Bidirectional large-through-flow low-residual-voltage TVS device
A low residual voltage and flow-through technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of isolation leakage, increase of TVS junction area, and decrease of product competitiveness, etc., and achieve large surge pass-through Flow capacity, not easy to break through, save area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
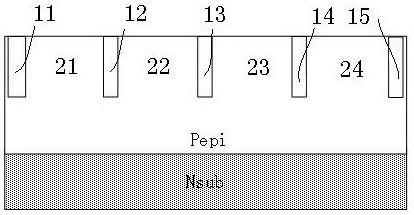
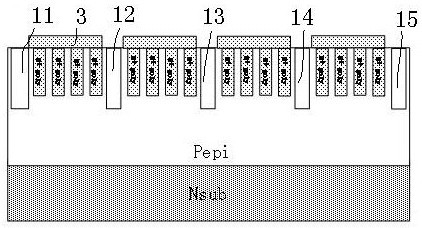
[0040] like Figures 1 to 5 As shown, a bidirectional large flow-through and low residual voltage TVS device forms a P-type epitaxial Pepi on the N+ substrate Nsub, and fills the P-type epitaxial Pepi with low-pressure tetraethoxysilane (LPTEOS) to a depth of 2--5um. Shallow trenches with a width of 1-1.2 μm, trench one 11, trench two 12, trench three 13, trench four 14, and trench five 15 are used as isolation grooves to form isolation areas 1 21, 2 22, and 2 with the same size and spacing. Three 23, isolation area four 24; each isolation area is provided with multiple polys with the same structure, equal spacing, depth of 1-4 μm and filled with N+ poly body 3; deposit a layer of SiO as a contact hole on the surface of N+ poly 2 The dielectric layer 4 retains the lead-out position of the N+ poly body 3 between every two isolation grooves, and deposits the metal layer 5 as the lead-out electrode; wherein, the lead-out electrodes of the isolation region 1 21 and the isolation r...
Embodiment 2
[0059] A TVS device with bidirectional large current flow and low residual voltage, which is similar to Embodiment 1, except that the N+ Poly body is changed to an N+ region, such as Figure 7 Shown:
[0060] Form P-type epitaxy on the N+ substrate, and use LPTEOS to fill shallow grooves with a depth of 2--5um and a width of 1-1.2um on the P-type epitaxy. Trench one 11, trench two 12, trench three 13, trench four 14, Trench 5 15 is used as an isolation groove to form four isolation areas 1 21, 2 22, 3 23, and 4 24 with the same size and spacing; each isolation area is provided with the same structure, equal spacing, and a depth of 1-4μm N+ region 3'; deposit a layer of SiO as a contact hole on the surface of N+ region 3' 2 The dielectric layer 4 retains the lead-out position of the N+ region 3' between every two isolation grooves, and deposits a metal layer 5 as the lead-out electrode; wherein, the lead-out electrodes of the isolation region 1 21 and the isolation region 3 23...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com