown in Table 1 were prepared, incubated at 60°C for 20 minutes, 95°C for 4 minutes, and then the samples were kept at 4°C.
[0049] Table 1:
[0050]
[0051] Step 2: Pre-amplification of genomic DNA. The pre-amplification primers used in this step include random primers (sequence: 5'GCTCTTCCGATCTKKKKKKKKKKN*N*N 3', wherein K represents G or T bases, and N represents random degenerate bases A / T / C / G , *represents sulfomodification) and specific primers, wherein the specific primers are designed for exon 2 and exon 3 of the HBB gene (NCBI ID: NM_000518, which is known to cause β-thalassemia due to its mutation), which The sequences are shown in Table 2 below (the underlined GCTCTTCCGATCT represents the general region in the specific primers).
[0052] ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2. Detecting the quality of the DNA sequencing library
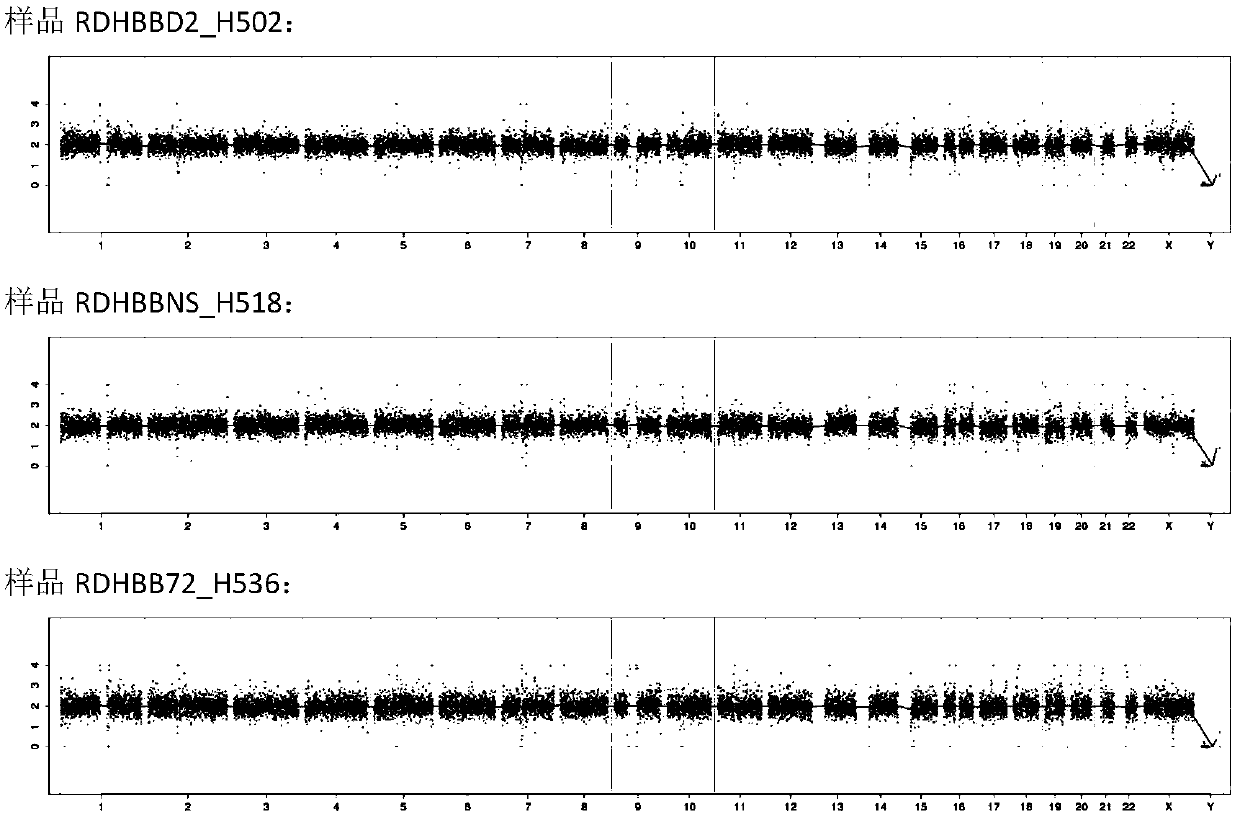
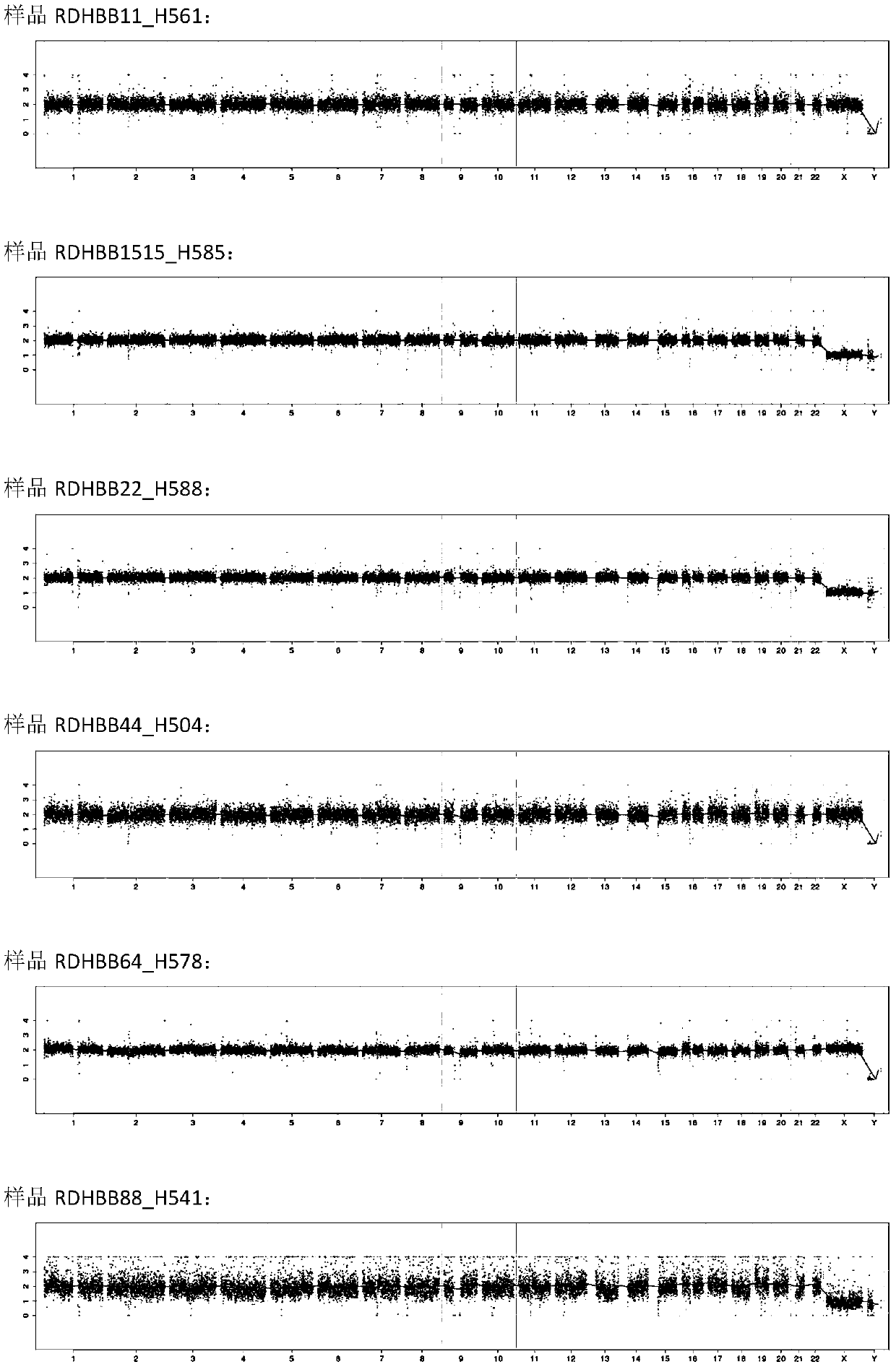
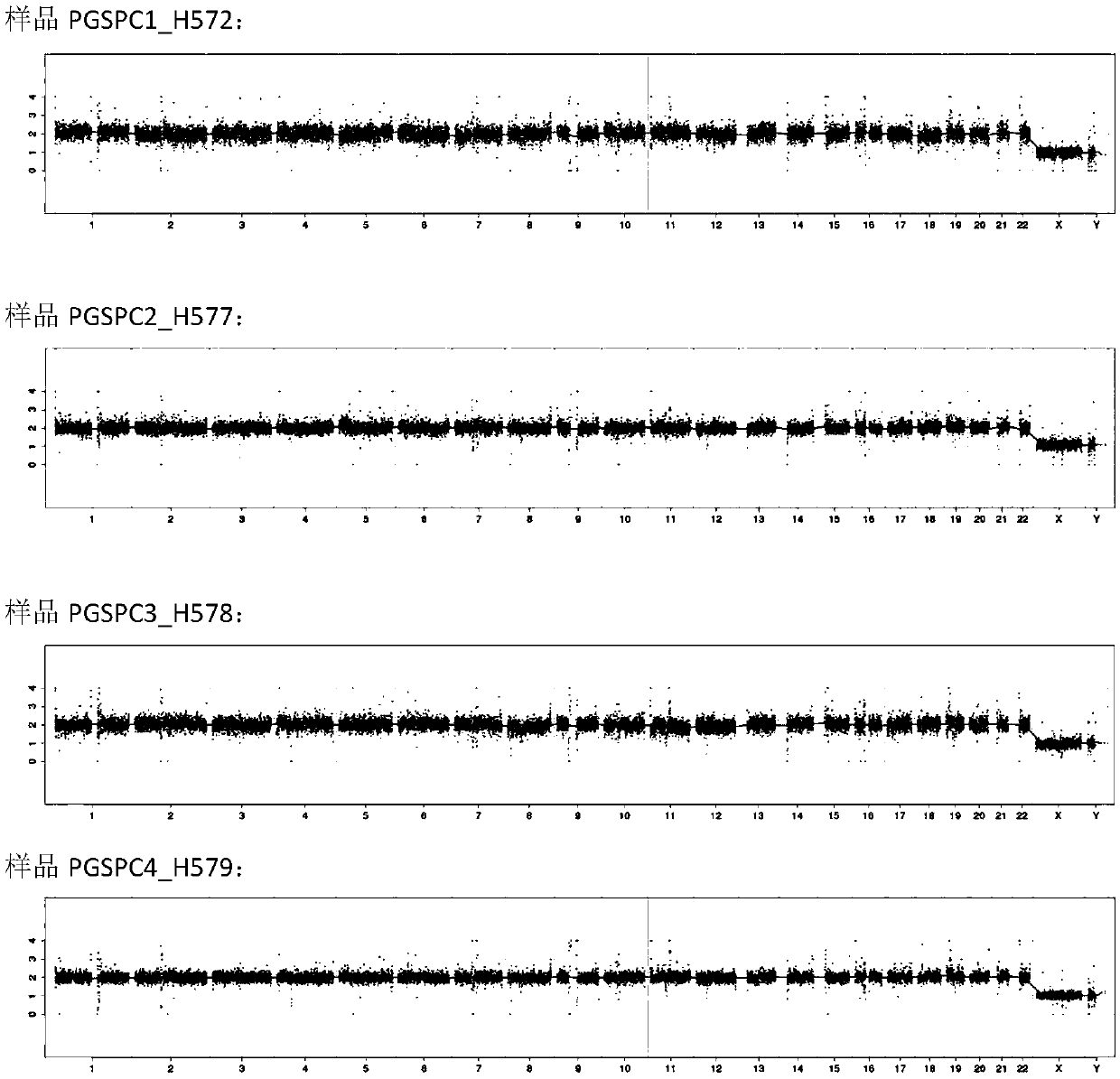
[0064] The DNA sequencing library prepared in Example 1 was purified, and then the concentration was detected by Qubit. The concentration of the blank control should be <10ng / μl, and the concentration of the sample should be ≥10ng / μl, and the samples whose concentration meets the requirements should be quantified by qPCR. According to the quantitative results of qPCR, the library was subjected to 36 bp single-end sequencing in accordance with the standard operating procedures of the sequencer. Compare the single-end sequencing results with the human genome reference sequence, detect the genome copy number variation of each sample, and analyze the library quality and HBB amplification results.
[0065] figure 1 The Manhattan plot of the high-throughput sequencing results of the three samples prepared according to Example 1 is shown. Such as figure 1As shown, the sequencing results of the three samples a...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3. Effect of the ratio of random primers to specific primers on the quality of the sequencing library
[0071] The DNA sequencing library was prepared according to the method of Example 1, the difference being that the composition and content of the pre-amplification primers are shown in Table 6 below:
[0072] Table 6
[0073]
[0074] The prepared DNA sequencing library was purified, and then the concentration was detected by Qubit. The concentration of the blank control should be <10ng / μl, and the concentration of the sample should be ≥10ng / μl, and the samples whose concentration meets the requirements should be quantified by qPCR. According to the quantitative results of qPCR, the library was subjected to 36 bp single-end sequencing in accordance with the standard operating procedures of the sequencer. Compare the single-end sequencing results with the human genome reference sequence, detect the genome copy number variation of each sample, and analyze t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com