Bending fatigue equipment for insulators
A technology of bending fatigue and insulators, applied in the direction of applying stable bending force to test the strength of materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as blank means
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments in the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other. The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
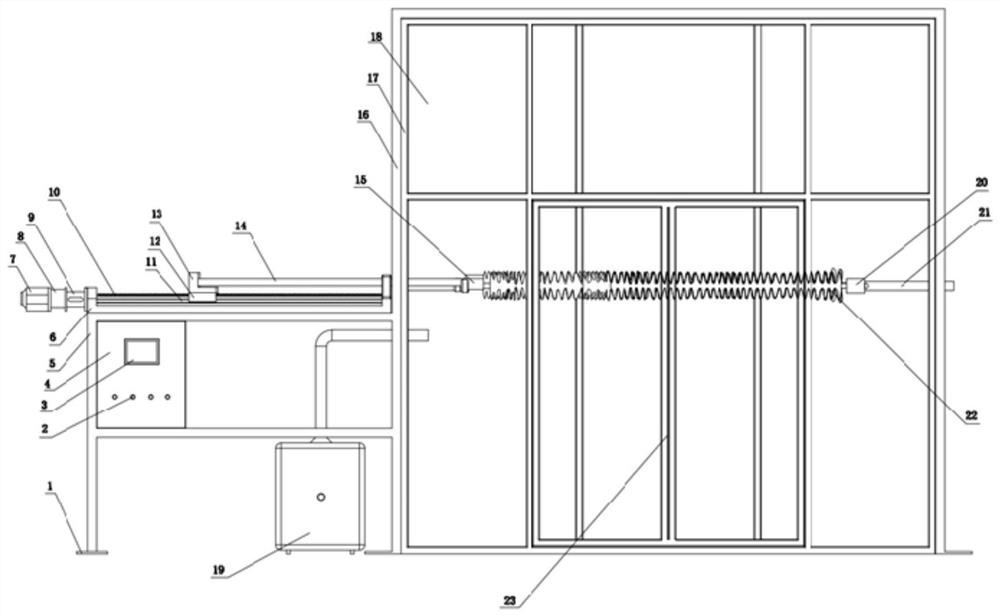
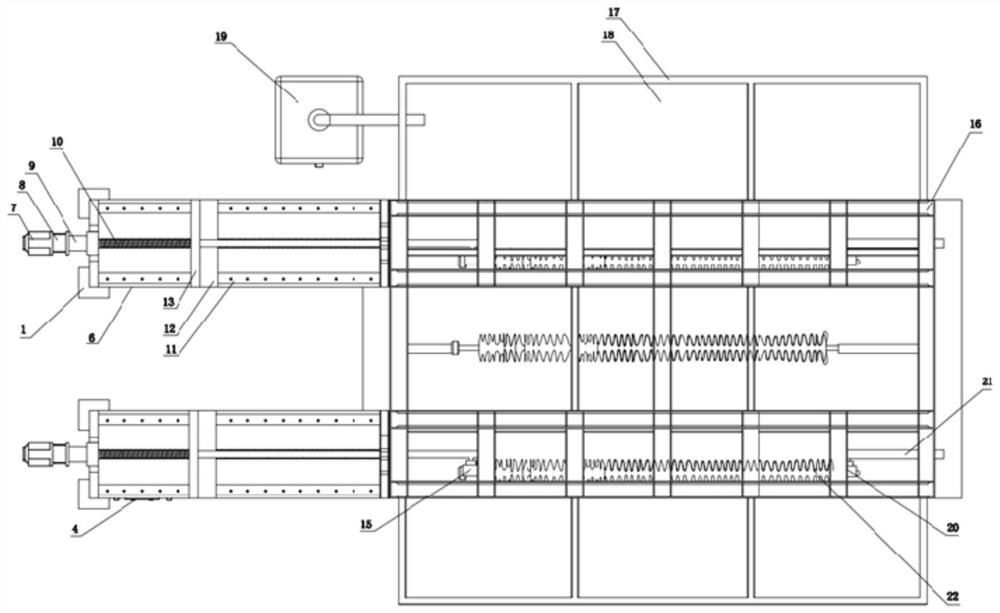
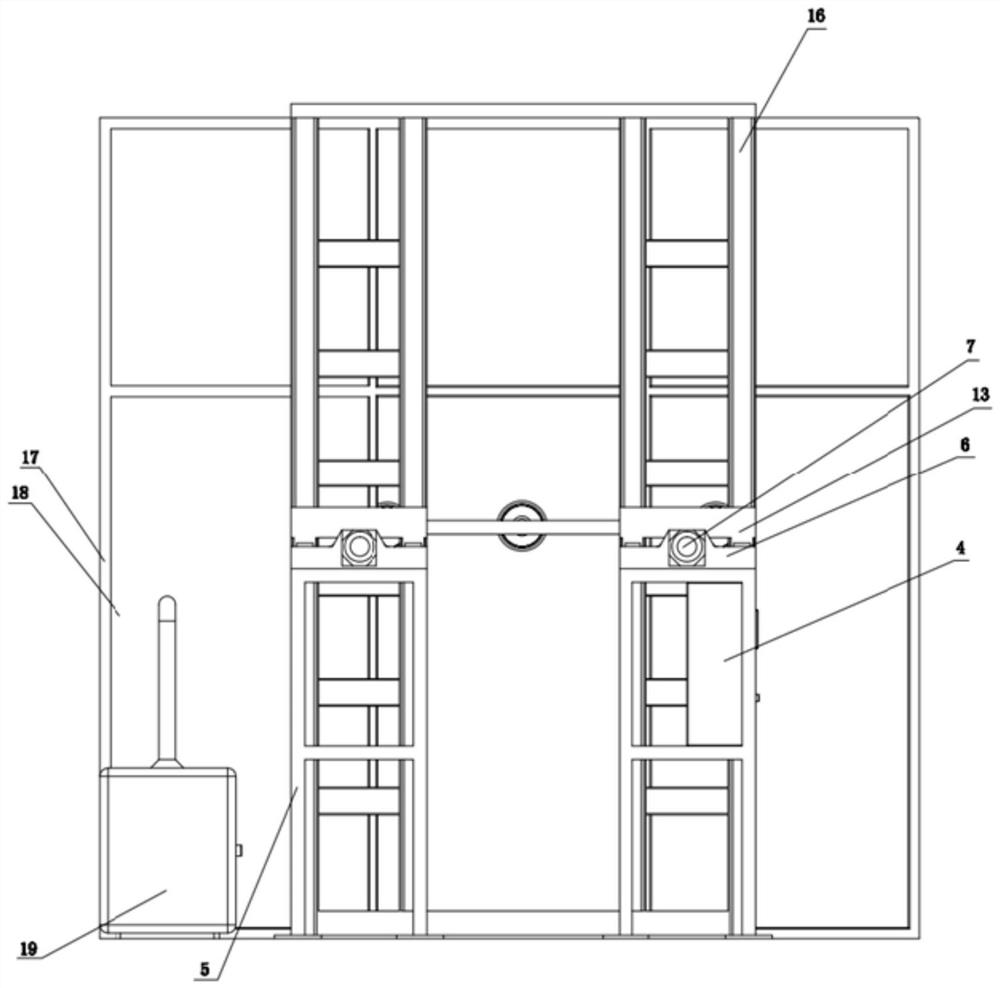
[0021] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a bending fatigue device for insulators, including a fog chamber 16, a fogging controller 19, a first connection component, a second connection component, a test composite insulator 22 and a bending application component. The mist chamber 16 has an inner chamber, and the fogging controller 19 is disposed outside the mist chamber 16 and communicated with the inner chamber. The first connection assembly and the second connection assembly are symmetrically arranged on two opposite side walls of the mist chamber 16, one end of the first connection assembly is placed in the mist chamber 16, and the other en...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com