Hybrid filter for filtering out fine and ultrafine dust
A technology of filter and water-based adhesive, which is applied in the direction of membrane filter, filtration separation, and dispersed particle filtration, etc. It can solve the problems of being unable to block the inhalation of Sox and NOx into the body, and achieve good removal rate and low air flow resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0040] Embodiment Manufacture of hybrid filter
[0041] Step 1: Preparation of Dip Solution
[0042] To manufacture a hybrid filter, an appropriate viscosity of cellulose nanofibers and an appropriate content of an aqueous binder play a role as important factors. The average diameter of the cellulose nanofibers was 20 nm, and water-dispersed polyurethane was used as the water-based binder. Cellulose nanofibers and a water-based binder were mixed in water to prepare an impregnation solution according to the composition shown in Table 1.
[0043] Step 2: Impregnation of the porous support
[0044] As the porous support, a soft reticulated polyurethane foam was used. In the immersion solution of various compositions prepared in the above-mentioned step 1, the soft reticulated polyurethane foam was fully immersed for about 10 minutes, and then taken out and dried at room temperature for one day to manufacture a hybrid filter.
[0045]It was observed by scanning electron...
experiment example 1
[0046] Evaluation of the impregnation amount of the mixture of cellulose nanofibers and aqueous binder in the hybrid filter
[0047] The impregnation amount was calculated by the following mathematical formula.
[0048] Impregnation amount = {(weight of dried foamed plastics after dipping-weight of foamed plastics before dipping) / weight of foamed plastics before dipping}×100
[0049] Table 1
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] As shown in Table 1 above, when the concentration of cellulose nanofibers is increased, the amount of impregnation tends to increase regardless of the content of the water-dispersible polyurethane binder. In addition, even if the concentration of the water-dispersible polyurethane used as a binder is lowered, the amount of impregnation tends to hardly decrease. Furthermore, the degree of formation of cellulose nanofiber films in the open cells of the flexible polyurethane foam increases as the content of cellulose nanofibers increases.
[0053] Regardin...
experiment example 2
[0054] Observation of the morphology of cellulose nanofibers adhered to the open cells of flexible polyurethane foam
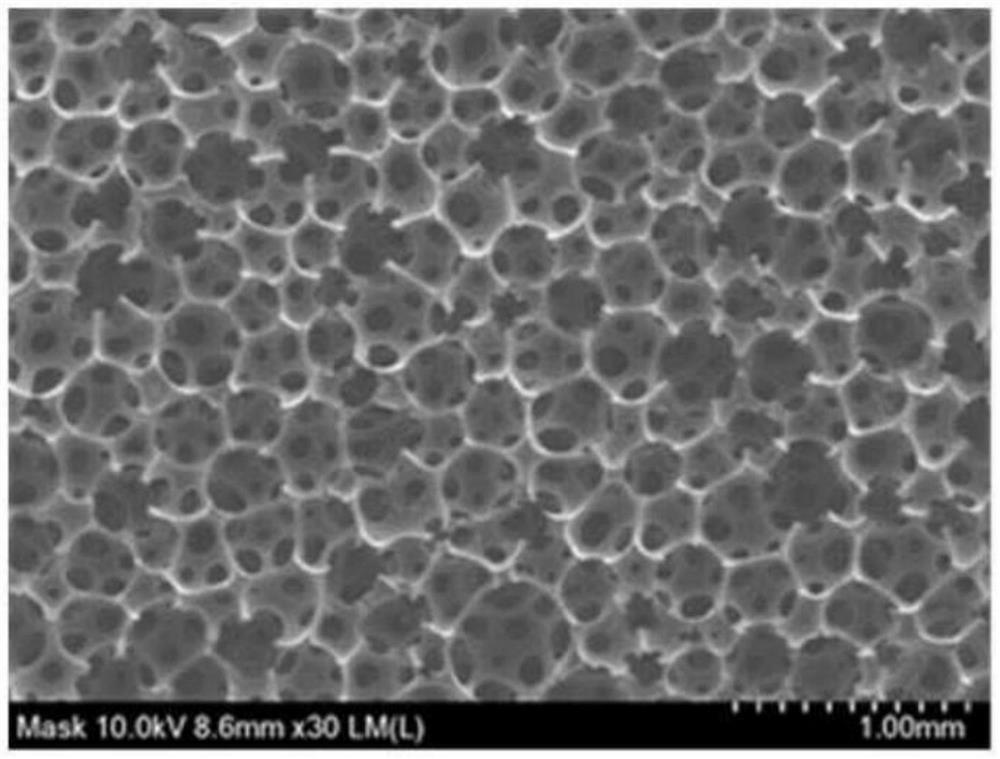
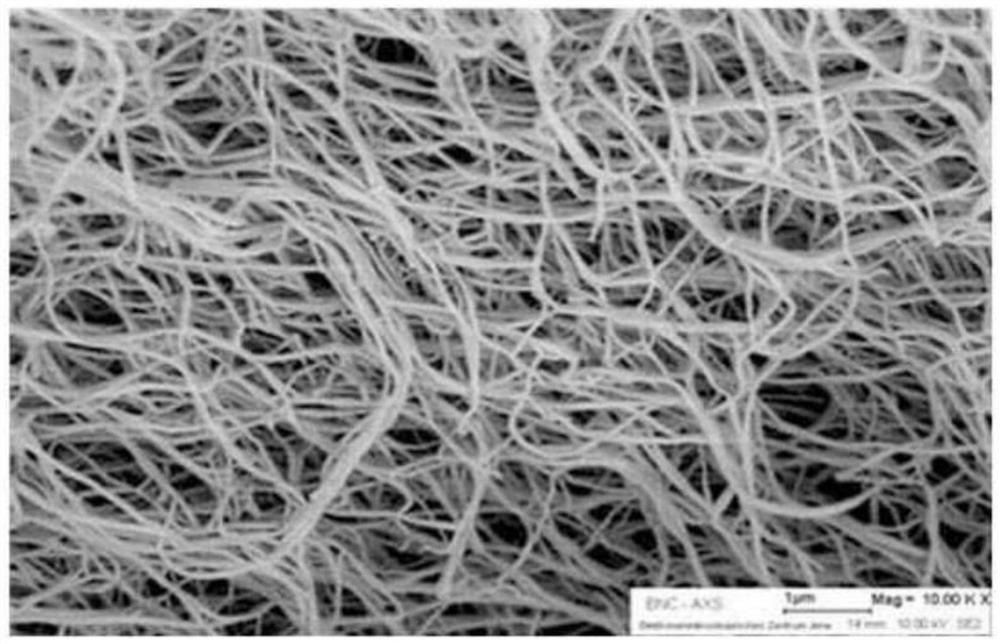
[0055] exist Figure 4 to Figure 6 The formation of cellulose nanofibrous membranes in the open cells of flexible polyurethane foams has been confirmed in .
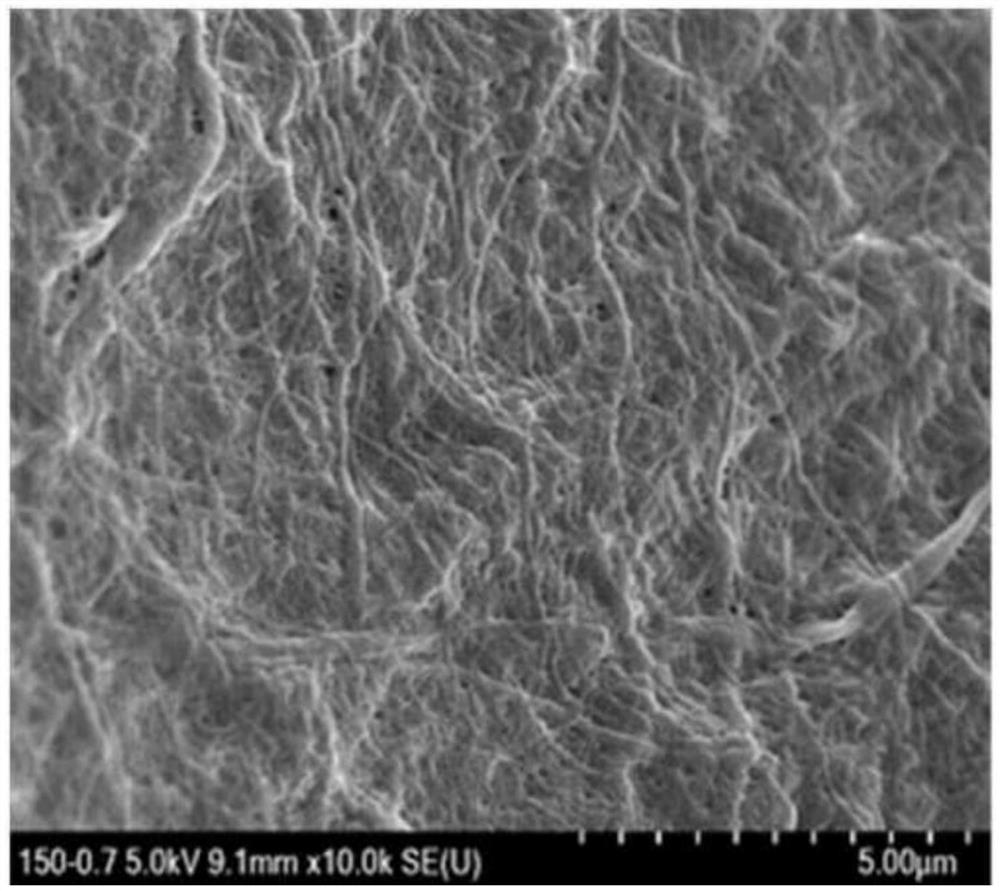
[0056] In this regard, in order to understand whether the nanofiber morphology with high specific surface area is still maintained in the cellulose nanofiber membrane, Figure 7 (Scale bar: 2 μm) Shown will be further enlarged Figure 4 to Figure 6 (Scale bar: 500 μm) After observation.
[0057] as Figure 7 As shown, it can be known that the cellulose nanofibers adhered in the fine structure of pores of the hybrid filter according to an embodiment of the present invention still maintain the fine nanofiber structure after adhesion.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com