Preparation method of a cellulose-based underwater adhesive hydrogel
A cellulose and hydrogel technology, which is used in the preparation of underwater adhesive hydrogels, can solve the problems of weak underwater adhesion and low self-healing efficiency of gels, and achieve good underwater adhesion. effect, excellent adhesion, excellent adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
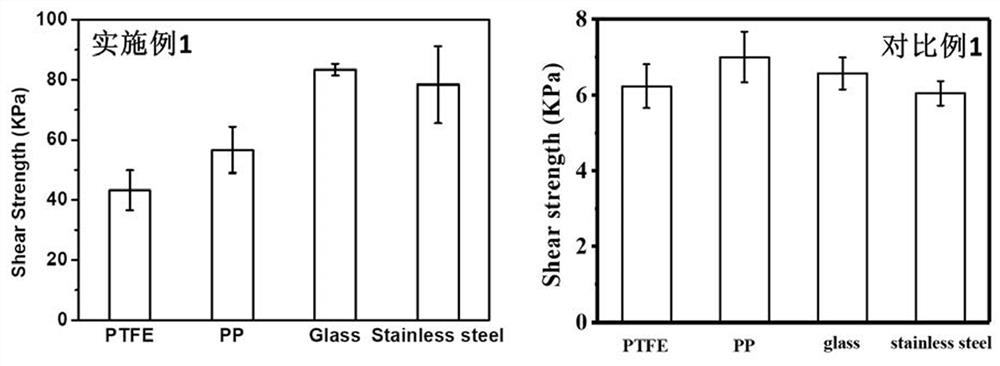
Embodiment 1
[0027] A preparation method of cellulose-based underwater adhesive hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
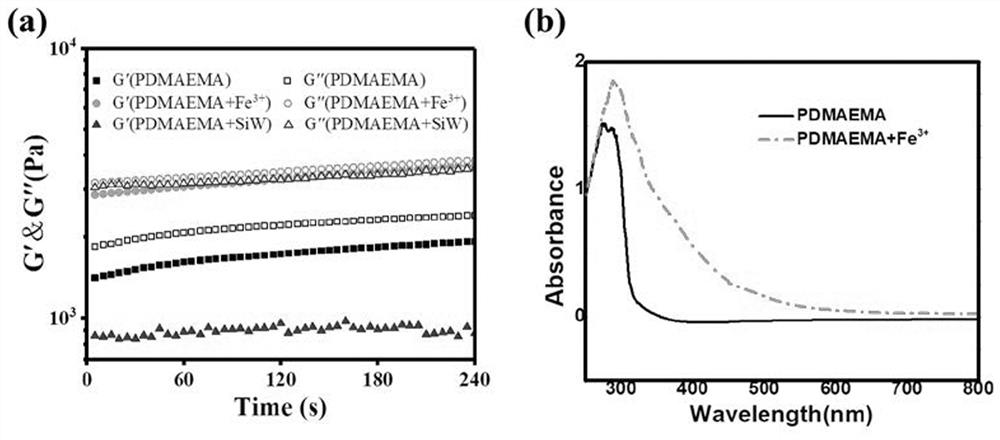
[0028] (1) Preparation of cellulose-heteropolyacid complex solution: under stirring, 120 mg of methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose and 20 mg of ferric chloride hexahydrate were dissolved in 3.5 mL of distilled water to form a cellulose mixture; Dissolve 80 mg of tungstosilicic acid in 0.5 mL of distilled water to obtain an aqueous solution of tungstosilicate; slowly drop the aqueous solution of tungstosilicate into the cellulose mixed solution, stir and mix evenly to obtain a cellulose-tungstosilicate precursor;
[0029] (2) Preparation of hydrogel: Take 4 mL of cellulose-tungstosilicate precursor obtained in step (1), add 2.4 g of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate monomer into it, stir and mix evenly, and then add the monomer Potassium persulfate with a molar mass of 1% was stirred evenly, and reacted at room temperature for 8 hours to obtain a brown-red hydrogel.
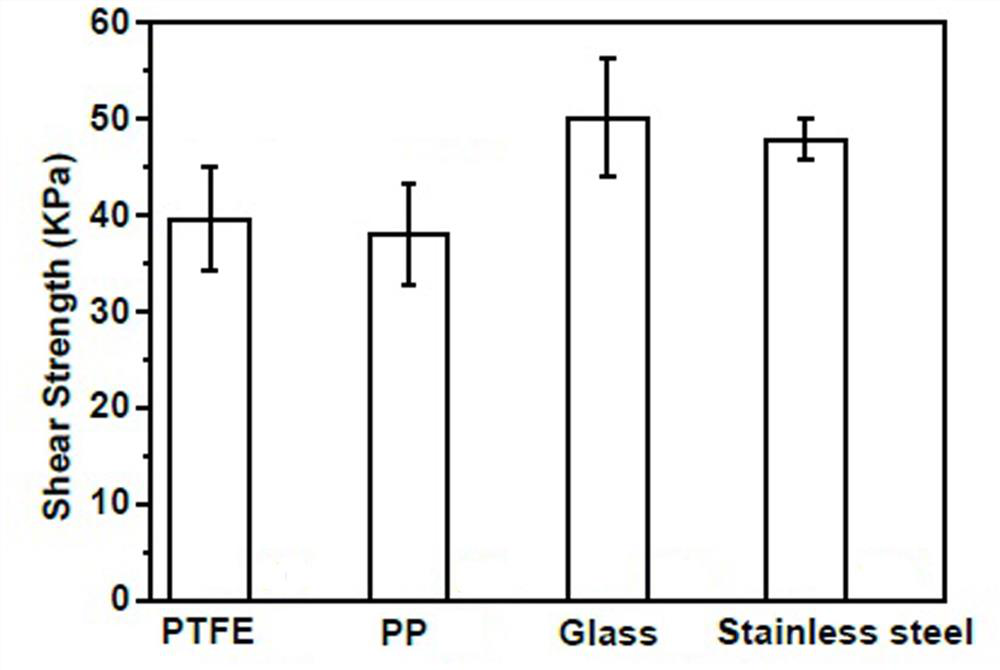
Embodiment 2
[0031] A preparation method of cellulose-based underwater adhesive hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Preparation of cellulose-heteropolyacid complex solution: under stirring, 120 mg hydroxyethyl cellulose and 20 mg ferric chloride hexahydrate were dissolved in 3.5 mL distilled water to form a cellulose mixture; 80 mg Dissolve tungstosilicic acid in 0.5 mL distilled water to obtain an aqueous tungstosilicic acid solution; slowly drop the aqueous tungstosilicic acid solution into the cellulose mixed solution, stir and mix evenly to obtain a cellulose-tungstosilicate precursor;
[0033] (2) Preparation of hydrogel: Take 4 mL of cellulose-tungstosilicate precursor obtained in step (1), add 2.4 g of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate monomer into it, stir and mix evenly, and then add the monomer Potassium persulfate with a molar mass of 1% was stirred evenly, and reacted at room temperature for 8 hours to obtain a brown-red hydrogel.
Embodiment 3
[0035] A preparation method of cellulose-based underwater adhesive hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Preparation of cellulose-heteropoly acid complex solution: under stirring, 120 mg of methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose and 20 mg of aluminum chloride hexahydrate were dissolved in 3.5 mL of distilled water to form a cellulose mixture; Dissolve 80 mg of tungstosilicic acid in 0.5 mL of distilled water to obtain an aqueous solution of tungstosilicate; slowly drop the aqueous solution of tungstosilicate into the cellulose mixed solution, stir and mix evenly to obtain a cellulose-tungstosilicate precursor;
[0037] (2) Preparation of hydrogel: Take 4 mL of cellulose-tungstosilicate precursor obtained in step (1), add 2.4 g of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate monomer into it, stir and mix evenly, and then add the monomer Potassium persulfate with a molar mass of 1% was stirred evenly, and reacted at room temperature for 8 hours to obtain a brown-red hydrogel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com