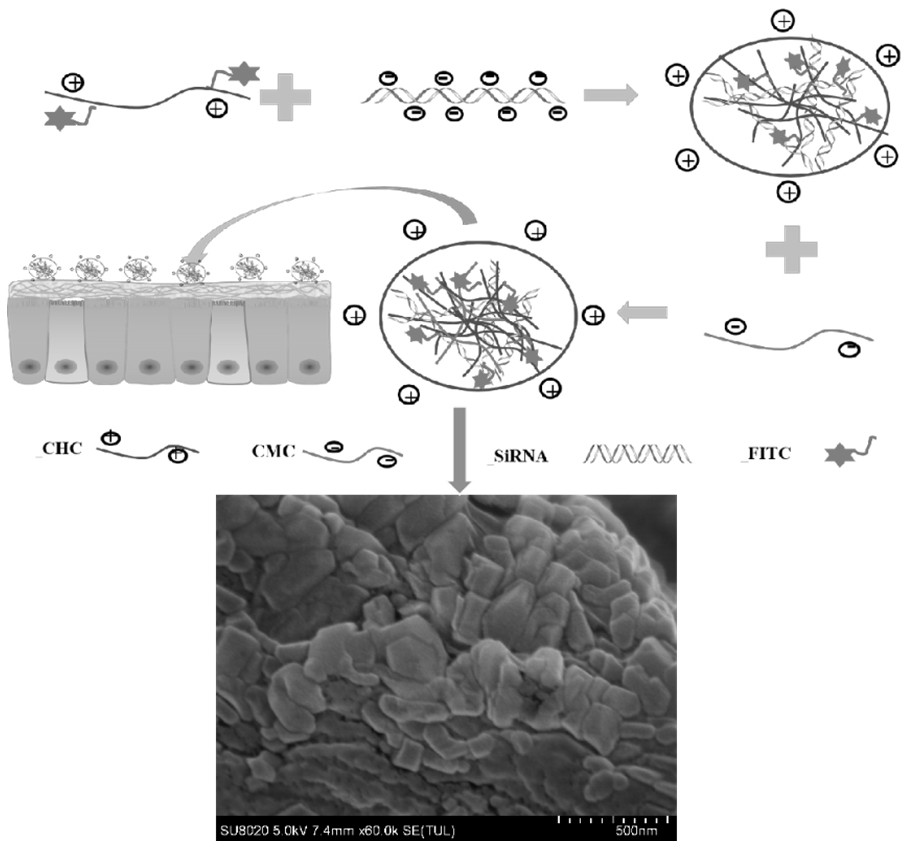
Preparation method of chitosan derivative nanoparticles for delivering siRNA
A technology of chitosan derivatives and nanoparticles, applied in the field of gene biology, to achieve the effect of simple method and good transfection effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The specific steps of preparing FITC-labeled chitosan hydrochloride powder are as follows:
[0026] 10 mg of chitosan hydrochloride was completely dissolved in 10 mg of deionized water to obtain a chitosan hydrochloride solution with a concentration of 1 mg / mL. Add 10 mL of 5.8 mg / L fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) solution (5.8 mg / L, anhydrous methanol) to the chitosan hydrochloride solution with a concentration of 1 mg / mL, and stir under a magnetic force (500 rpm). ) For 4 h. Then, 1 M hydrogen hydroxide (NaOH) was added to adjust the pH to 10, and FITC-labeled chitosan hydrochloride was precipitated. The free FITC was washed with ultrapure water and centrifuged until no fluorescence was detected in the supernatant. Finally, the FITC-labeled chitosan hydrochloride powder was obtained by freeze-drying.
[0027] Prepare siRNA-CDNPs according to the siRNA, different volumes of CHC and different volumes of CMC (600μL, 500μL, 400μL, 300μL) in Table 1. The preparation steps ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Application of siRNA-CDNPs in simulating colon cancer cell environment siRNA controlled release:
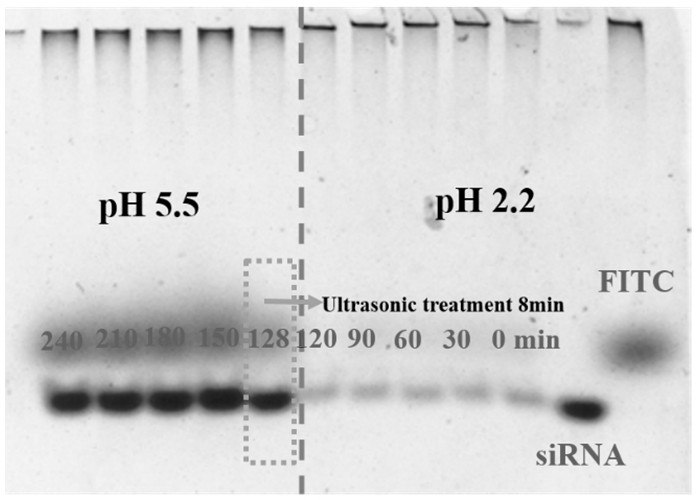
[0034] Take the siRNA-CDNPs prepared in Example 1 and incubate them in a gastric environment (pH = 2.2, 120 rpm) at 37°C for different times, up to 120 min. Then mix the above acidic solution with NaOH (1 M) and adjust the pH to a weak acid (pH = 5.5). Then sonicate for 8 min, incubate at 37°C, shake well (120 rpm) for 112 min. Obtain samples at predetermined times (0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 128, 150, 180, 210, and 240 min). The samples were analyzed by 5% (w / v) polyacrylamide gel, 120 mV electrophoresis in 1×TBE buffer, the gel was stained with ethidium bromide, and the gel imager FLA 7000 was used to observe the results. figure 2 Shown.
[0035] By analyzing the siRNA content at pH 2.2 and pH 5.5, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was used to detect the release of siRNA in siRNA-CDNPs. figure 2 The red arrow and white arrow in indicate unencapsulated siRNA and FITC. The rele...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Application of siRNA-CDNPs that are effectively internalized by HT-29 cells:
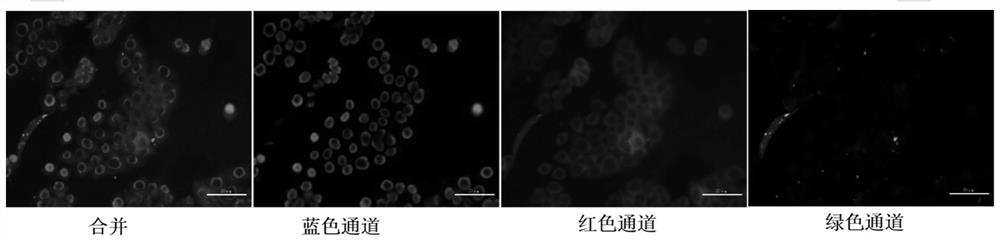
[0038] Take the siRNA-CDNPs prepared in Example 1 and incubate colon cancer cells (HT-29) to analyze the transfection effect of siRNA. The specific steps are as follows: 100μL siRNA-CDNPs (containing 0.55 nmol siRNA) are added to HT-29 cells (1×10 5 / Well) incubate for 16 h. Then the added siRNA-CDNPs were gently absorbed, and the cells were washed three times with PBS. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde PBS for 15 min, washed twice with PBS, and nuclear stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamino-2-phenylindole) for 10 min. The cells were washed again with PBS, rinsed with ultrapure water, and placed on a microscope slide. Take a fluorescence image with a fluorescence microscope, the results are as follows image 3 Shown.
[0039] The siRNA-CDNPs prepared in Example 1 were added to colon cancer cells (HT-29), and the transfection effect of siRNA was analyzed. The results are as follows image 3 Sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com