A key exchange domain that controls changes in the lipid chain length of lipopeptides and its mutants and applications
A technology of exchanging structures and domains, applied in the biological field, to achieve the effect of reducing toxic and side effects, promoting clinical medicine, and increasing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
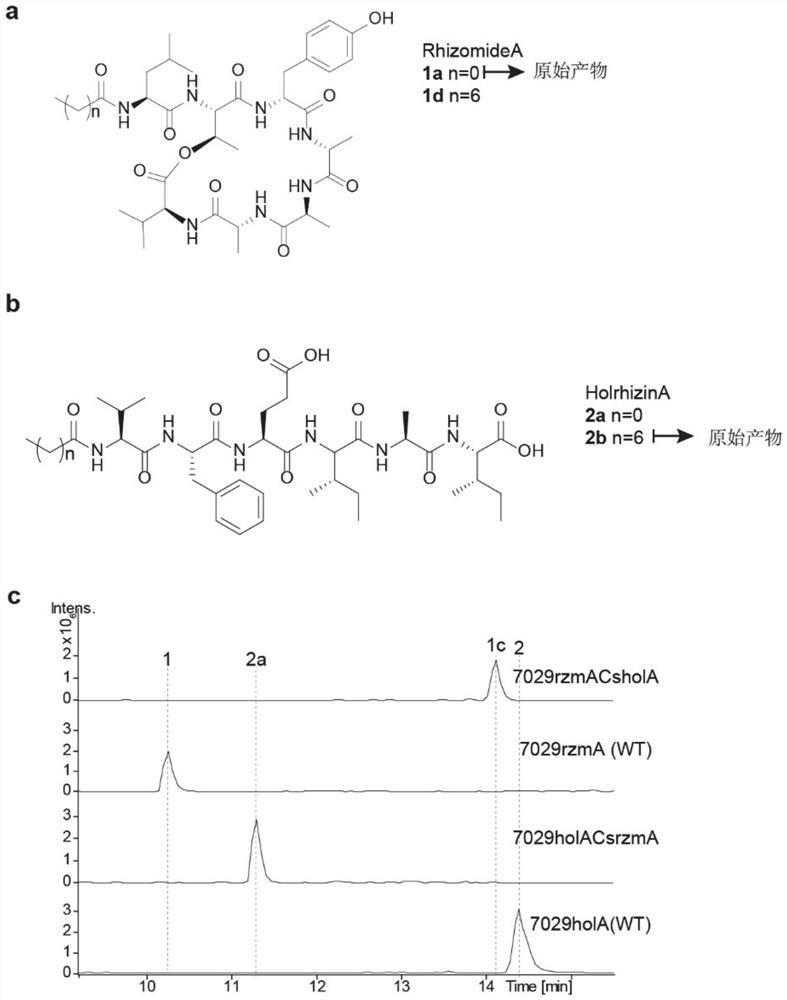
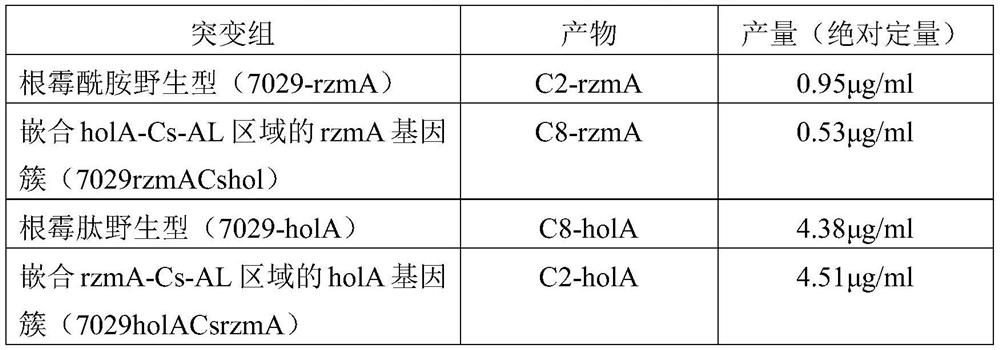
[0026] The Cs-AL regions of rzmA and holA were exchanged to obtain mutants rzmACsholA and holACsrzmA, and the catalytic activities of the mutants were verified from in vitro and in vivo levels. That is, the ability of the full-length rzmA / holA gene cluster and the corresponding mutants to catalyze the formation of the final product rzmA / holA and its derivatives shall prevail (the structure shown in figure 1 , a, b), absolute quantification was used for quantification. After separation and purification of derivatives and wild-type lipopeptide products, they were used as standards to quantify mutants. The quantitative instrument was liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
[0027] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0028] (1) According to antismash ( https: / / antismash.secondarymetabolites.org / #! / start ) predicted the Cs-AL region of rzmA and holA, and determined their amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2.
[0029] (2) Usin...
Embodiment 2
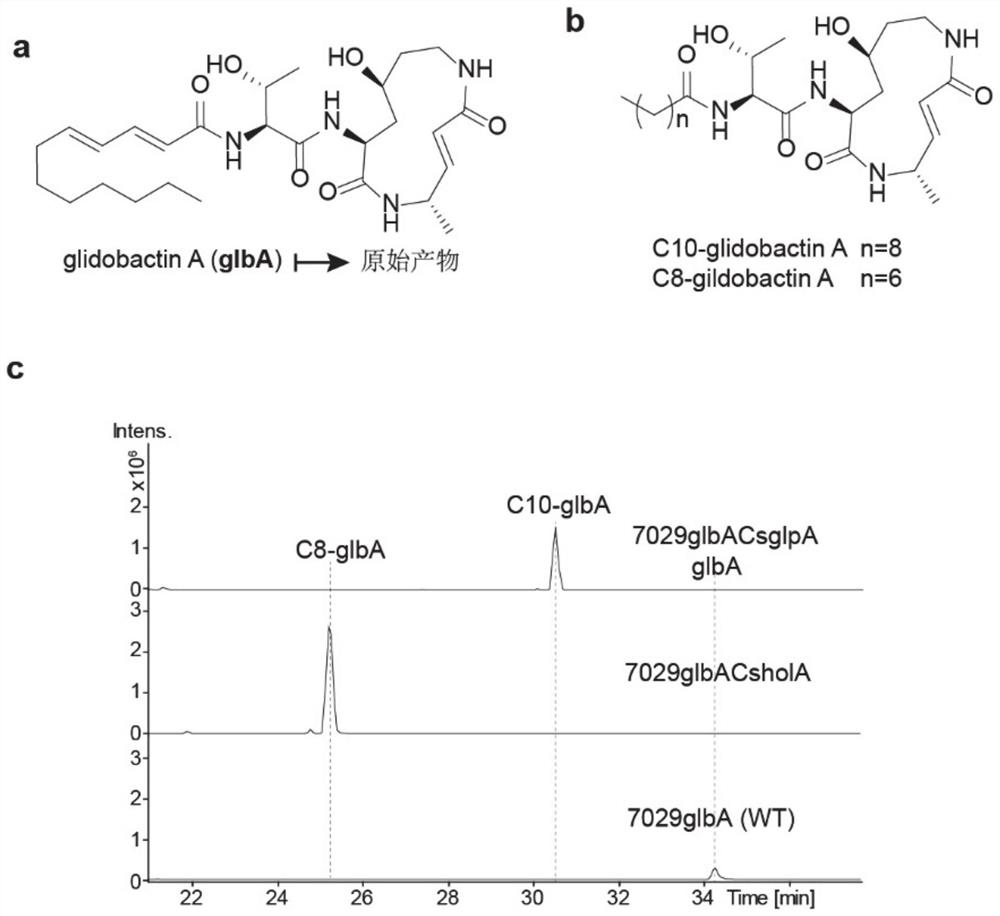
[0036] Further, the glbA gene cluster derived from DSM7029 was manipulated to replace the Cs-AL region of glbA with Cs-AL from holA of heterologous bacteria DS19002 and Cs-AL of glpA from homologous bacteria DSM7029. The obtained mutants were glbACsholA and glbACsglpA respectively, and the catalytic activities of the mutants were verified from in vitro and in vivo levels. That is, the ability of the full-length glbA gene cluster and the corresponding mutants to catalyze the formation of the final product glbA and its derivatives shall prevail (structures such as figure 2 , shown in a, b), absolute quantification was used for quantification. After separating and purifying the derivatives and wild-type lipopeptide products, the mutants were quantified by using them as standards. The quantitative instrument was liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
[0037] The Red / ET recombination system and operation in DSM7029 involved in the embodiment 2 all adopt document 3 (Wang...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com