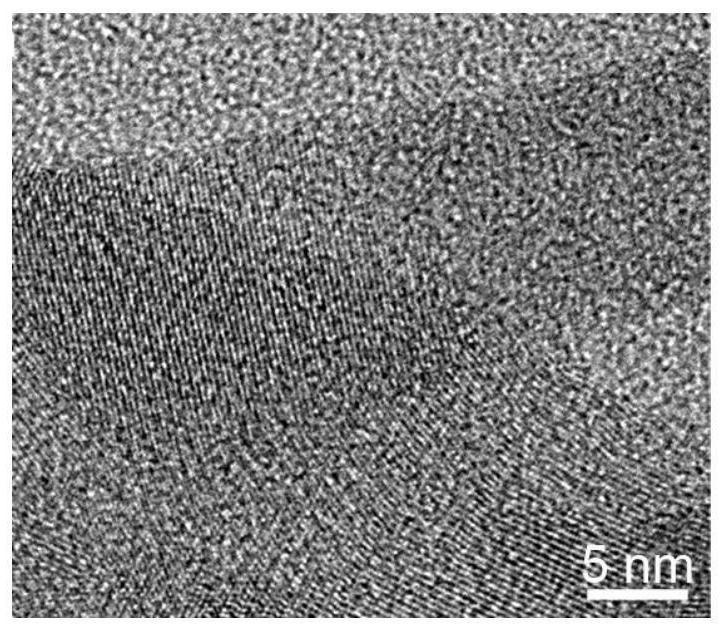
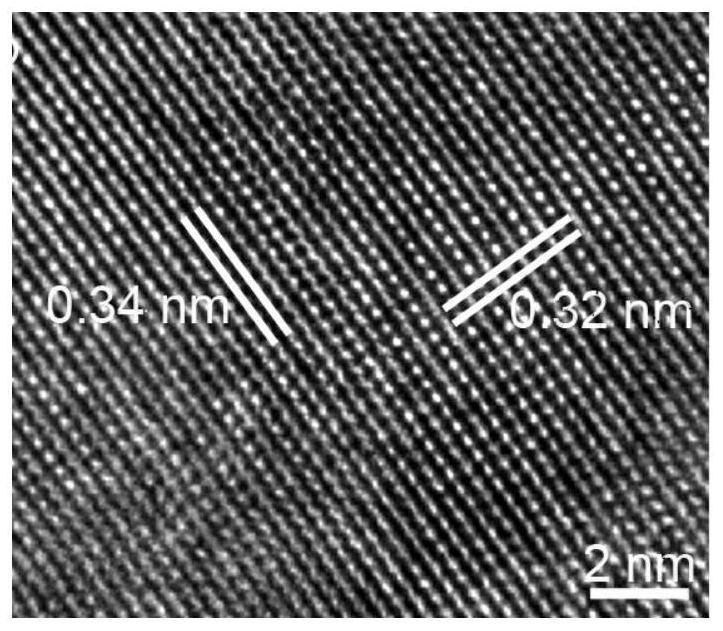
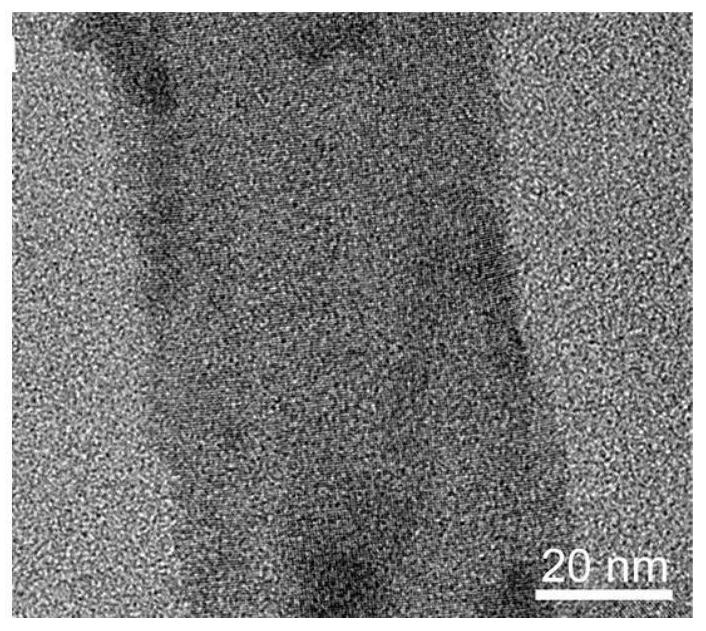
Preparation of ethylenediamine-coated cadmium telluride nanobelt photocatalyst and separation method of uranium in radioactive wastewater
A technology of radioactive wastewater and photocatalyst, which is applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalyst, radioactive purification, organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, etc., and can solve the problem of lack of active adsorption sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A preparation method of ethylenediamine-coated sulfur cadmium telluride nanobelt photocatalyst, comprising the following steps:
[0045] Step 1. Preparation of cadmium sulfide nanobelts: Add 1 mmol of cadmium chloride to 30 mL of ethylenediamine, stir evenly, add a mixture of 1 mmol of sulfur powder and tellurium powder, continue stirring evenly, add 3 mL of hydrazine hydrate, and stir for 30 min to obtain a mixed solution; The mol ratio of described sulfur powder and tellurium powder is 0.95:0.05;
[0046] Step 2. Transfer the mixed solution to a 45mL stainless steel reaction kettle and react at 120°C for 8 hours. After the reaction, the product is collected by centrifugation, washed three times with pure water and ethanol respectively, and the final precipitate is vacuum-dried at 60°C to obtain sulfur Cadmium Telluride Nanoribbon Photocatalyst, CdS 0.95 Te 0.05 -EDA; wherein EDA represents ethylenediamine;
Embodiment 2
[0048] A preparation method of ethylenediamine-coated sulfur cadmium telluride nanobelt photocatalyst, comprising the following steps:
[0049] Step 1. Preparation of cadmium sulfide nanobelts: Add 1 mmol of cadmium chloride to 30 mL of ethylenediamine, stir evenly, add a mixture of 1 mmol of sulfur powder and tellurium powder, continue stirring evenly, add 3 mL of hydrazine hydrate, and stir for 30 min to obtain a mixed solution; The mol ratio of described sulfur powder and tellurium powder is 0.9:0.1;
[0050]Step 2. Transfer the mixed solution to a 45mL stainless steel reaction kettle and react at 120°C for 8 hours. After the reaction, the product is collected by centrifugation, washed three times with pure water and ethanol respectively, and the final precipitate is vacuum-dried at 60°C to obtain sulfur Cadmium telluride nanoribbon photocatalyst; i.e. CdS 0.90 Te 0.1 -EDA.
Embodiment 3
[0052] A preparation method of ethylenediamine-coated sulfur cadmium telluride nanobelt photocatalyst, comprising the following steps:
[0053] Step 1. Preparation of cadmium sulfide nanobelts: Add 1 mmol of cadmium chloride to 30 mL of ethylenediamine, stir evenly, add a mixture of 1 mmol of sulfur powder and tellurium powder, continue stirring evenly, add 3 mL of hydrazine hydrate, and stir for 30 min to obtain a mixed solution; The mol ratio of described sulfur powder and tellurium powder is 0.8:0.2;
[0054] Step 2. Transfer the mixed solution to a 45mL stainless steel reaction kettle and react at 120°C for 8 hours. After the reaction, the product is collected by centrifugation, washed three times with pure water and ethanol respectively, and the final precipitate is vacuum-dried at 60°C to obtain sulfur Cadmium Telluride Nanoribbon Photocatalyst, CdS 0.80 Te 0.2 -EDA.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com