Semiconductor light-emitting element
A light-emitting element and semiconductor technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of uneven current expansion, affecting the uniformity of luminous brightness of semiconductor light-emitting elements, and poor current expansion effect of electrode extension strips, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
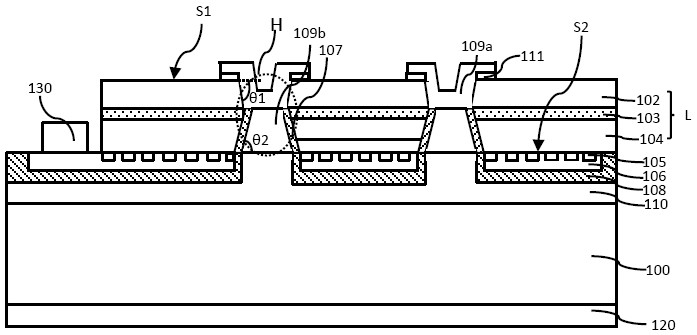
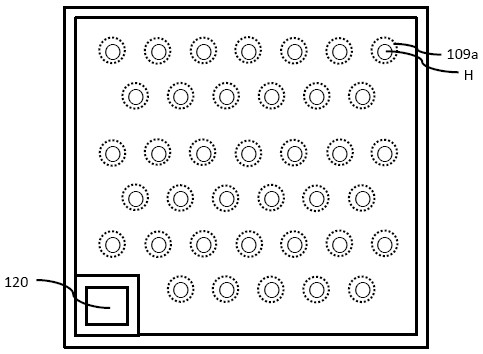
[0056] The present invention provides the following semiconductor light-emitting element, such as figure 1 The cross-sectional schematic diagram shown, which includes the following stacked layers: 100: substrate; L: semiconductor epitaxial stack; 102: first conductivity type semiconductor layer; 103: active layer; 104: second conductivity type semiconductor layer; 105: dielectric layer ; 106: second electrode metal layer; 107: side wall insulating layer; 108: second insulating layer; 109: electrical connection structure; 109a: the first section of the electrical connection structure; 109b: the first section of the electrical connection structure Second stage; 110: first electrode metal layer; 120: first electrode; 130: second electrode.
[0057] The details of each structural stack layer are described below.
[0058] The substrate 100 is a conductive substrate, and the conductive substrate can be silicon, silicon carbide, or a metal substrate, and the metal substrate is prefe...
Embodiment 2
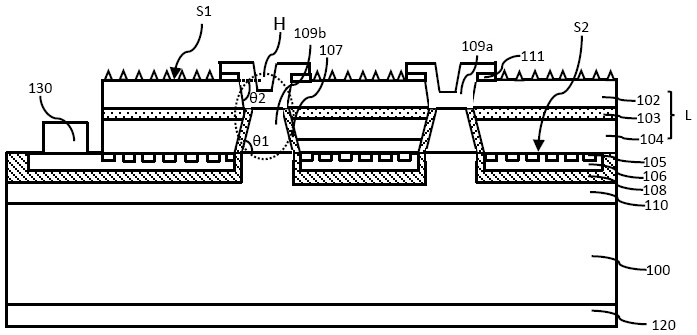
[0082] In this embodiment, if image 3 As shown, the difference from Example 1 is that the upper surface of the first conductive type semiconductor layer in Example 1 is smooth, and in the area covered by the static elimination connection structure in Example 2, the first conductive type semiconductor layer The remaining area of the first surface of the first surface has a roughened structure. By roughening the remaining area of the first surface of the first conductive type semiconductor layer, the light output of the semiconductor light emitting element can be increased, thereby improving the luminous efficiency of the semiconductor light emitting element.
Embodiment 3
[0084] In this embodiment, if Figure 4 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the first section of the through hole in Embodiment 1 has a certain inclination angle, the first section of the through hole in Embodiment 3 is set to be vertical, and the first section of the through hole is vertical. Sections expose the first conductive type semiconductor layer 102. The segmented arrangement of the through holes is convenient for the operation of the manufacturing process, can reduce the aperture of the through holes, and reduce the area of the sacrificed light-emitting region caused by digging holes, which can reduce the Luminance loss of the semiconductor light-emitting element; at the same time, the through-hole setting can improve the uniformity of current distribution, thereby improving the uniformity of luminous brightness and luminous efficiency of the semiconductor light-emitting element.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com