Application of long-chain non-coding RNA as biomarker to diagnosis of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI)
A long-chain non-coding, acute kidney injury technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of poor specificity of serum creatinine, lack of targeted drugs, missing, etc., and achieve high fluid stability, high prediction efficiency, and high sequence homology Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, establish novel CI-AKI rat model
[0027] (1) 20 rats were randomly divided into the CI-AKI group and the control group, and were dehydrated for 24 hours. Six hours before exposure to the contrast agent, the rats in the two groups were injected with furosemide 15ml / kg intraperitoneally; Iopromide, a hypotonic contrast agent, was administered at 15 mL / kg, and the control group received the same amount of normal saline;
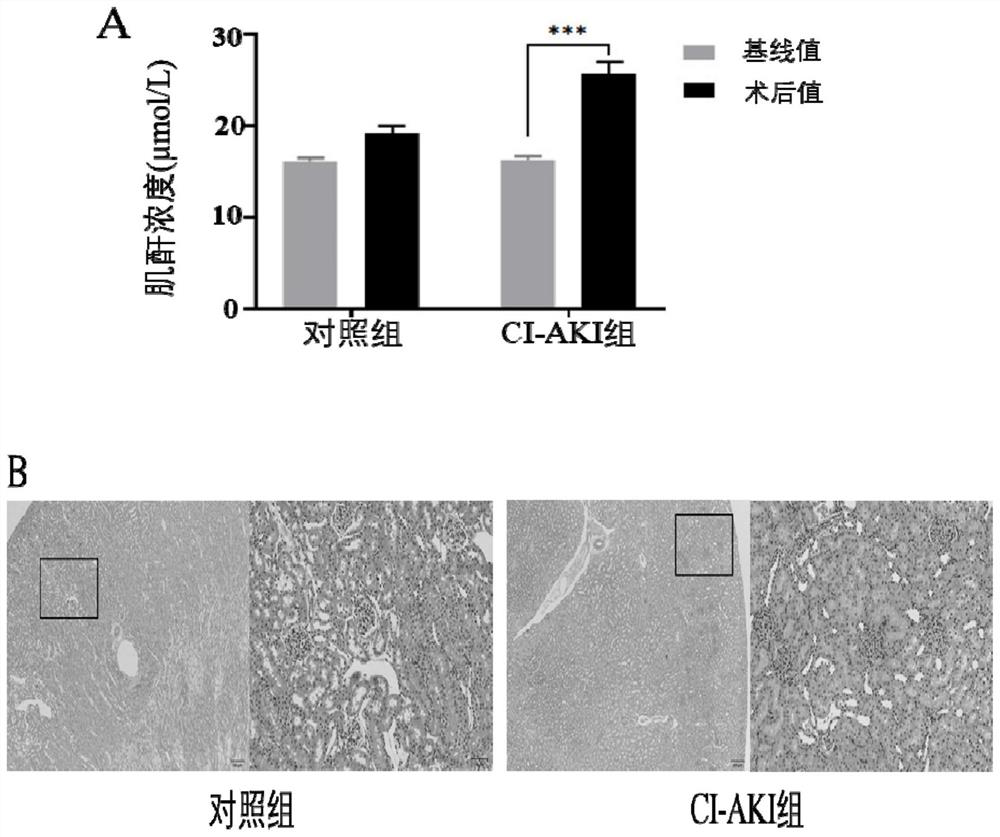
[0028] (2) All rats were sacrificed 24 hours after being exposed to the contrast medium, and kidney tissue was collected, and blood samples were collected from the orbital vein at baseline and 24 hours after administration; the serum creatinine (Scr) concentration in the blood samples was detected. (results such as figure 1 A). figure 1 The results of A show that the Scr concentration of the rats in the experimental group has increased by 56.81% on average, indicating that the Scr concentration of the rats in the experimental group has ...
Embodiment 2
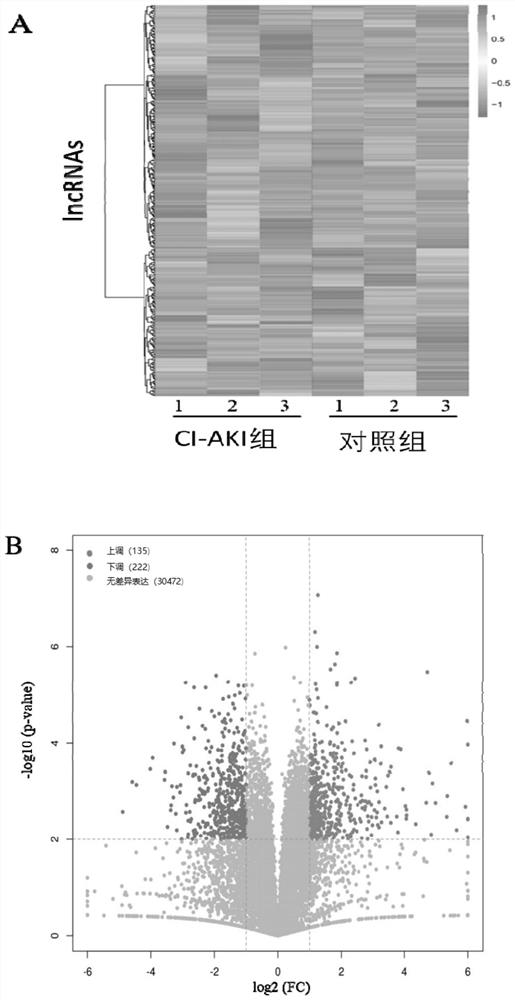
[0030] Example 2. Detection of lncRNAs profile in kidney tissue of CI-AKI rats by next-generation sequencing technology
[0031] (1) Extraction and purification of RNA: TRizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was used to extract total RNA in kidney tissue of CI-AKI rats according to conventional methods. Ribo-Zero rRNA Removal Kit (Epicentre) was used to remove ribose RNA according to the instructions to purify total RNA.
[0032](2) Analysis of RNA purity and quality: measure the concentration and purity of total RNA with a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo FisherScientific, Wilmington, DE). When OD260 / OD280 is 1.8-2.2, it is considered that the concentration of total RNA is consistent with RNA Sequencing standard. And check the quality of RNA sample with Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer and RNA 6000 nanometer kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Samples with an RNA integrity of 8 or higher were considered acceptable, and acceptable RNA was stored at -80°C.
[0033] (3) Us...
Embodiment 3
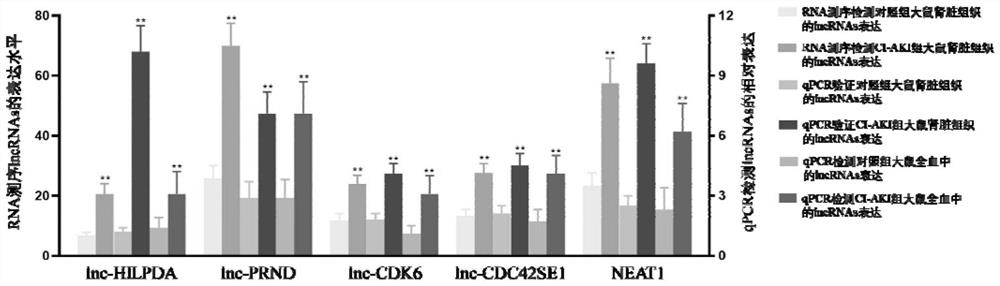
[0037] Example 3. Reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (Reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, RT-qPCR) was used to verify the expression of 14 lncRNAs in kidney tissue and whole blood of CI-AKI rats. Proceed as follows:
[0038] (1) Referring to the above RNA extraction method, extract RNA from rat kidney tissue, and use PrimeScript TM RT Reagent Kit (RR037) randomly selects 6mers and oligo-dT primers (Takara, Japan) to reverse transcribe RNA into cDNA;
[0039] (2) Design primers for the above 14 lncRNAs respectively, using GAPDH as an internal reference, the primer sequences of lncRNAs and GAPDH are shown in Table 1.
[0040] (3) in TB Premix Ex Taq TM II (TliRNaseH Plus, RR820) performs quantitative real-time PCR, adding fluorescent groups to the PCR reaction system, and using the accumulation of fluorescent signals to monitor and continuously analyze the entire PCR process in real time;
[0041] (4) D...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com