Polyester and fiber
A technology of polyester and fiber, which is applied in the field of monomer composition and ratio to form the polyester, and can solve the problems of expensive and difficult acquisition of low-melting nylon raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
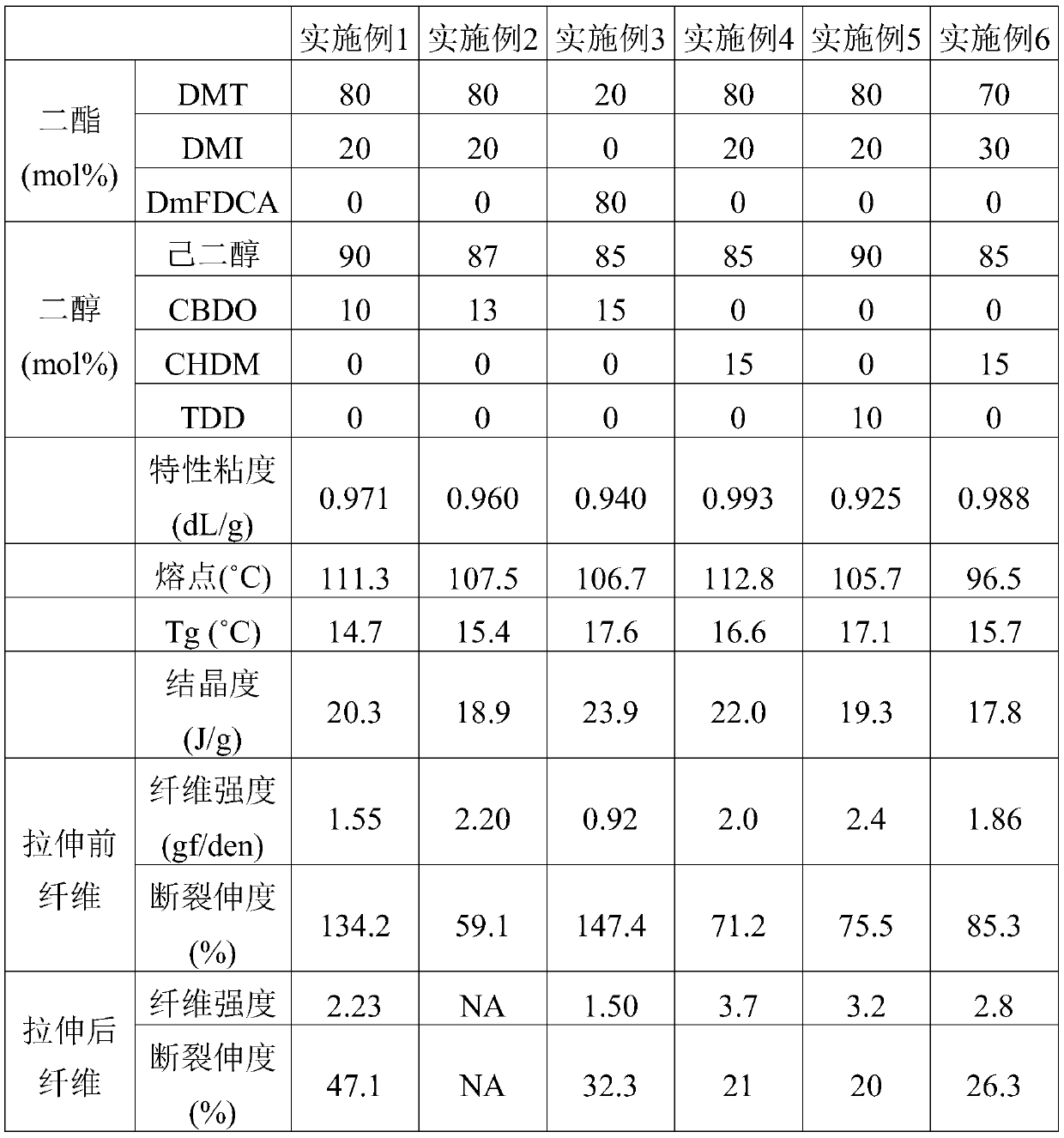
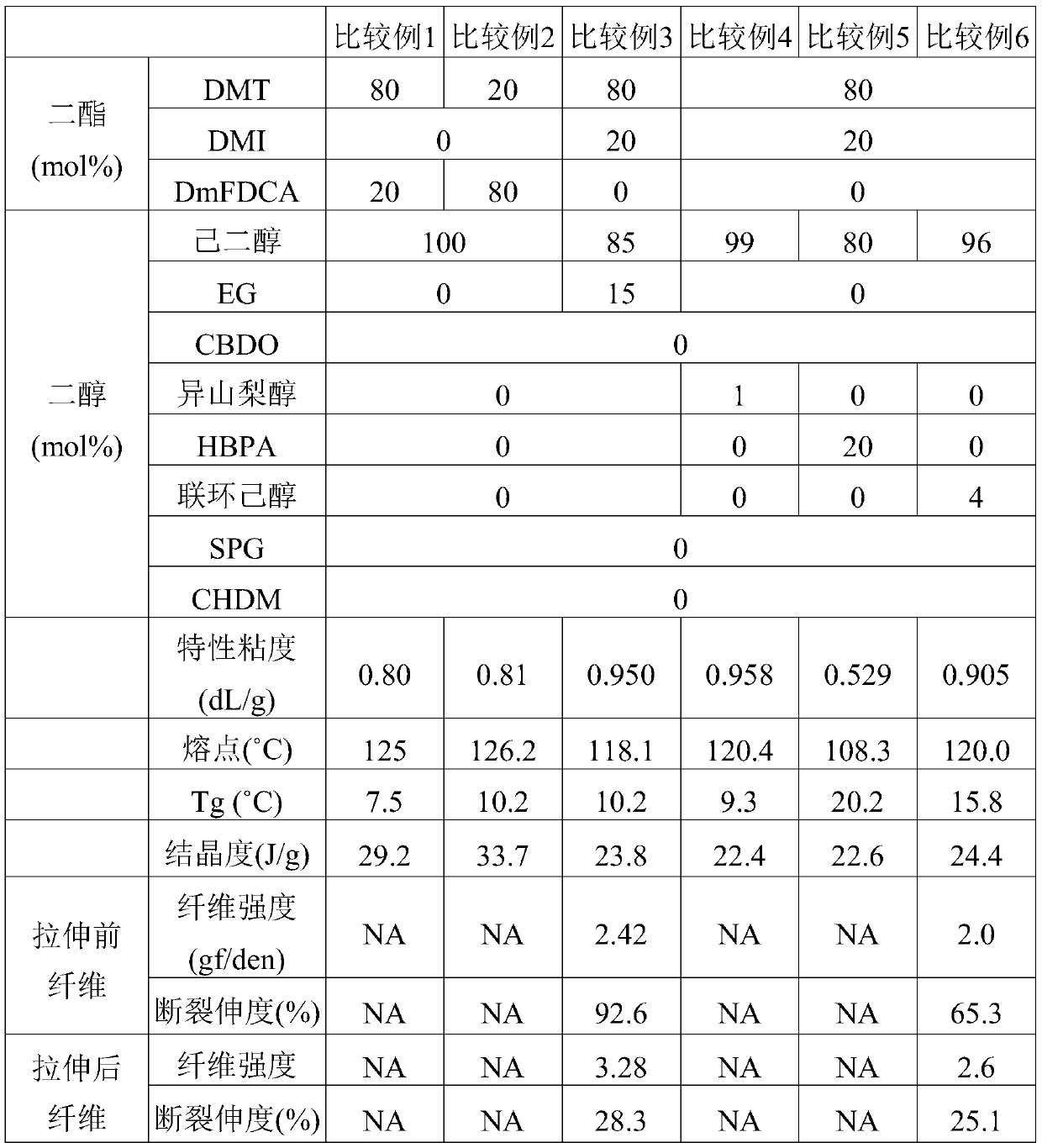
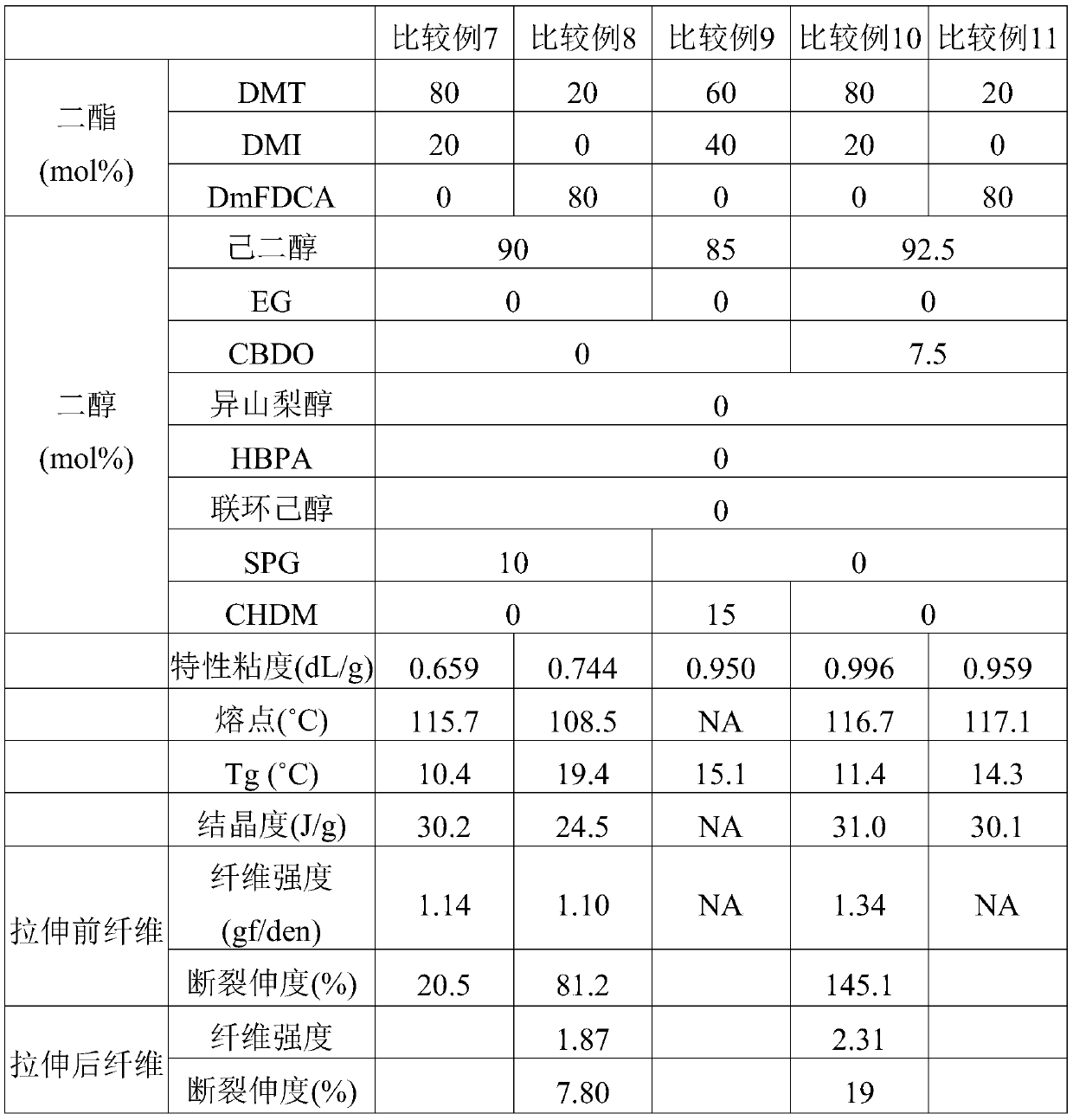
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026]With 300 grams (1.545mol) of DMT, 75 grams (0.386mol) of DMI, 34.8 grams (0.241mol) of CBDO, 320 grams (2.7mol) of ethylene glycol, and 200ppm (based on theoretical product weight) of Zinc acetate is added in the reaction tank. Nitrogen was introduced, heated to 200°C, and the stirring speed was 150 rpm to carry out the transesterification reaction. After continuing the reaction for three hours, the condensed methanol was removed and 0.055 g of thermal stabilizer phosphoric acid (the same molar amount as zinc acetate) and 0.0778 g of C-94 titanium catalyst (150 ppm, based on theoretical product weight) were added. The pressure in the reaction system was gradually reduced to 50 torr within 30 minutes to remove excess hexanediol monomer. Gradually heat the temperature to 280° C. and gradually reduce the reaction pressure to below 1 torr, and continue the reaction for 120 minutes. Finally, the vacuum was broken with nitrogen and the heating and stirring were stopped, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] With 300 grams (1.545mol) of DMT, 75 grams (0.386mol) of DMI, 41.7 grams (0.29mol) of CBDO, 320 grams (2.7mol) of ethylene glycol, and 200ppm (based on theoretical product weight) of Zinc acetate is added in the reaction tank. Nitrogen was introduced, heated to 200°C, and the stirring speed was 150 rpm to carry out the transesterification reaction. After continuing the reaction for three hours, the condensed methanol was removed and 0.055 g of thermal stabilizer phosphoric acid (the same molar amount as zinc acetate) and 0.0778 g of C-94 titanium catalyst (150 ppm, based on theoretical product weight) were added. The pressure in the reaction system was gradually reduced to 50 torr within 30 minutes to remove excess hexanediol monomer. Gradually heat the temperature to 280° C. and gradually reduce the reaction pressure to below 1 torr, and continue the reaction for 120 minutes. Finally, the vacuum was broken with nitrogen and the heating and stirring were stopped, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] With 75 grams (0.386mol) of DMT, 284.3 grams (1.545mol) of DmFDCA, 55.6 grams (0.386mol) of CBDO, 320 grams (2.7mol) of hexanediol, and 200ppm (based on theoretical product weight) of Zinc acetate is added in the reaction tank. Nitrogen was introduced, heated to 200°C, and the stirring speed was 150 rpm to carry out the transesterification reaction. After continuing the reaction for three hours, the condensed methanol was removed and 0.055 g of thermal stabilizer phosphoric acid (the same molar amount as zinc acetate) and 0.0778 g of C-94 titanium catalyst (150 ppm, based on theoretical product weight) were added. The pressure in the reaction system was gradually reduced to 50 torr within 30 minutes to remove excess hexanediol monomer. Gradually heat the temperature to 280° C. and gradually reduce the reaction pressure to below 1 torr, and continue the reaction for 120 minutes. Finally, the vacuum was broken with nitrogen and the heating and stirring were stopped, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com