Power equipment environment noise identification method based on time domain and frequency domain self-similarity
A power equipment, self-similar technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of weakening effective data, difficult to filter out strong background noise, difficult to adapt to complex and changeable environmental noise, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
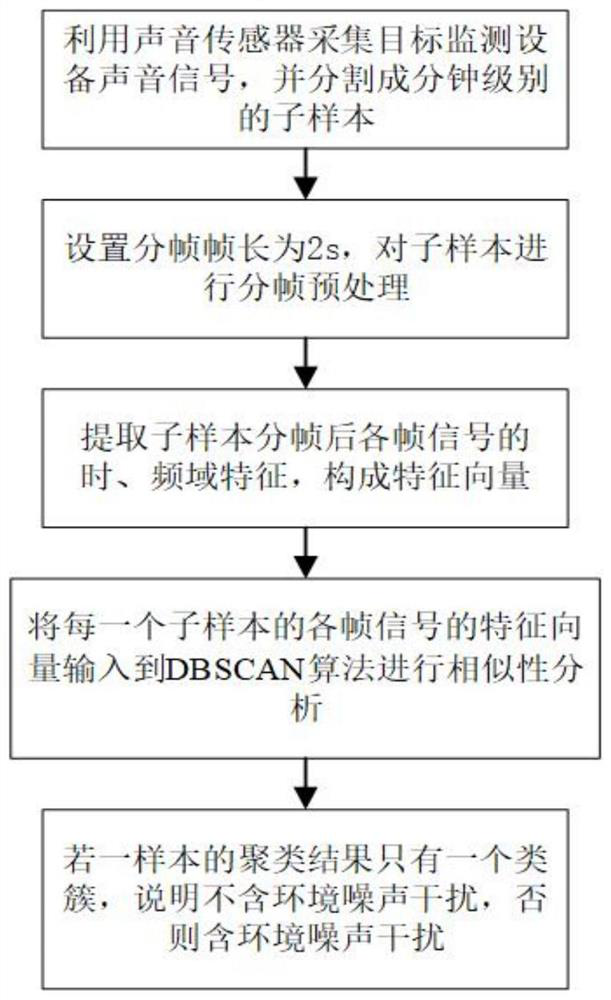
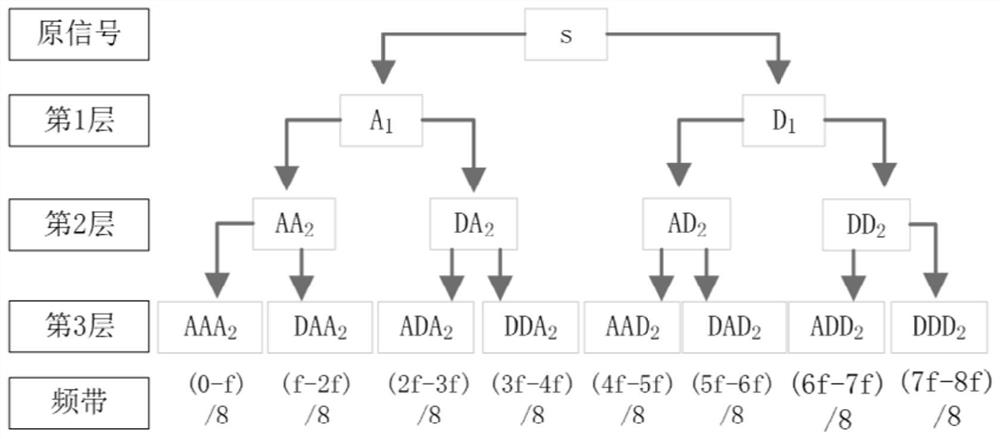
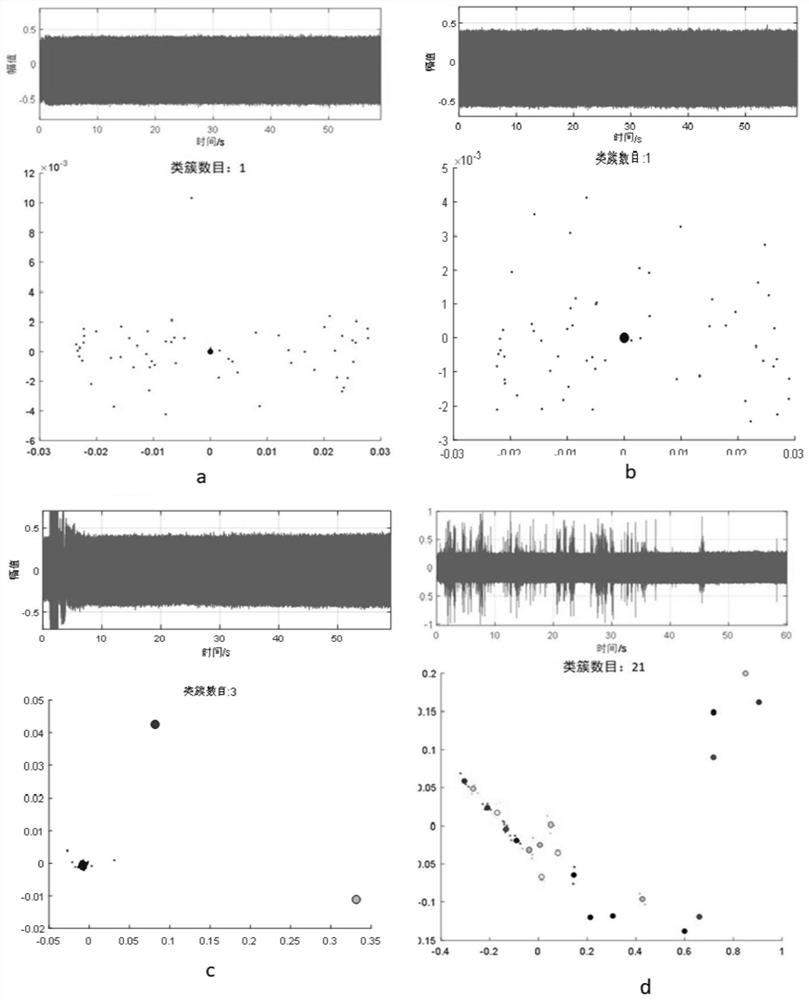
[0034] In the power distribution room, the sound sensor is used to continuously record the audio data of the distribution transformer. The sensor sampling frequency is 48kHz, and the collected audio is divided into sound samples according to the length of 60s; the Hamming window is used for each sample. If the frame length is too small, the details will be over-magnified, which will reduce the similarity of samples with similarities. However, if the frame size is too large, the details will be smoothed, and it is easy to ignore noise interference. Based on a large number of experimental analysis, set the frame length to 2s. When the frame shift is 1s, the sample is divided into 59 frames, the time domain and frequency domain features of each frame are extracted, and the similarity analysis based on DBSCAN clustering is performed. figure 1 .
[0035] The example in this article uses the mean value, peak value, root mean square value, variance, crest factor, kurtosis, shape fact...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com