Pair of refraction and diffraction mixed type light and thin Alvarez zoom glasses
A technology of refraction, mixing, and glasses, which is applied in the field of glasses, can solve problems such as limiting the flexibility of surface shape selection, and achieve the effects of light weight, convenient use, and thin lens thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049]A kind of light and thin Alvarez zoom glasses of refraction-diffraction hybrid type, comprise frame, eyeglass and control part; Described each lens is made of two Alvarez lenses of refraction-diffraction hybrid type complementary in surface shape; In order to reduce the thickness of single Alvarez lens, Use the fold-diffraction hybrid surface shape. The central area of the Alvarez lens of the refraction-diffraction hybrid type is a continuous surface shape, and the edge area is a diffraction microstructure, and the distribution area of the continuous surface shape and the diffraction microstructure is determined according to the thickness limit of the zoom lens; the diffraction microstructure is based on The processing conditions and scalar diffraction meet the conditions and design requirements, and the thickness distribution of the diffraction microstructure is preferred; each lens is fixed on the guide rail of the mirror frame through a slider, and one or The two ...
Embodiment 2
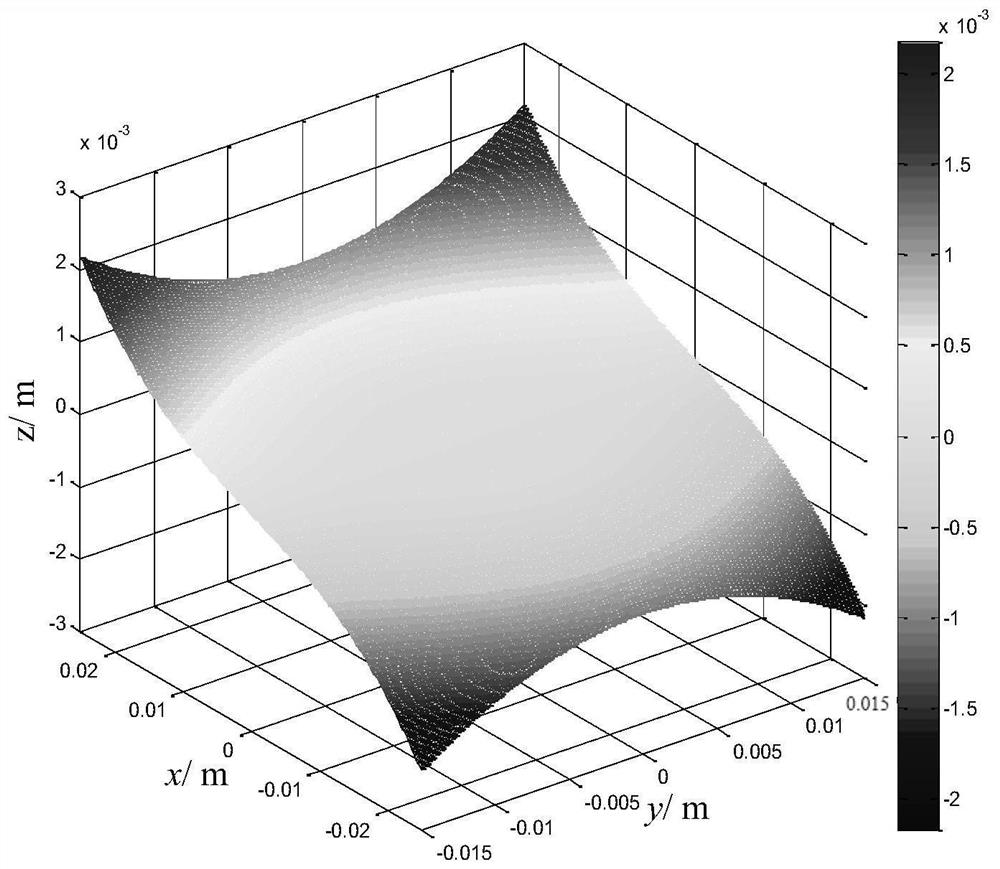
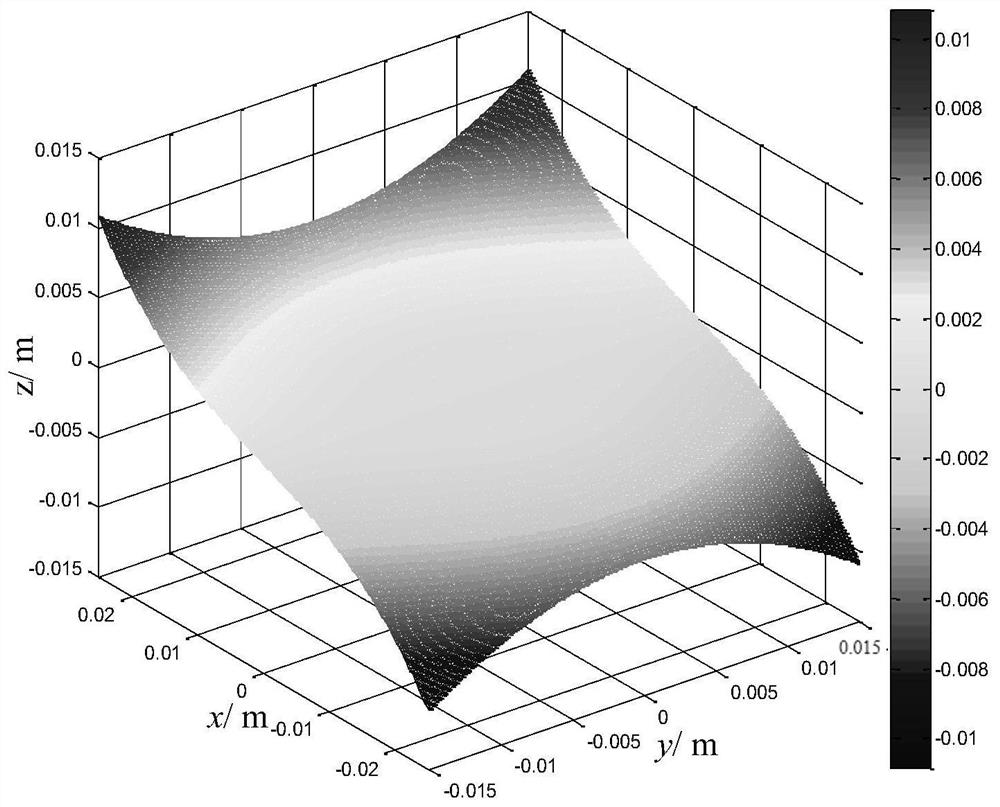
[0069] Let n=1.5, if d=0.001m changes 100 degrees, then A=1000m -2 . If the value ranges of x and y are respectively ±0.025m and ±0.015m, and the thickness of a single refraction-diffraction hybrid Alvarez lens is 2mm, and λ=587.5618nm, then when hour, is a continuous surface shape; when hour, is the diffractive microstructure; when hour, is a diffractive microstructure, where mod represents a modulo operation. When m(x,y)=20, the curved surface is shown in Figure 4(a), and the diffraction microstructure in the edge region is shown in Figure 4(b).
[0070] The edge region diffraction microstructure is quantified as 4-step distribution, as shown in Fig. 4(c).
Embodiment 3
[0072] In the above two embodiments, m(x, y) is taken as 20, and it can be seen from Fig. 4(b) that the height of the diffractive microstructure is 23.5 μm, and the width is less than 30 μm.
[0073] Taking the situation shown in Figure (4) as an example, different positive integers m(x, y) can be selected according to the processing conditions.
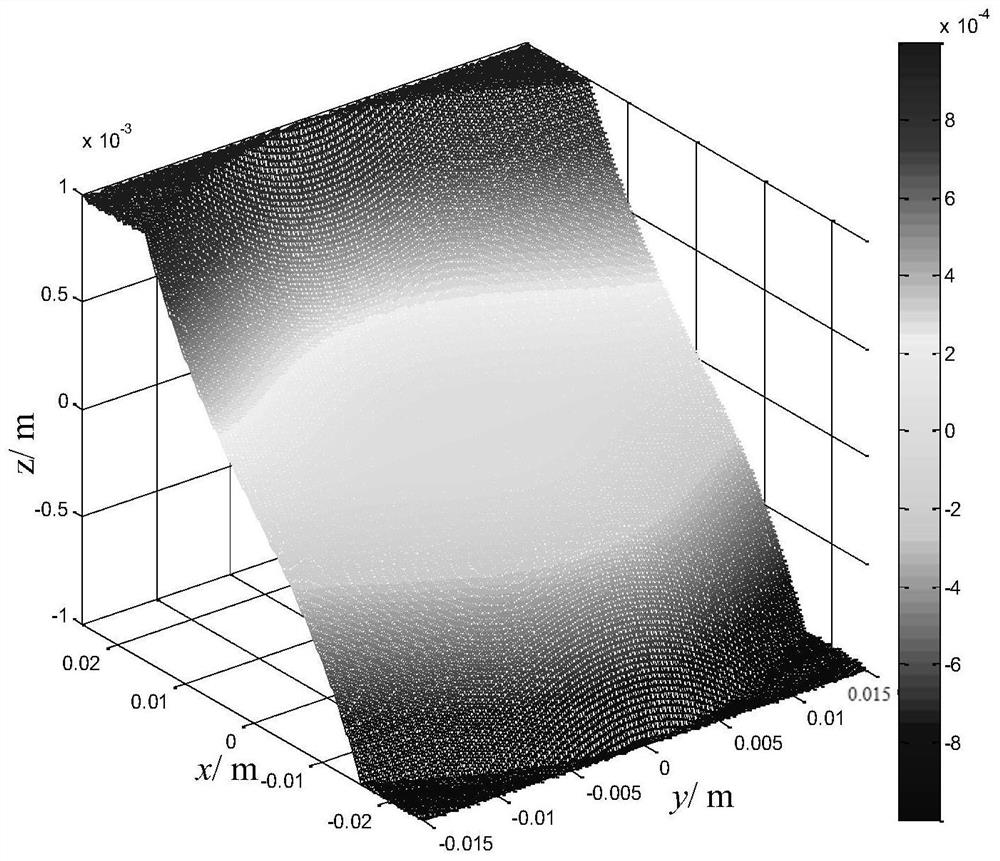
[0074] Taking the cross-section when y=0 as an example, in the diffraction microstructure, when -0.025m Figure 6 As shown, the width of the diffractive microstructure is greater than the width of the diffractive microstructure in the region of -0.0195m
[0075] Figure 7 Central cross-section of a single hybrid Alvarez lens with different positive integer values selected for different regions. While ensuring easy processing, the thickness of a single Alvarez lens is greatly reduced.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com