Early diagnosis marker for cervical cancer caused by HPV infection based on plasma exosome protein and application of early diagnosis marker
A diagnostic marker and early diagnosis technology, which can be applied to medical preparations, drug combinations, and pharmaceutical formulations containing active ingredients, can solve problems such as adverse effects, patient discomfort, and lack of prognostic judgment. Extraction is convenient and easy to operate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Example 1. Correlation between plasma exosome Mortalin expression and cervical cancer stage
[0089] Protein non-labeled quantitative technology (Lable-free) can perform mass spectrometry analysis on protein enzymatic peptides through liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry without specific quantitative labeling reagents. By analyzing mass spectrometry data, the signal intensity of specific peptides between samples is compared, thereby To achieve the purpose of relative quantification of the protein corresponding to the peptide.
[0090] The present invention uses Lable-free to verify the correlation between the expression level of plasma exosome Mortalin and the stage of cervical cancer. Specific steps are as follows:
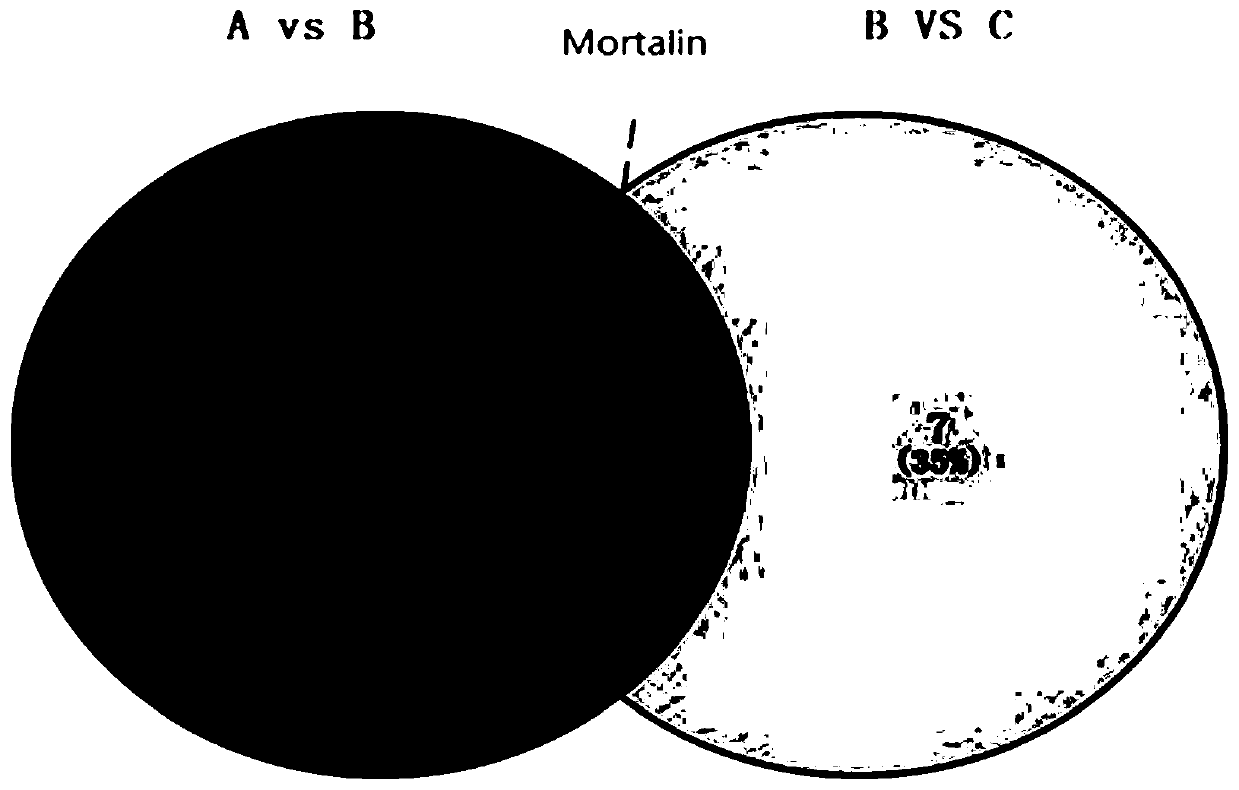
[0091] (1) Take blood samples from 10 patients in each of the precancerous lesion group (uterine intraepithelial neoplasia, CIN, group A), cancer group (cervical cancer, group B) and healthy control group (group C), and divide the 10 patients The samp...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2. Correlation between HPV infection and up-regulation of exosome mortalin expression
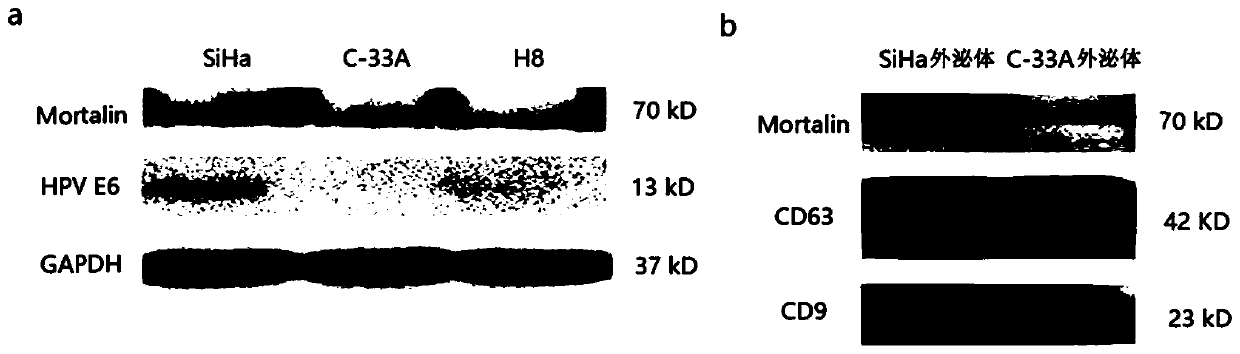
[0102] Cervical cancer cell lines SiHa (HPV+) and C-33A (HPV-) and immortalized cervical epithelial cells H8 were selected to represent HPV-positive (HPV+) cervical cancer cells, HPV-negative (HPV-) cervical cancer cells and precancerous lesion cells, respectively. Caski is also HPV positive. The correlation between the HPV characteristic protein HPV E6 / E7 and the expression of mortalin in cells and exosomes was compared.
[0103] Extraction of intracellular exosomes
[0104] The specific method is as follows:
[0105] (1) Fetal bovine serum (FBS) was diluted with PRIM1640 medium at a volume ratio of 4:1, and centrifuged at 160,000 g for 16 h in an ultrahigh-speed centrifuge to remove serum exosomes. The obtained diluted serum was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter for aseptic treatment. Take 50ml of the above treated diluted serum, mix it with 50ml PRIM1640 medium, and ma...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Example 3 In vitro cell experiment of exosome Mortalin on malignant transformation of immortalized cervical epithelium
[0136] Immortalized cervical epithelial cells H8, as HPV-infected positive cells, are immortalized cells without canceration, and the mechanism of canceration has not yet been elucidated. This part explains that cervical cancer-derived exosome mortalin has a malignant transformation function on H8 cells, suggesting that the effect of exosome mortalin may be one of the mechanisms of H8 carcinogenesis.
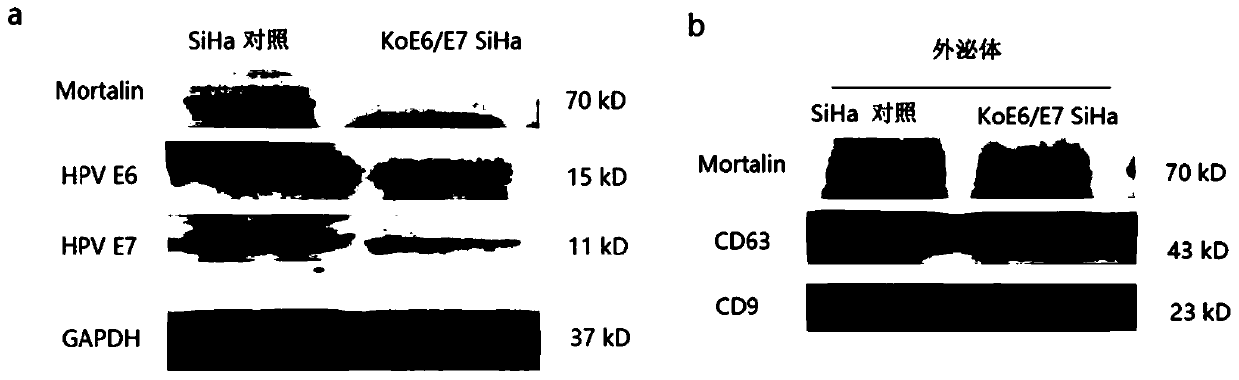
[0137] Knockdown Mortalin SiHa (KdMorSiHa / KdMS) and Knockdown Mortalin Caski (KdMorCaski / KdMC) cell lines were constructed using lentiviral Mortalin shRNA. Both SiHa and Caski are cervical cancer cell lines, and H8 cells are immortalized cervical epithelial cells. Both cell lines were confirmed to be successfully constructed in previous experiments, and it was confirmed that the expression of Mortalin in their exosomes was relatively reduced.
[0138] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com