Gene regulation via conditional nuclear localization of gene modulating polypeptides
A technology for gene and target regulation, which can be applied to polypeptides containing positioning/targeting motifs, activity regulation, genetic engineering, etc., and can solve problems such as reduced immune cell response and reduced effectiveness of immunotherapy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
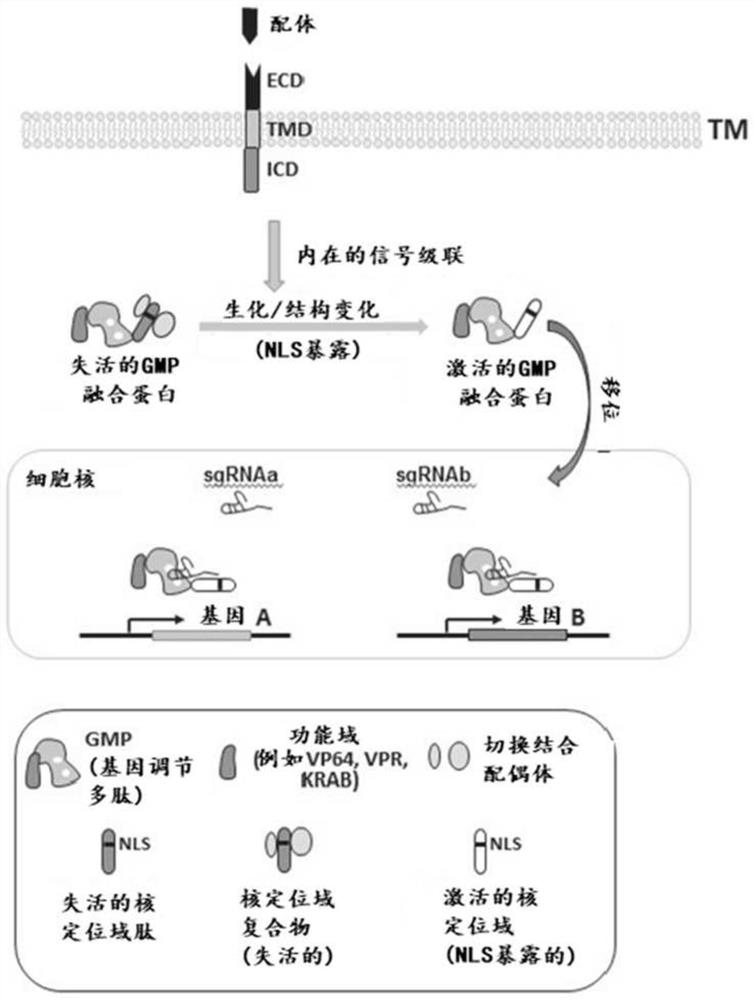
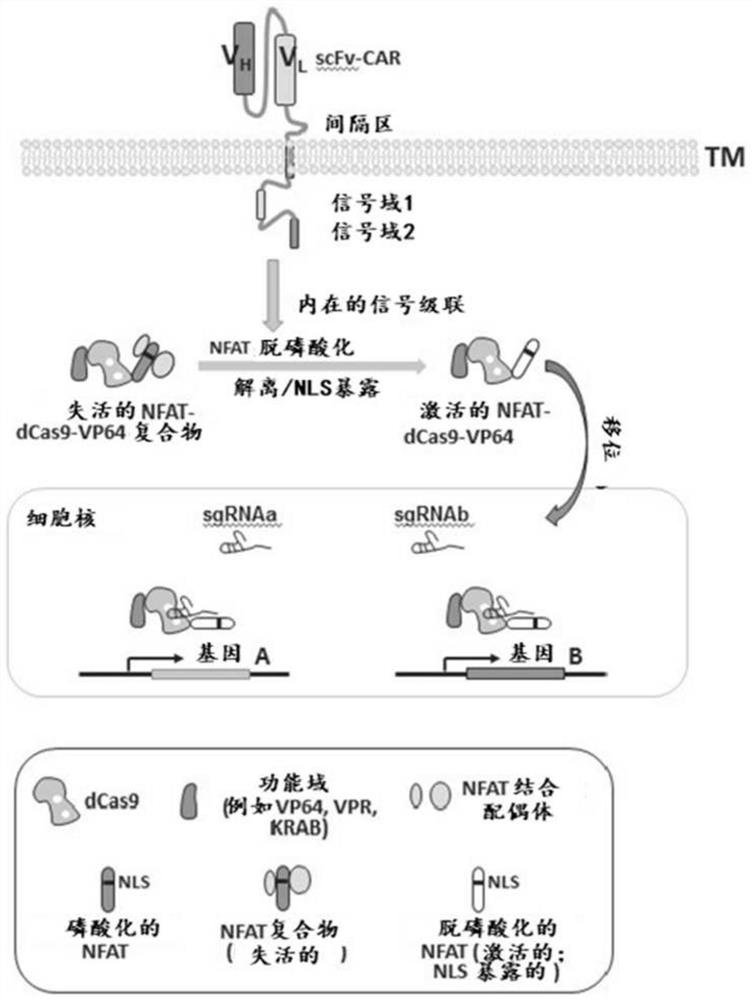
[0479] Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) is a family of T lymphocyte activation-specific transcription factors consisting of five members: NFATc1, NFATc2, NFATc3, NFATc4 and NFAT5. The NFAT response element (recognition sequence) is a transcriptional element in the IL-2 enhancer that, in the absence of physiological activation of T lymphocytes by antigen receptors or by combined treatment of T cells with ionomycin and PMA, Usually has no stimulatory effect on transcription.
[0480] In resting T cells, NFAT can exist in the cytoplasm in a phosphorylated state. In this state, nuclear localization signals (NLS) can be masked by phosphorylated serine residues or other inhibitory NFAT-binding proteins. Upon cellular activation, NFAT can be directly dephosphorylated by calcineurin (CN), and the NFAT NLS can then be exposed due to a conformational change or dissociation of an inhibitory binding partner, allowing NFAT nuclear translocation (Shibasaki, F. et al., 1996, Natu...
Embodiment 2
[0481] Example 2: CAR activation-dependent GFP protein expression mediated by N-NFATc2-dCas9-VP64 fusion protein
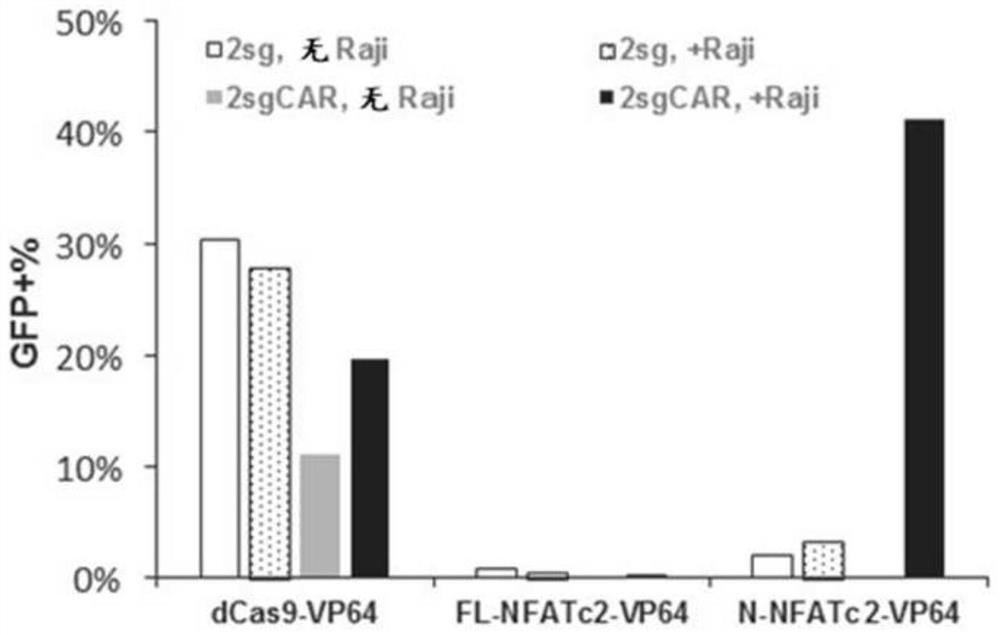
[0482] Upregulation of the GFP reporter gene using a catalytically inactive (dCas9) system. T cell activation-induced activity was observed when dCas9 was fused to the NFATc2 N-terminal domain and transfected into Jurkat T cells containing a GFP-targeting sgRNA and a GFP reporter gene ( Figure 3A and Figure 3B ).
[0483] Two stable Jurkat-derived cell lines (2sg and 2sg-CAR) were transfected with the indicated DNA constructs and BFP expression constructs, respectively, and then stimulated with CD19+ Raji cells. Two days later, cells were harvested for flow cytometry analysis. Raji-stimulated cells were stained with anti-CD3-APC780 and CD22-PE before sampling in the flow cytometer. CD3+CD22- cells were gated as Jurkat-derived cells. Transfected cells were gated for data analysis using BFP expression. The 2sg cell line contains both a GFP reporter gene and ...
Embodiment 3
[0486] Example 3: Down-regulation of target genes
[0487] A catalytically inactive (dCas9) system as described in Example 2 was used to downregulate target genes. In this example, dCas9 is fused to a transcriptional repressor (eg, KRAB) rather than a transcriptional activator (eg, VP64). When dCas9-KRAB was fused to the N-terminal domain of NFATc2 (N-NFATc2-dCas9-KRAB) (SEQ ID NO:36) and transfected with sgRNA targeting the PD1 gene into the Jurkat T cell line expressing the CD19 CAR, Downregulation of PD1 was observed in activated T cells ( Figure 5 ).
[0488] Jurkat cells and Jurkat-derived cell lines constitutively expressing the CD19 CAR were transfected with N-NFATc2-dCas9-KRAB constructs and Gal4 control or PD1 sgRNA constructs, and then stimulated with CD19+ Raji cells one day later. After three days, cells were harvested for flow cytometry analysis. Raji-stimulated cells were stained with anti-CD22-APC and PD1-PE prior to sample collection in the flow cytometer....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com