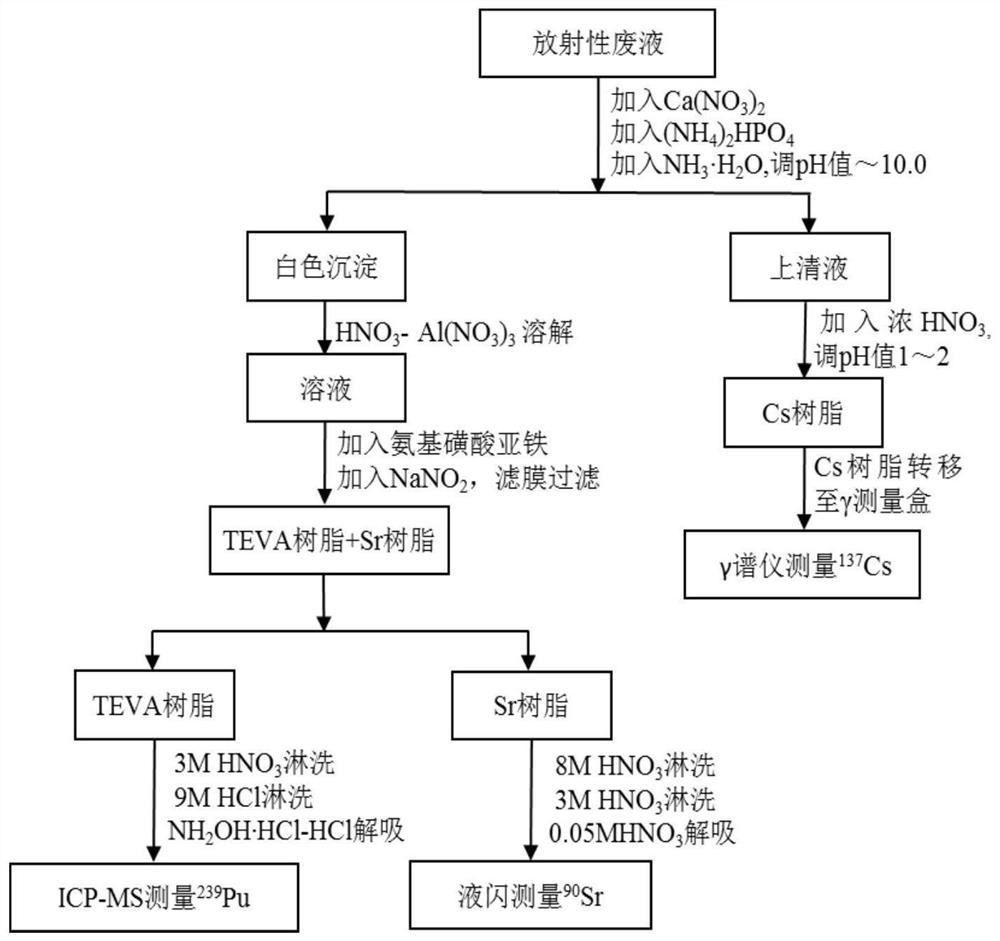
Rapid joint analysis method for Pu-239, Sr-90 and Cs-137 in waste liquid
A technology of pu-239 and cs-137, applied in the field of rapid combined analysis of Pu-239 and Cs-137 in waste liquid, and Sr-90, which can solve the problems of large amount of secondary waste liquid, cumbersome process and long analysis period.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] (1) Take 1L of radioactive waste liquid produced in the laboratory in a beaker, after acidification, add 242 Pu 5pg diluent, stir well, as the test solution; add 2mL1.25mol / L Ca(NO 3 ) 2 , place the sample on a heating plate at 50°C for 20 min; add 0.75 mL of phenolphthalein indicator and 5 mL of 3.2 mol / L (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 solution; slowly add concentrated ammonia water to the solution, and stir continuously with a glass rod, and phenolphthalein determines the titration end point to generate Ca at this time. 3 (PO 4 ) 2 Precipitate; the precipitate naturally settled for 2 hours, and the supernatant was siphoned out; the remaining samples were transferred to a 250mL centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 3500rpm for 10min, the precipitate was separated, and the supernatant was poured out; the precipitate was washed with 10mL of water, and then centrifuged at 3500rpm for 10min. Separate the precipitate, pour off the supernatant, and combine all supernatants;
[0048] (2) U...
Embodiment 2
[0065] (1) Take 1L of radioactive waste liquid produced in the laboratory in a beaker, after acidification, add 242 Pu 10pg diluent, stir well, as the test solution; add 2mL1.25mol / L Ca(NO 3 ) 2 , place the sample on a heating plate at 60°C for 15 min; add 0.75 mL of phenolphthalein indicator and 5 mL of 3.2 mol / L (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 solution; slowly add concentrated ammonia water to the solution, and stir continuously with a glass rod, and phenolphthalein determines the titration end point to generate Ca at this time. 3 (PO 4 ) 2 Precipitate; the precipitate naturally settled for 3 hours, and the supernatant was siphoned out; the remaining samples were transferred to a 250mL centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 3500rpm for 10min, the precipitate was separated, and the supernatant was poured out; the precipitate was washed with 10mL of water, and then centrifuged at 3500rpm for 10min. Separate the precipitate, pour off the supernatant, and combine all supernatants;
[0066] (2) ...
Embodiment 3
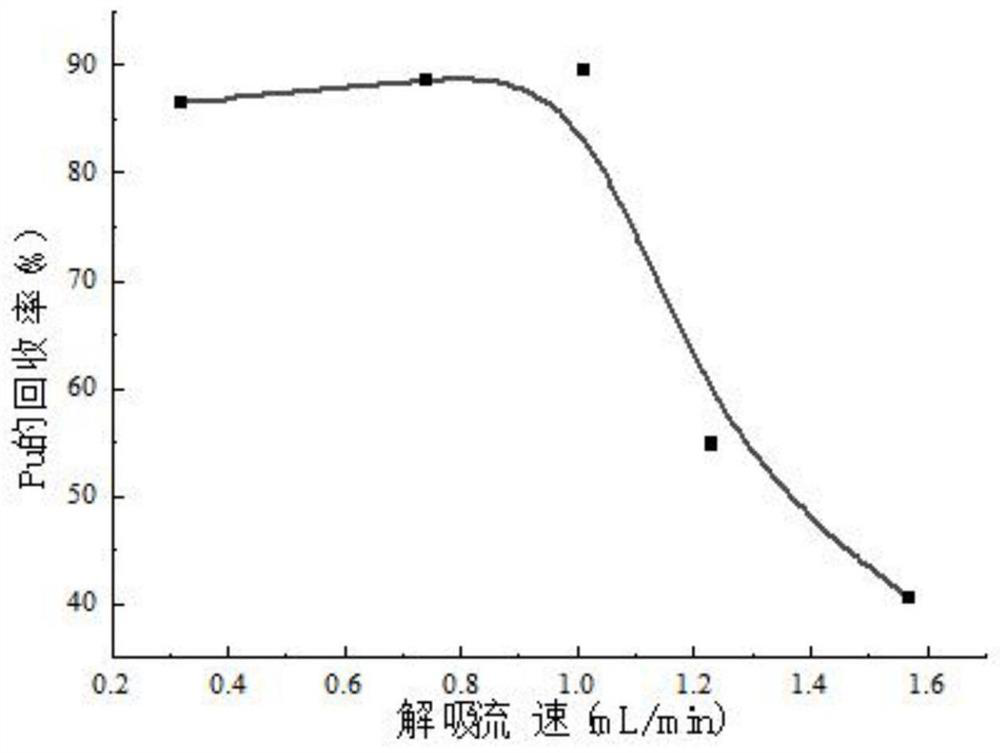
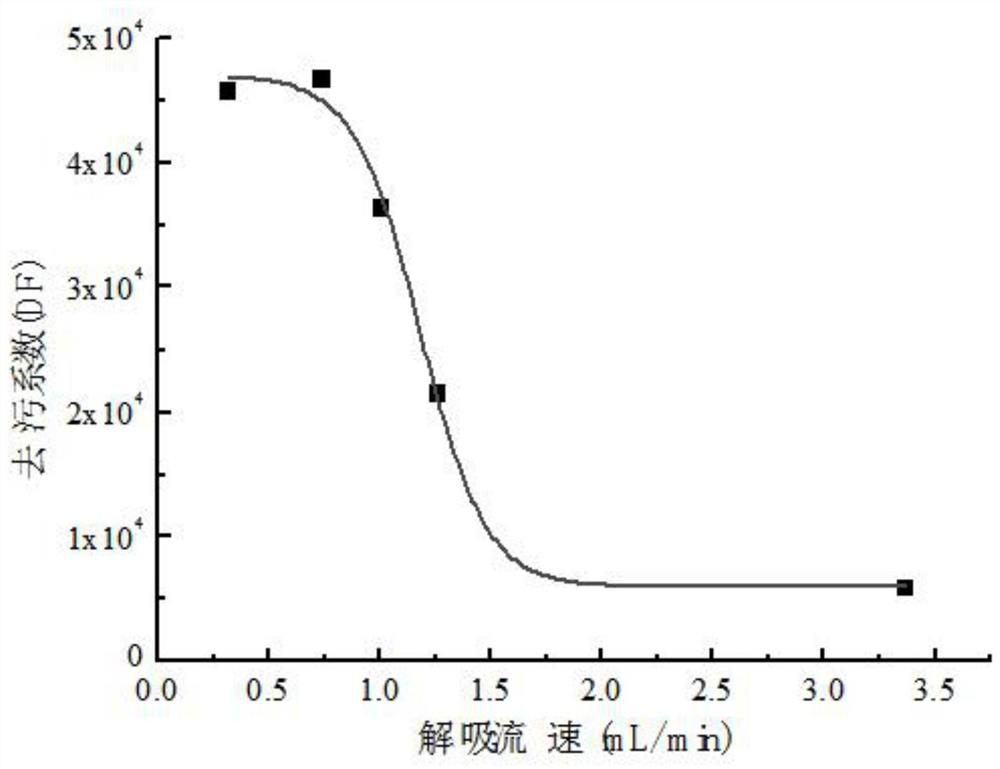
[0082] In order to test and verify the separation process, take 1L of ultrapure water from 3 groups, after acidification, add 10pg of 242 Pu, 4 mg 133 Cs and 4mg 88 As the test solution in Example 1, Sr is analyzed according to the process of Example 1. The difference from Example 1 is that in step (3), directly use ICP-MS to measure the concentration of Sr in the desorption solution of the TEVA resin column. 242 The Pu content is used to calculate the recovery rate, and the experimental results are shown in Table 1.
[0083] Table 1 Pu, Sr and Cs recoveries (%)
[0084]
[0085] The recoveries of plutonium, strontium and cesium in the three samples were all relatively high.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com