Unmanned vehicle lane changing decision-making method and system based on adversarial imitation learning
A technology of unmanned vehicles and decision-making methods, which is applied in the field of unmanned autonomous vehicles and can solve problems such as weak model generalization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] The present embodiment discloses a decision-making method for changing lanes of unmanned vehicles based on confrontational imitation learning, through which the unmanned vehicles can switch lanes correctly and safely, and the method includes the following steps:
[0082] Step S1. Describe the lane-changing decision-making task of the unmanned vehicle as a partially observable Markov decision process.
[0083] In this embodiment, the lane-changing decision-making task of an unmanned vehicle is described as a partially observable Markov decision process, as follows:
[0084] Step S11, determine state O t Space: including the driving state of the vehicle, the front and rear vehicles in the vehicle lane, and the vehicles closest to the vehicle on the left and right lanes [l,v 0 ,s f ,v f ,s b ,v b ,s lf ,v lf ,s lb ,v lb ,s rf ,v rf ,s rb ,v rb ];
[0085] in:
[0086] l is the lane where the vehicle is located, v 0 is the vehicle’s self-vehicle speed; in th...
Embodiment 2
[0143] This embodiment discloses an unmanned vehicle lane change decision system for implementing the unmanned vehicle lane change decision method based on confrontational imitation learning in Embodiment 1, including:
[0144] A task description module, which is used to describe the lane-changing decision task of an unmanned vehicle as a partially observable Markov decision process;
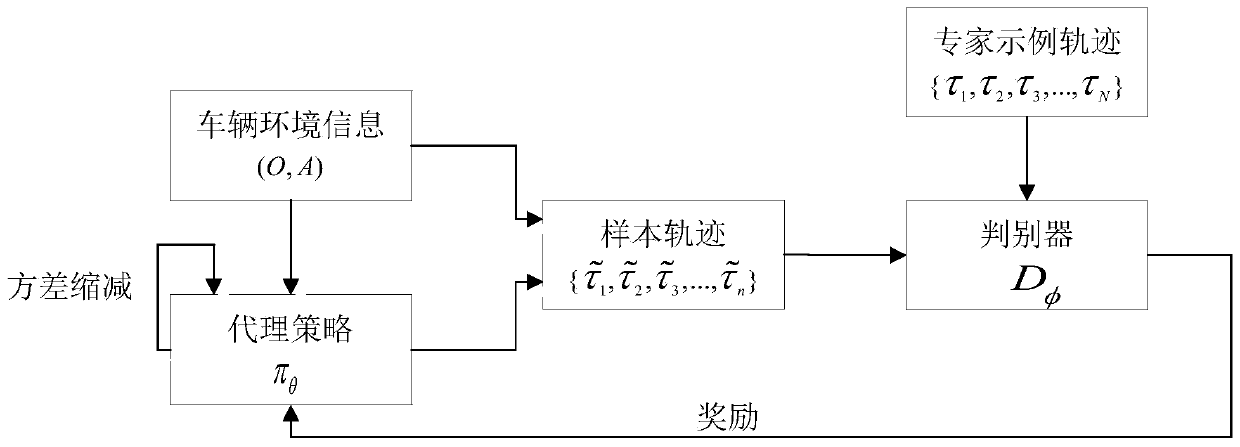
[0145] The building block of the lane-changing decision model is used to use the anti-imitation learning method to train from the examples provided by the professional driving demonstration to obtain the lane-changing decision model of the unmanned vehicle; wherein, in the training process, the anti-imitation learning method is based on variance reduction Policy gradient learning strategy to simulate professional driving performance;
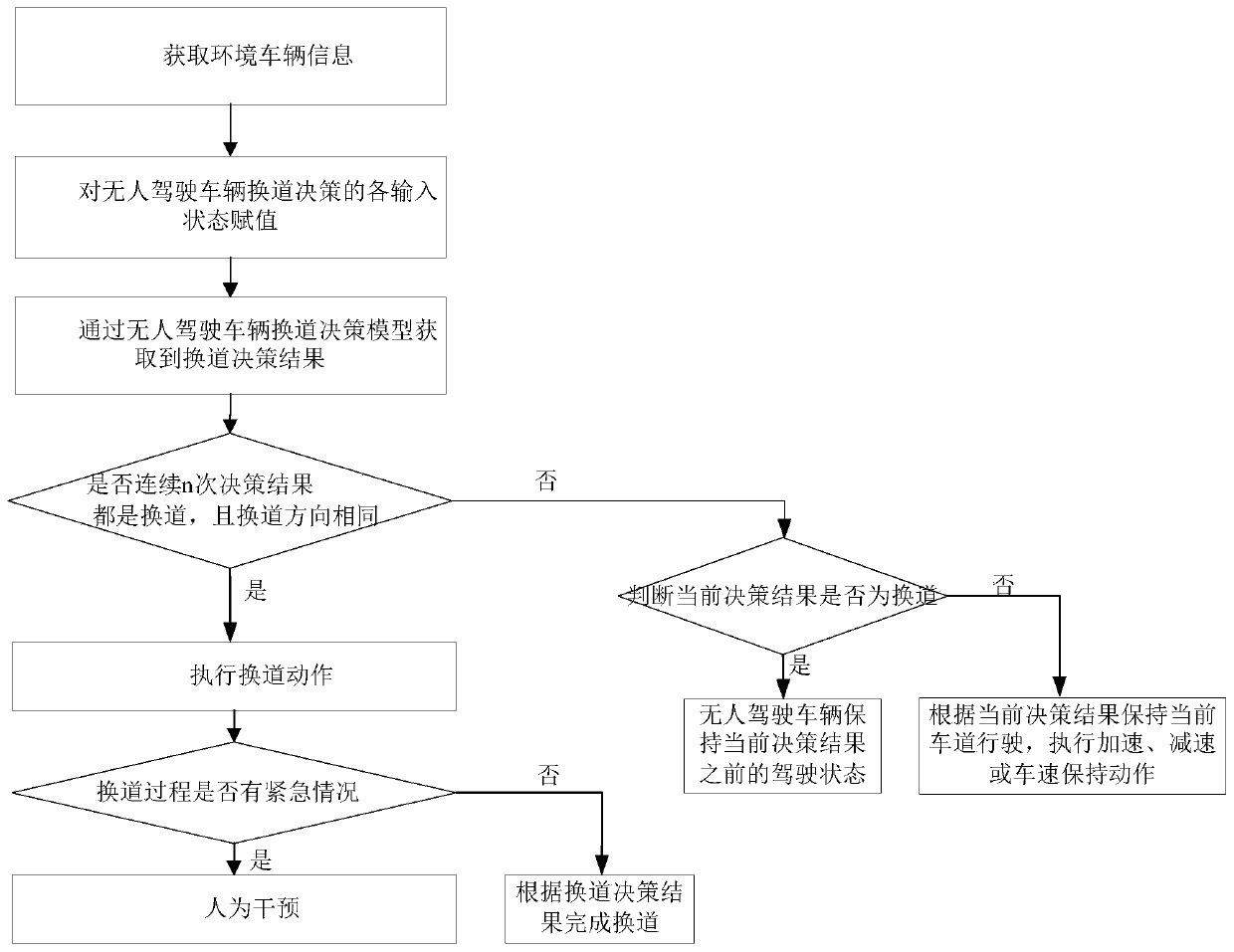
[0146] The environmental vehicle information acquisition module is used to obtain the current environmental vehicle information during the unmanned driving proces...
Embodiment 3
[0157] This embodiment discloses a storage medium, which stores a program. When the program is executed by a processor, the method for lane-changing decision-making for an unmanned vehicle based on confrontational imitation learning as described in Embodiment 1 is implemented, as follows:
[0158] Describe the lane-changing decision task of unmanned vehicles as a partially observable Markov decision process;
[0159] Use the confrontational imitation learning method to train from the examples provided by professional driving demonstrations to obtain the lane change decision model of unmanned vehicles; in the training process, the confrontational imitation learning method is based on the learning strategy of variance reduction strategy gradient to simulate professional driving Performance;
[0160] During the unmanned driving process of the vehicle, the currently acquired environmental vehicle information is used as the input parameter of the unmanned vehicle lane change decisi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com