Method for synchronously identifying floating algae and benthic algae in aquatic ecosystem
An ecosystem and benthic algae technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as specific amplification and identification of prokaryotic algae, influence composition and ecological function exploration and evaluation, etc., to improve species annotation effect, repeatable high sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
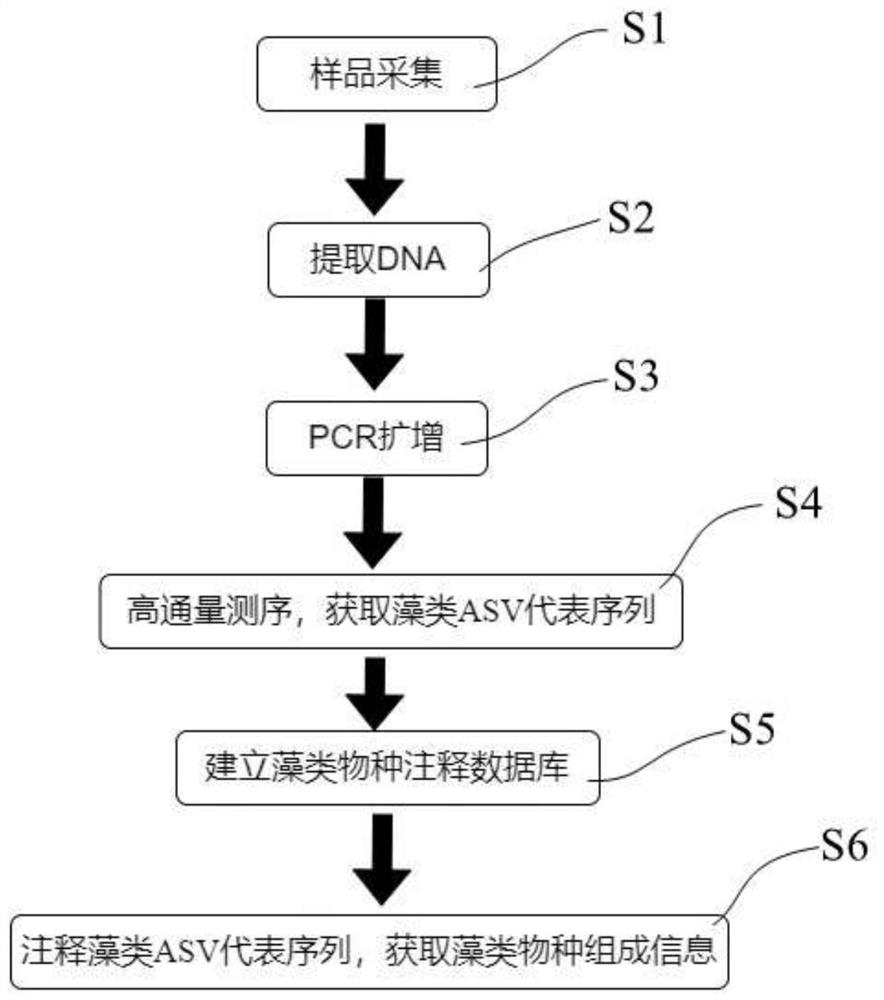
[0031] In this embodiment, the water body of a drinking water source is taken as an example, and the planktonic algae and benthic algae in the water body are monitored and identified by using the method of the present invention.
[0032] 1. Sample collection and pretreatment
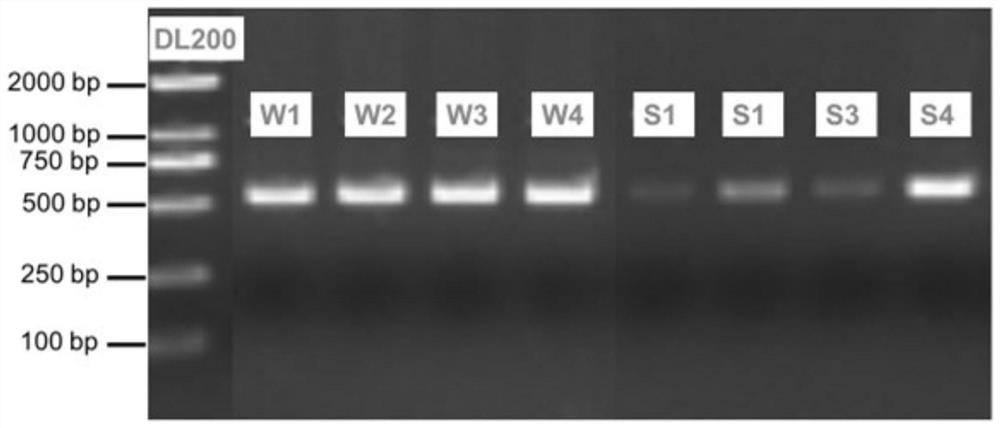
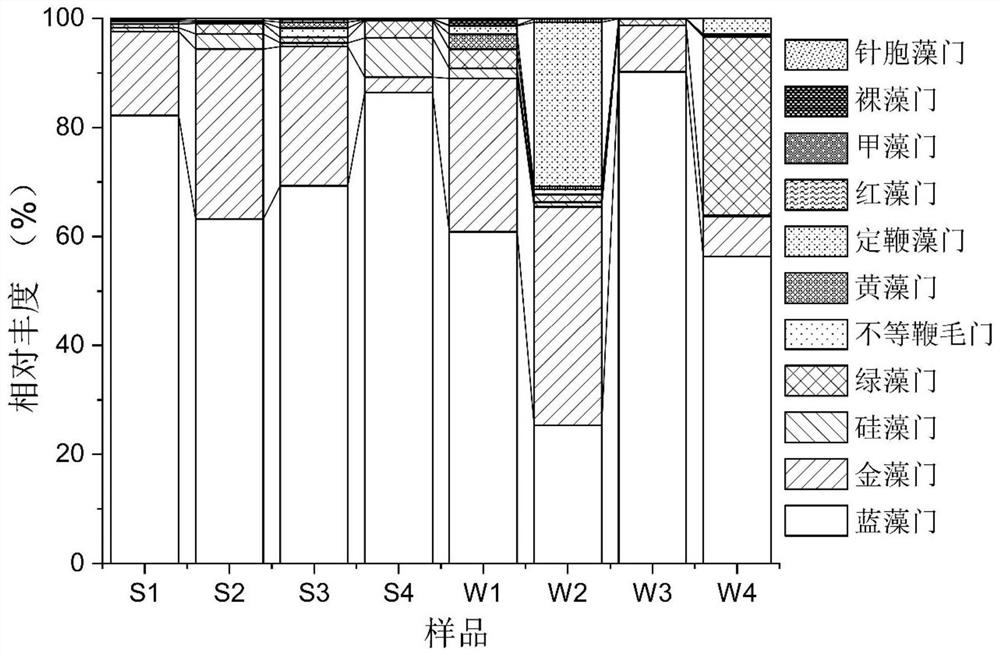
[0033] Four monitoring stations were selected for sampling, and the water samples collected from the four stations were marked as W1-W4, and the corresponding sediment samples were marked as S1-S4, respectively, and the species of algal communities in each sample were monitored.
[0034] Surface water was collected from each monitoring site separately, mixed to obtain 5L surface water samples, refrigerated and transported back to the laboratory at 4°C, and all collected water samples were covered with 0.22 μm polycarbonate membranes (Millipore, USA) within 24 hours. ), and store the filter membrane carrying the filtrate in a -80°C refrigerator.
[0035] At each monitoring station, 20 mL of surface sedim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com