T cell and nanoparticle connection method based on click chemistry
A nanoparticle and connection method technology, applied in the field of nanomedicine, can solve the problems of low efficiency, unstable connection method, poor specificity, etc., and achieve the effects of avoiding false signals, fast and easy labeling, and stable labeling products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
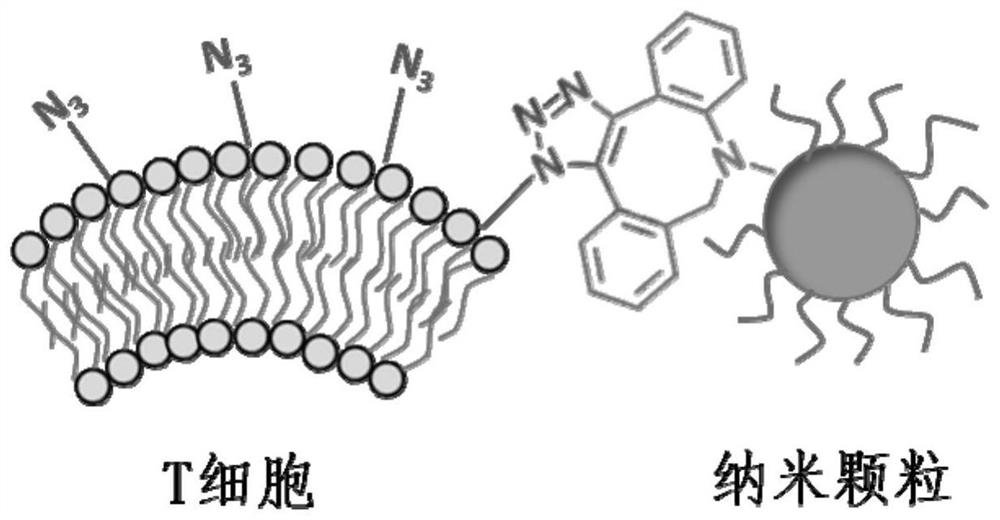
[0035] The working principle of the present invention using click chemistry to label cells with fluorescent quantum dots can be found in figure 1 . Through the diphenylcyclooctyne group (-DBCO)-azide (-N 3 ) linked click chemistry method, the nanoparticles (INPs-DBCO) and the azide (-N 3 ) covalently bind to form a highly efficient link between T cells and nanoparticles.
[0036] Concrete steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0037] Step 1: Preparation of T cells
[0038] (1) T cell extraction and expansion: the peripheral blood of healthy volunteers was collected, and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated. The specific operation is: collect blood in the anticoagulant tube, add 1:1 normal saline, another tube is added with a separation solution equal to the volume of normal saline, the mixture of normal saline and blood is added to the separation solution along the tube wall, then 800g, 30min After centrifugation, the layers are general...
Embodiment 2
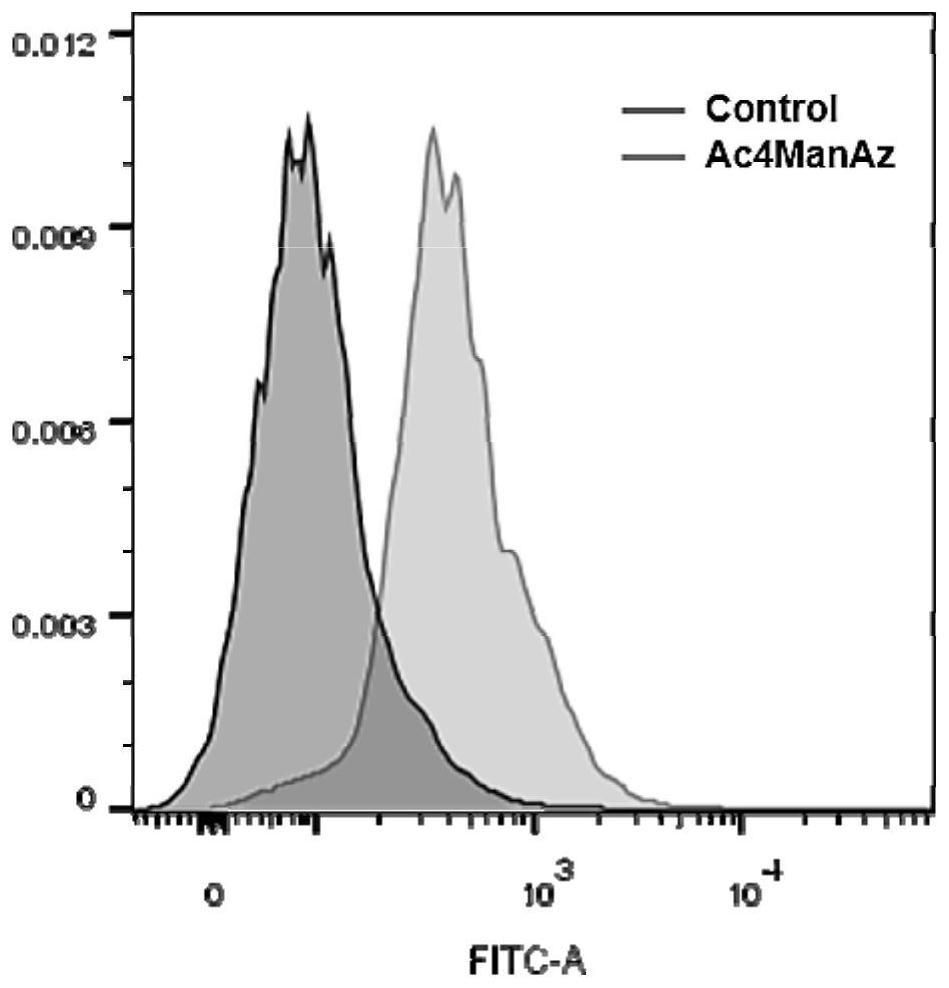
[0047] Measuring the expression of azide group metabolism on the surface of T cell membrane by flow cytometry
[0048] like figure 2 As shown by flow cytometry data, the azide group (-N 3 ) was labeled with FITC dye, and the flow peak of the T cell group incubated with the sugar molecule tetraacetyl-N-azidoacetylmannosamine (Ac4ManAz) was separated from the flow peak of the control group (Control) that was not incubated with the sugar molecule The obvious difference indicates that the T cell group incubated with sugar molecules was successfully labeled with FITC dye, and the azide group was successfully expressed on the surface of the T cell membrane.
Embodiment 3
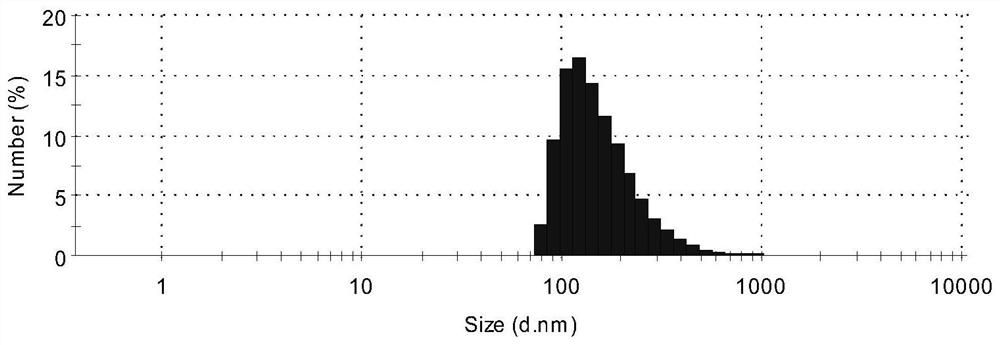
[0050] Particle Size Detection of Indocyanine Green Polymer Nanoparticles (INPs)
[0051] like image 3 As shown, the INPs prepared by the ultrasonic hydration method were used to detect the particle size of the nanoparticles using a Malvern particle size analyzer, and the average particle size of the INPs nanoparticles was about 160nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com