Method for intracellular delivery of protein
A protein and protein solution technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as easy to be removed, protein cannot function, CPPs short half-life, etc., to achieve the effect of avoiding chemical bond modification, excellent biocompatibility, and simple operation steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Take boron halide clusters (Na 2 B 12 Br 12 ) and labeled cytochrome C, the solvent is 1×PBS, the total volume is 100 μL, mixed thoroughly for 10 min, and sterilized by filtration through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane;
[0024] (2) Add 300 μL DMEM to the 24-well plate where NIH-3T3 cells were cultured, and add 100 μL of the mixture in step (1), incubate for 6 hours, boron halide clusters (Na 2 B 12 Br 12 ) with a final concentration of 150 μM, and labeled cytochrome C concentrations of 2.5 μM, 5.0 μM and 10.0 μM;
[0025] (3) Aspirate the mixture in the 24-well plate in step (2), wash with 1×PBS three times, stain and fix the cells;
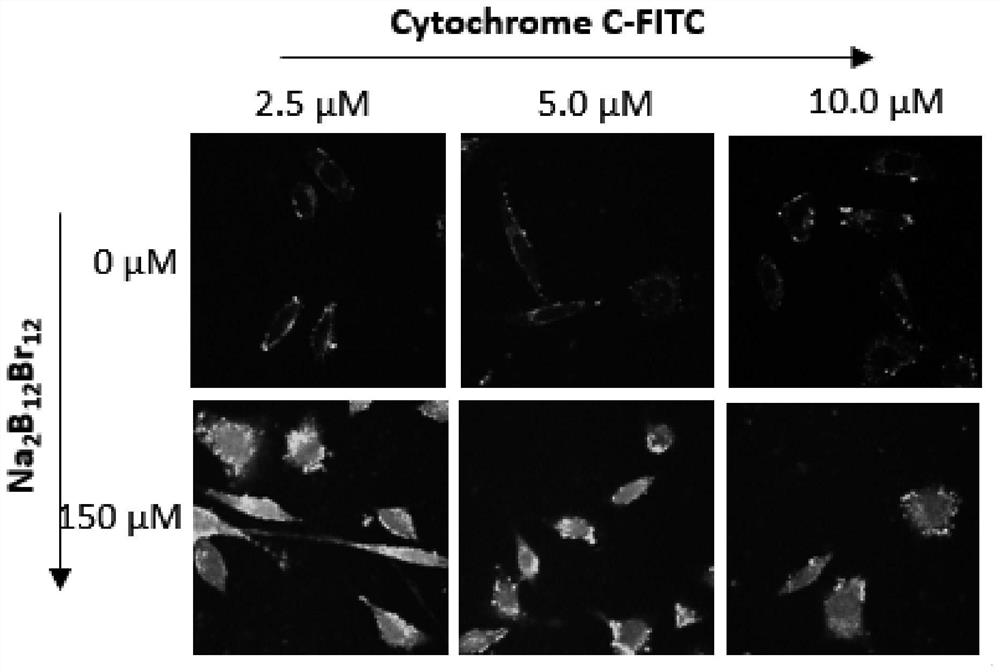
[0026] (4) Carry out confocal imaging of the cells using a confocal microscope to observe the distribution of labeled cytochrome C in the cells. The distribution of proteins in the cells can be seen in the fluorescent channel of 500-530nm labeled cytochrome C, from figure 2 Boron halide clusters (Na 2 B 12 Br 12 ) can effici...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) boron halide clusters (Cs) with a mass ratio of about (1~5):1 2 B 10 Br 10 ) and labeled cytochrome C, the solvent is 1×PBS, the total volume is 100 μL, mixed thoroughly for 10 min, and sterilized by filtration through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane;
[0029] (2) Add 300 μL DMEM to the 24-well plate where NIH-3T3 cells were cultured, and add 100 μL of the mixture in step (1), incubate for 6 hours, boron halide clusters (Cs 2 B 10 Br 10 ) with a final concentration of 150 μM, and labeled cytochrome C concentrations of 2.5 μM, 5.0 μM and 10.0 μM;
[0030] (3) Aspirate the mixture in the 24-well plate in step (2), wash with 1×PBS three times, stain and fix the cells;
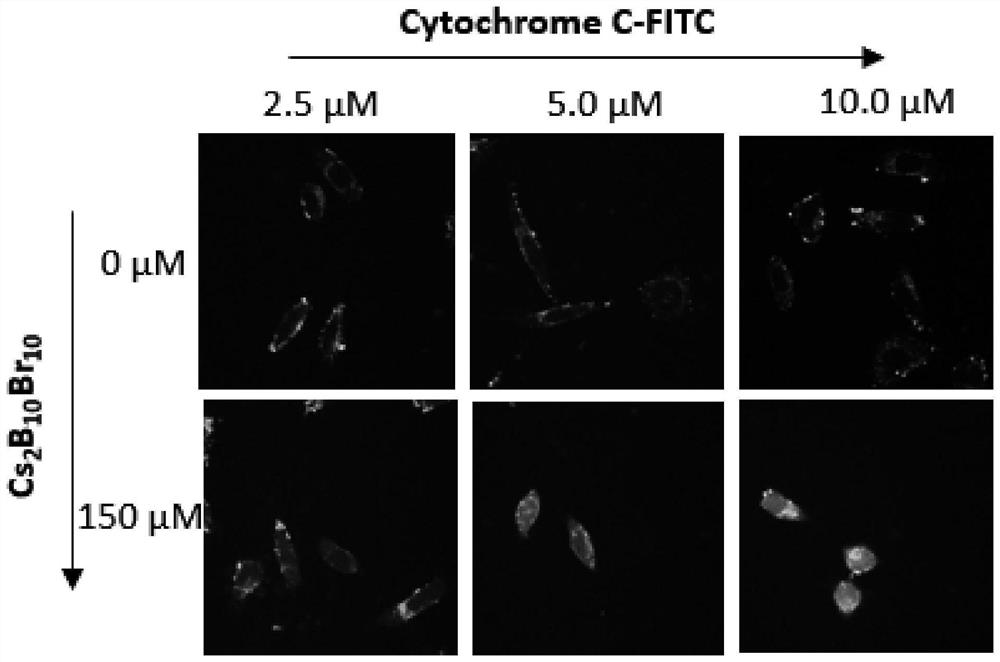
[0031] (4) Carry out confocal imaging of the cells using a confocal microscope to observe the distribution of labeled cytochrome C in the cells. The distribution of proteins in the cells can be seen in the fluorescent channel of 500-530nm labeled cytochrome C, from image 3 boron halide clusters (C...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Take boron halide clusters (Na 2 B 12 Br 12 ) and labeled cytochrome C, the solvent is 1×PBS, the total volume is 100 μL, mixed thoroughly for 20 minutes, and sterilized by filtration through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane;
[0034] (2) Add 300 μL DMEM to the 24-well plate in which HeLa cells were cultured, and add 100 μL of the mixture in step (1), incubate for 6 hours, boron halide clusters (Na 2 B 12 Br 12 ) final concentration is 200 μM, and the concentration of labeled cytochrome C is 1.0 μM;
[0035] (3) Aspirate the mixture in the 24-well plate in step (2), wash with 1×PBS three times, stain and fix the cells;
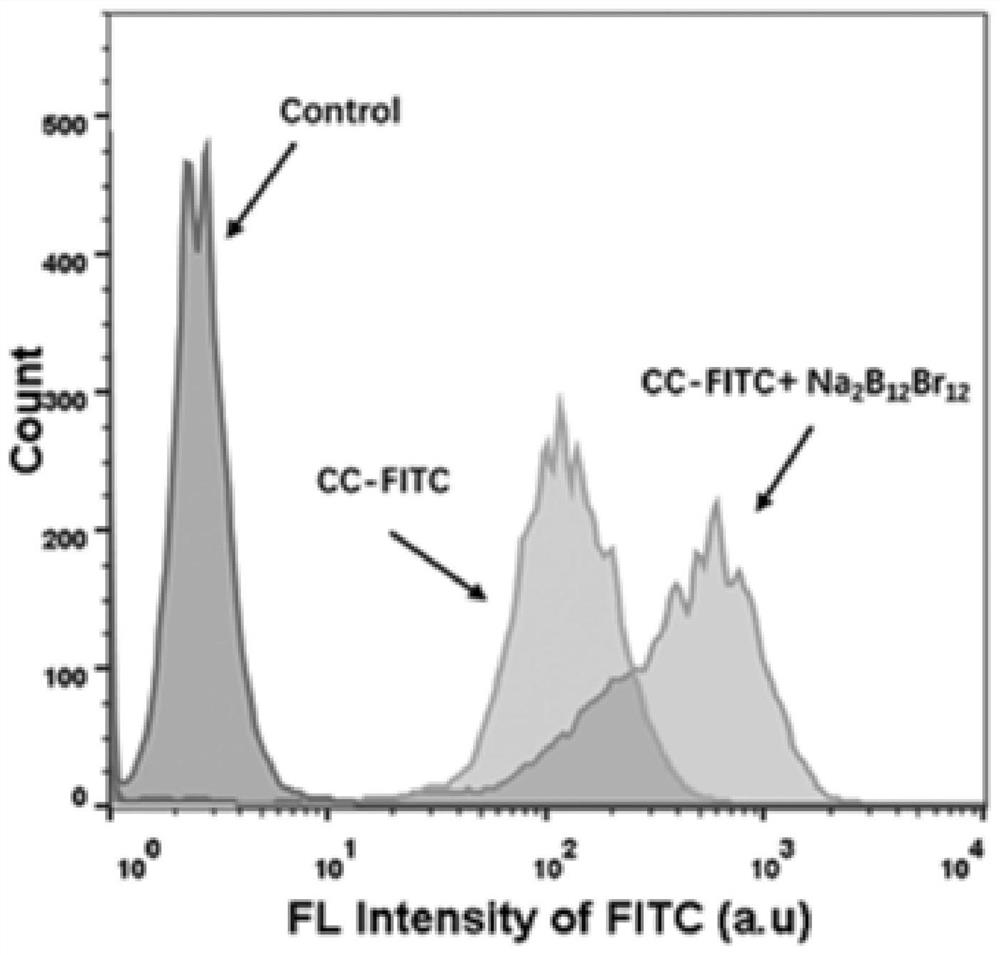
[0036] (4) Use a confocal microscope to perform confocal imaging of the cells to observe the distribution of the labeled cytochrome C in the cells. The fluorescent channel of the labeled cytochrome C at 630-670nm can be used to see the distribution of proteins in the cells. Flow cytometry The instrument detects the efficiency of labeled cytochro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com