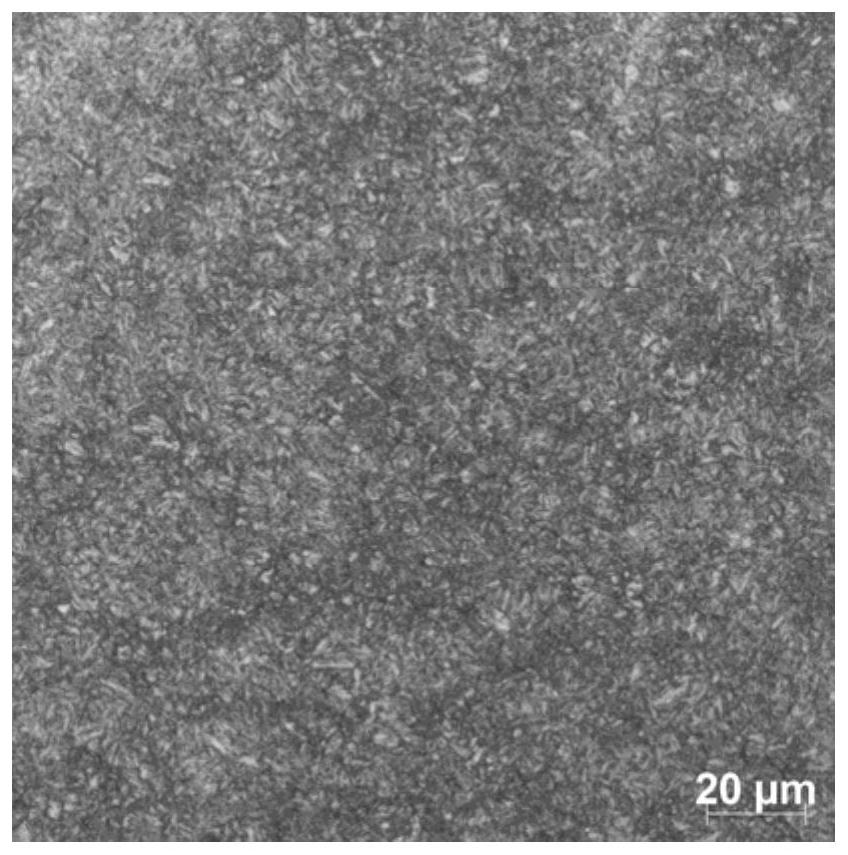
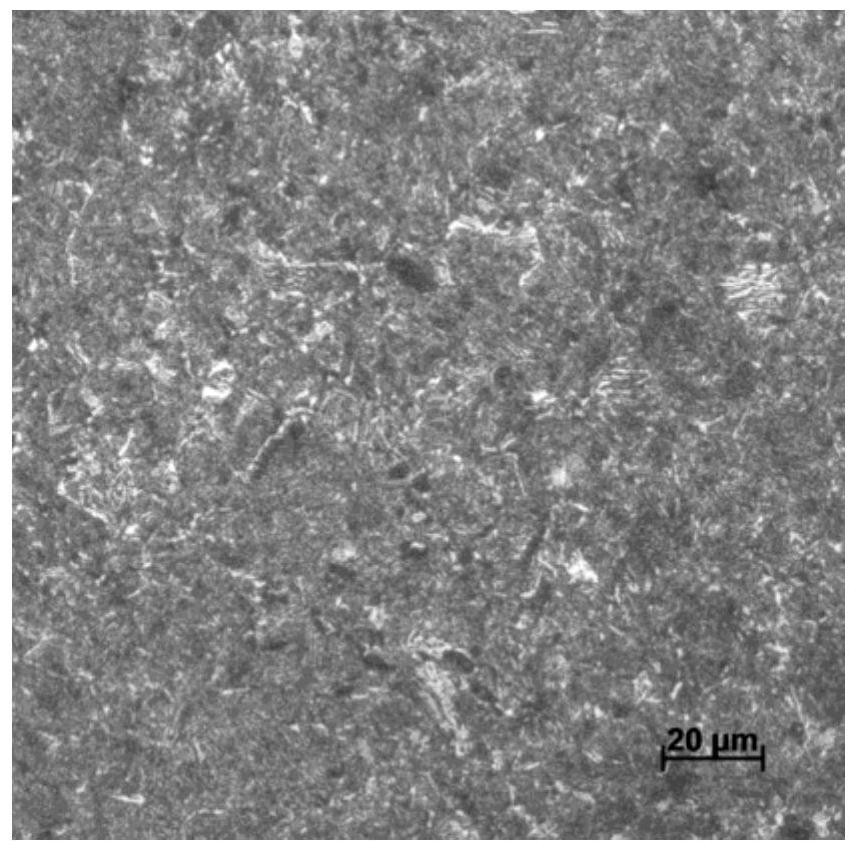
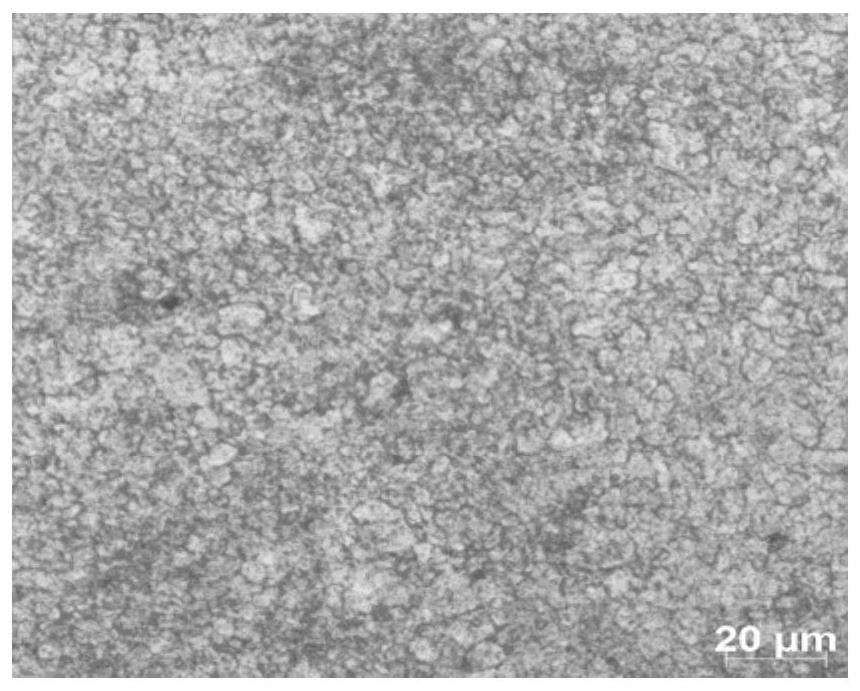
High-speed rail axle with long fatigue life and speed of not less than 400 kilometers per hour, and laser quenching method of high-speed rail axle
A technology of laser quenching and fatigue life, which is applied to axles, wheels, vehicle parts, etc., can solve the problems of low fatigue performance and inability to meet the application requirements of high-speed rail axles, achieve surface hardness and strength improvement, good and uniform cooling, and reduce effective tension The effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A laser quenching method for high-fatigue life and speed ≥ 400 kilometers per hour for high-speed rail axles, comprising the following process:
[0040] Axle blank forging→rough turning of rough axle→axle end face processing→heat treatment process→axle outer circle finish turning process→axle inner hole boring processing→cylindrical grinding→flaw detection→laser quenching→cylindrical grinding.
[0041] See Table 1 for the weight percentages of the chemical components of the high-fatigue life and speed ≥ 400 kilometers per hour high-speed rail axle described in Example 1. The balance not shown in Table 1 is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0042] The above heat treatment process includes: normalizing + quenching + high temperature tempering;
[0043] Specifically: normalizing process: heat the steel for high-speed rail axles to 920°C, keep it warm for 5 hours, and then air-cool it to below 400°C;
[0044] Quenching process: heat the high-speed rail axle steel after nor...
Embodiment 1-3
[0062] Table 4 Embodiment 1-3 laser quenching process
[0063]
[0064] 6) Fine grinding the surface of the axle after laser quenching.
[0065] Embodiment 2-Example 3 and Comparative Example 1 adopt the same composition and production method as Example 1, the difference is that the laser quenching process of Example 2-Example 3 is different from Example 1; The same quenching process parameters, the difference is that the composition and heat treatment process of Example 4 are different from those of Example 1; Comparative Example 1 does not use laser quenching, and Comparative Example 2 adopts the same quenching process parameters as Example 1, the difference is that Comparative Example 2 Composition and heat treatment process are different from embodiment 1. The laser quenching process of each embodiment and comparative example is shown in Table 4.
[0066] Embodiment 1-4 (after laser quenching) and comparative example 1 (not carrying out laser quenching), comparative e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fatigue strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com