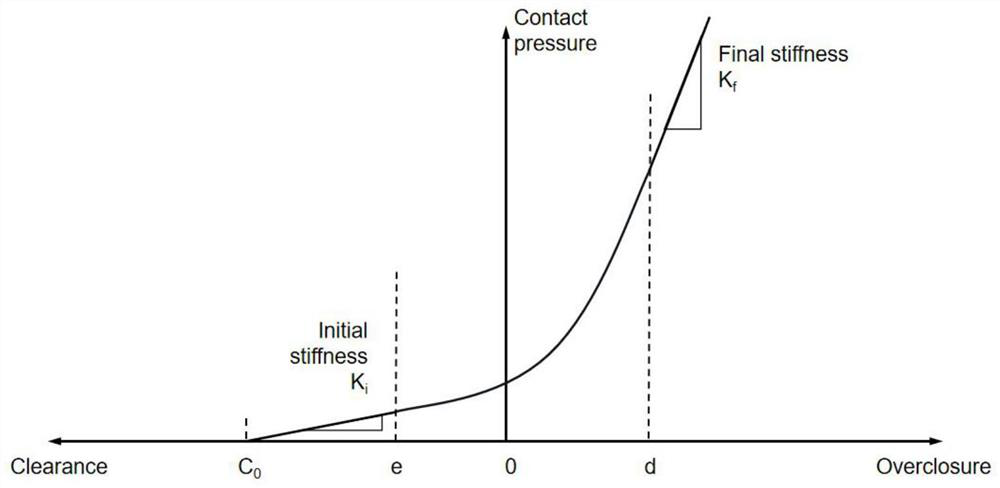
Modeling method for simulating low-speed cutting process of fiber reinforced composite material
A composite material and modeling method technology, which is applied in the field of finite element model modeling for low-speed cutting process simulation of fiber-reinforced composite materials, can solve problems such as interlayer damage, fiber monofilament and matrix damage in macroscopic simulation methods, and achieve The effect of high practical significance and guiding value, reducing the number of experiments and reducing time cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
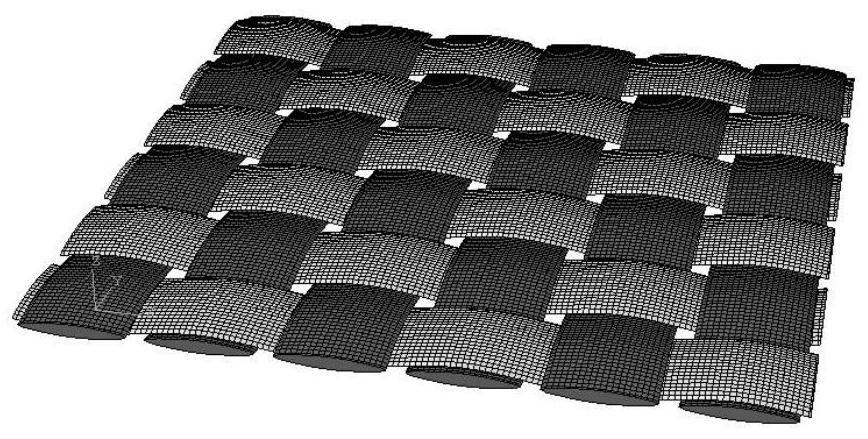
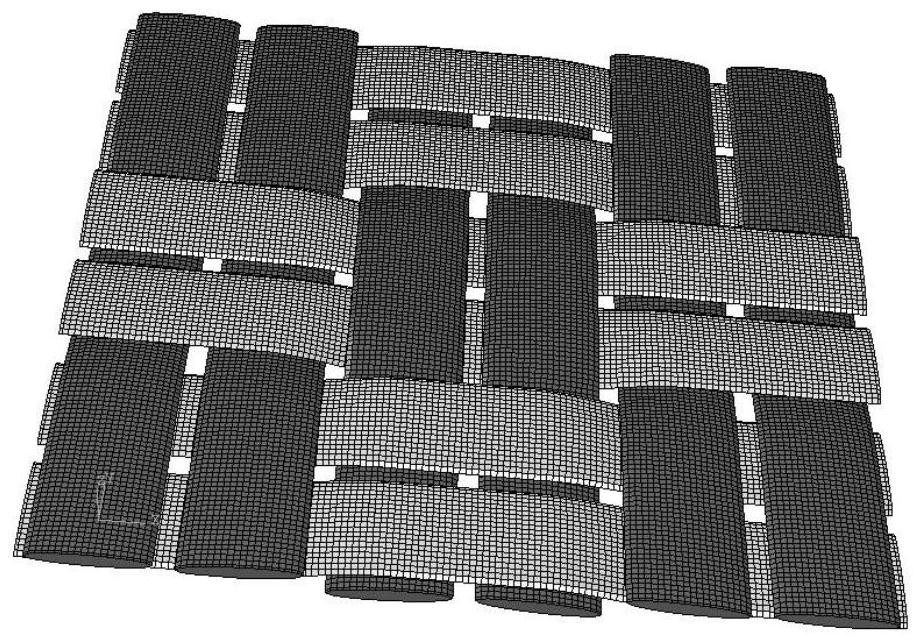
[0055] Example 1 is the simulation of the cutting process of the plain weave method. The weaving method is to cross every other fiber tow. The cross section of the fiber tow is ideally assumed to be an ellipse, with the long diameter of the ellipse being 2 mm and the short diameter being 0.5 mm. , there are six vertically and horizontally, and its fiber weaving structure is as follows: figure 2 shown.
example 2
[0056] Example 2 is a simulation of the cutting process of the plain weave structure, which is different from the weaving structure of Example 1 and Example 2. In Example 2, the weaving method crosses every two fiber tows. Also respectively set up six tows in the vertical and horizontal directions in the example 2, and its tow section is identical with example 1, and long diameter is 2mm, and short diameter is 0.5mm, and its fiber weaving structure is as follows: image 3 shown.
example 3
[0057] Example 3 Simulation of the cutting process of the composite material with twill weave structure. Different from Example 1 and Example 2, the tows of Example 3 are crossed every second fiber tow, and the crossing positions of adjacent fiber tows are different by one fiber tow width. The fiber parameters in the model are 2mm in long diameter and 0.5mm in short diameter, and its fiber weaving structure is as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0058] The matrix model calculates its length, width, and height based on the established fiber model. According to the fiber section, the thickness of the matrix cuboid should be greater than 1mm. Therefore, the length, width, and height of the matrix cuboid are defined as 13mm×13mm×1.1mm.
[0059] For tool models (see attached Figure 8 ), the tool size is set at 4mm in diameter, and the tool size is customized according to the different tool sizes used in drilling. In the examples herein, the cutter diameter is set to 4mm, so that the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com