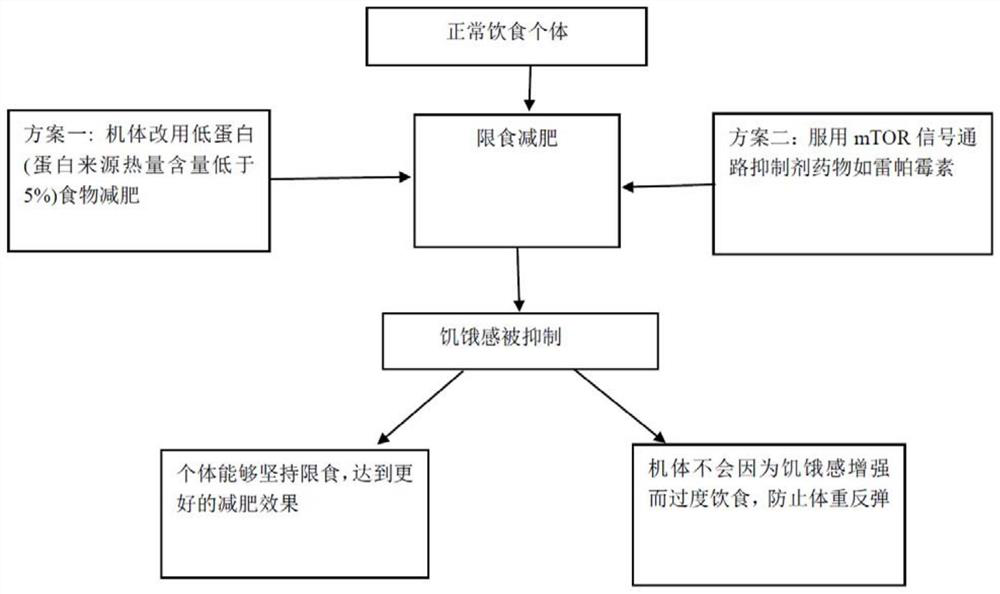
Starvation intervention method based on macro nutrient component change and mTOR signal inhibitor, and application thereof
A technology of inhibitors and nutrients, applied in the field of pharmacology, can solve problems such as weight loss failure and weight rebound, and achieve the effect of reducing body weight and body fat and improving metabolism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
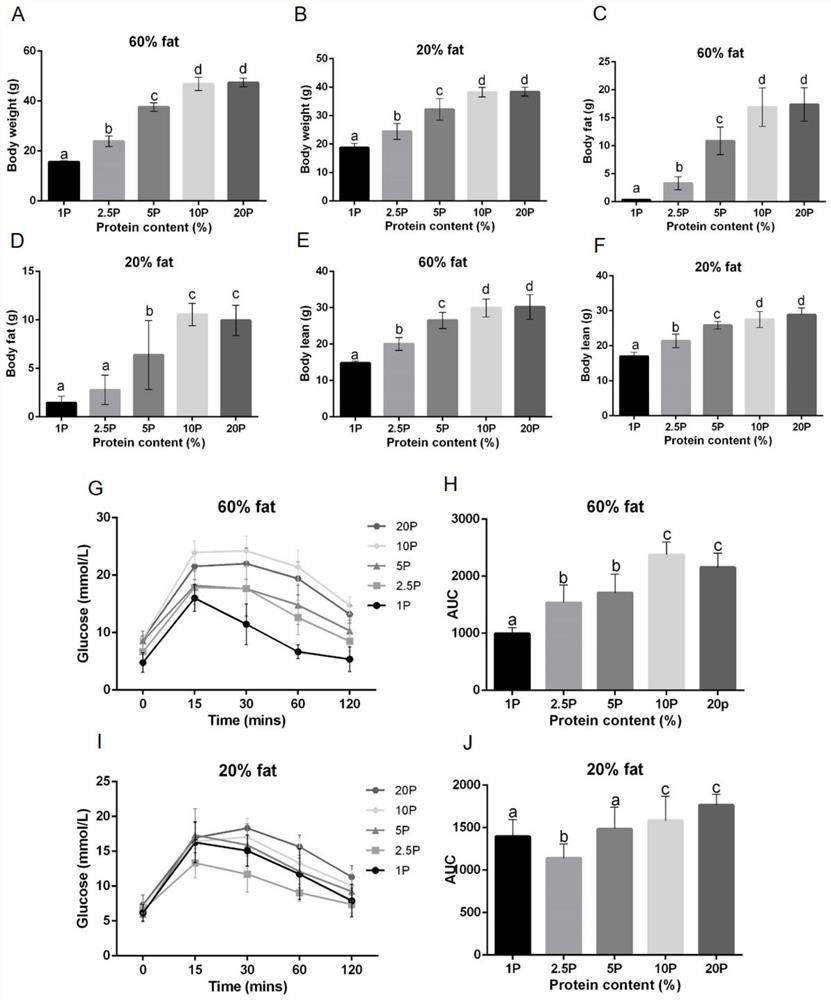
[0033] Embodiment 1 low-protein diet animal experiment
[0034]The low-protein diet treatment experiment was conducted with male mice C57BL / 6N. Ten specially designed foods were shared among the mice experiments. Among the ten kinds of specially designed foods, five kinds of foods are fixed in which the fat content is 60% (the ratio of energy), and the protein content is from 1% to 20%, specifically 1%, 2.5%, 5%, and 10% respectively. % and 20%, and the remaining energy is supplemented by carbohydrates, so the carbohydrate contents of these five foods are 39%, 37.5%, 35%, 30% and 20% respectively. The main components of carbohydrates are corn starch (Corn starch), maltodextrin (Maltodextrin 10) and sucrose (Sucrose), and the contents of sucrose and cellulose in all foods are respectively fixed at 5% of the total food energy. The fat content of the other five foods is 20%, and the protein content is the same as the above five foods, which are 1%, 2.5%, 5%, 10% and 20% respect...
Embodiment 2
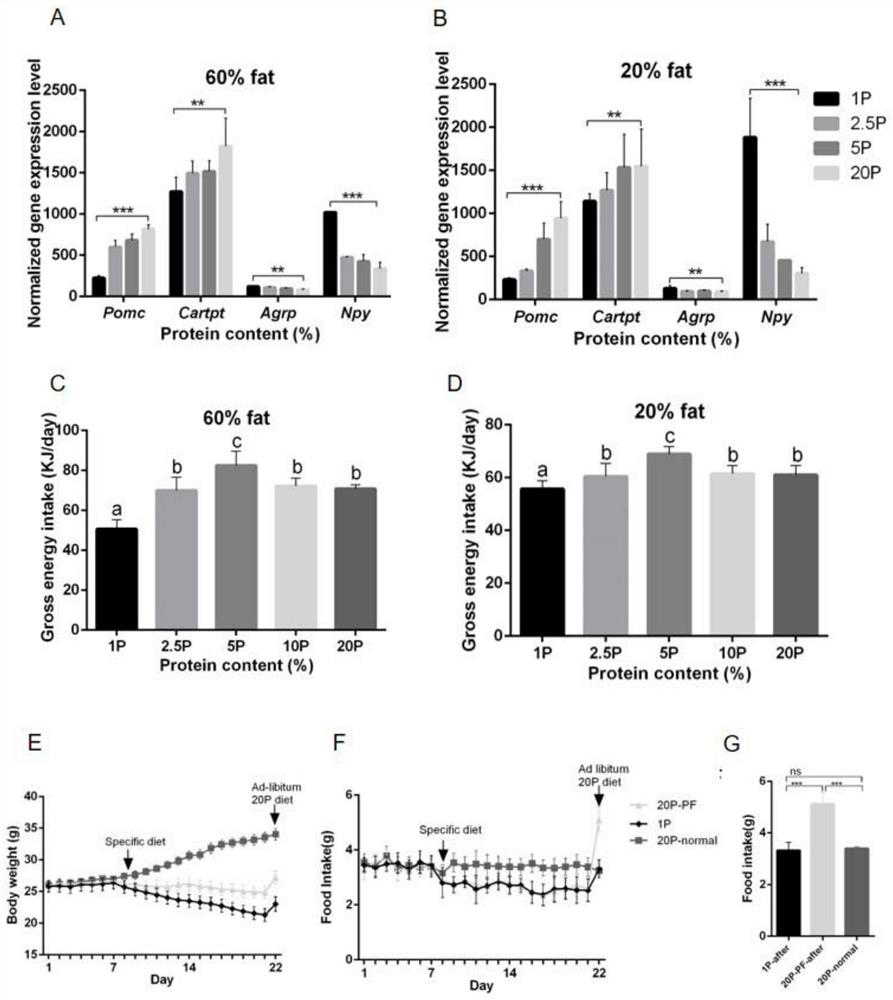
[0043] Example 2 Correlation between low protein treatment and hypothalamus starvation pathway
[0044] In order to explore the effect of foods with different protein content on the gene expression signaling pathway in mouse hypothalamus, the present invention carried out transcriptome sequencing and analysis.
[0045] The present inventors conducted a general linear model analysis on the genes of the hunger signaling pathway, and treated mice with 10 kinds of food as described in Example 1 for 12 weeks, with the fat content in the food as a factor and the protein content as a covariate. The results showed that the four genes Pomc, Cartpt, Agrp and Npy in the starvation pathway were significantly correlated with the protein content in food (p=2.2×10 -4 , p=0.008, p=0.008 and p=8.77×10 -5 ). The specific change form is that the expression of Pomc and Cartpt in the low protein group (1%, 2.5% and 5%) is significantly reduced, while the expression of Agrp and Npy is significant...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3 Low protein treatment mice food intake significantly reduces
[0047] A previous study by the present inventors found that when mice were fed with food restriction after two weeks of food restriction and then fed back to normal food, they would consume less food than normal food (about 3.5g / day) Significantly increased (about 5g / day), therefore in order to explore whether 1% low-protein food processing mice also have retaliatory overeating behavior when feeding normal protein food, the following experiments were designed:
[0048] The standard diet of normal diet 20% protein 10% fat 70% carbohydrate was fed to the mice for a week, and then the mice were divided into 3 groups, wherein the first group was treated with a low-protein diet of 60% fat 1% protein 39% carbohydrate ( 1P), the second group of mice simulated the food intake of the 1% low-protein treatment group and gave the food of 60% fat 20% protein 20% carbohydrate (called 20% matching Feeding gro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com