Time domain in-memory computing array structure based on magnetic random access memory
A random access memory and computing array technology, applied in the field of high-energy-efficiency circuit design, can solve the problems of low calculation and quantization accuracy, achieve high quantization accuracy, reduce overall power consumption, and reduce memory access power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
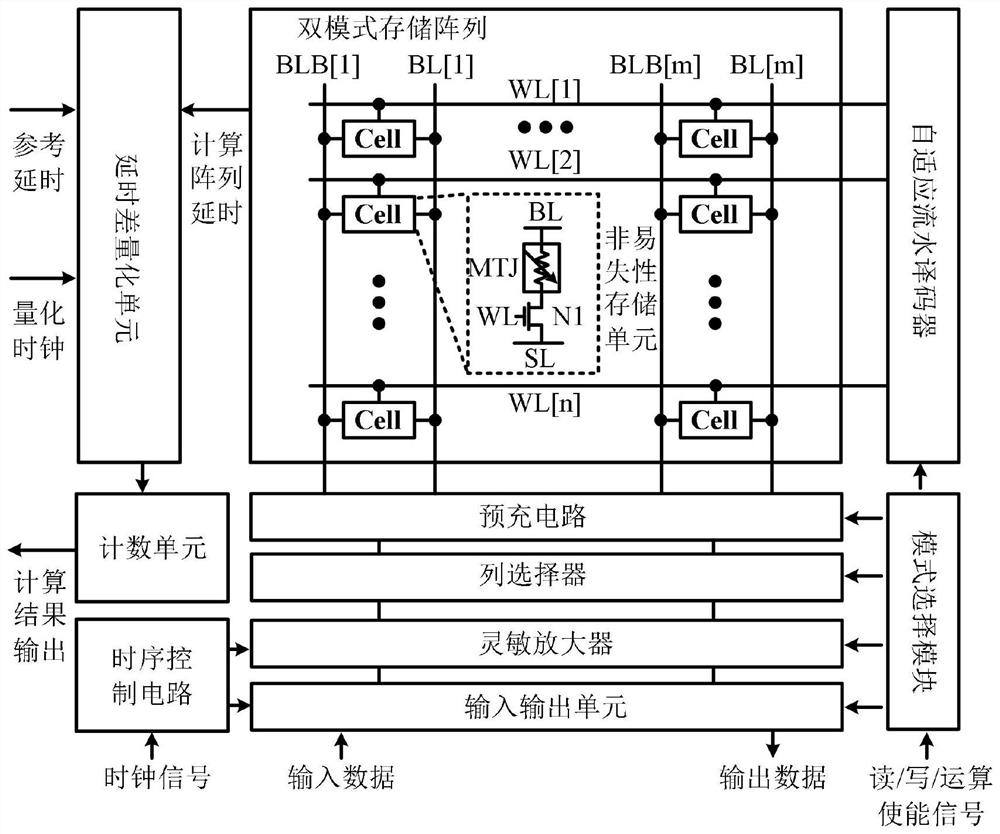
[0094] In-memory computing circuit suitable for fully connected binary neural network, including: dual-mode storage array, adaptive pipeline decoder, pre-charging circuit, column selector, sense amplifier, input and output unit, delay difference quantization unit , counting unit, timing control circuit and mode selection module.
[0095]
[0096] In the formula (2), the weight matrix M is mapped in the dual-mode storage array disclosed by the present invention as:
[0097]
[0098] The mapping method is that the weight matrix M in the formula (2) is transposed along the diagonal as in the formula (3), and the matrix coordinates after the transposition are stored in the storage unit in the dual-mode storage array disclosed by the present invention.
[0099] In the formula (2), the activation value vector V is mapped as:
[0100]
[0101] The mapping method is that the activation value vector V in the formula (2) is applied in the form of a word line signal in the dual...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com