Genetically engineered cyanobacteria for growth in unsterilized conditions using antibiotic-free selection
A technology of genetic engineering, cyanobacteria, applied in the field of metabolically engineering cells to increase their ability to compete with contaminating microorganisms without antibiotics, which can solve problems such as the risk of horizontal gene transfer of antibiotic resistance cassettes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0113] Embodiment 1: method
[0114] Standard molecular biology techniques known in the art and not specifically described were generally followed as described in Green and Sambrook and Russel, Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Springs Harbor Laboratory, New York (2012).
[0115] cell growth conditions
[0116] Synechococcus PCC 7002 (a gift from Prof. Donald Bryant, Penn State University, USA) using the D7 micronutrient [Arnon et al., Biochim BiophysActa.357:231-45 (1974)], according to Supplemented with 12mM sodium nitrate (AD7-NO 3 ), 4mM cyanurate (AD7-Cya) or 2mM melamine (AD7-Mel), and vitamin B 12 (0.01 mg / L) in medium A [Stevens et al., J Phycol. 9:427-430 (1973)] in photoautotrophic growth. For phosphite-utilizing strains, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (Pho) was replaced by potassium dihydrogen phosphite (Phi, Rudong Huayun Chemical Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, China) at 0.370 mM (Pho 1x or Phi1x). Solid medium was prepared by supplementing the above medium w...
Embodiment 2
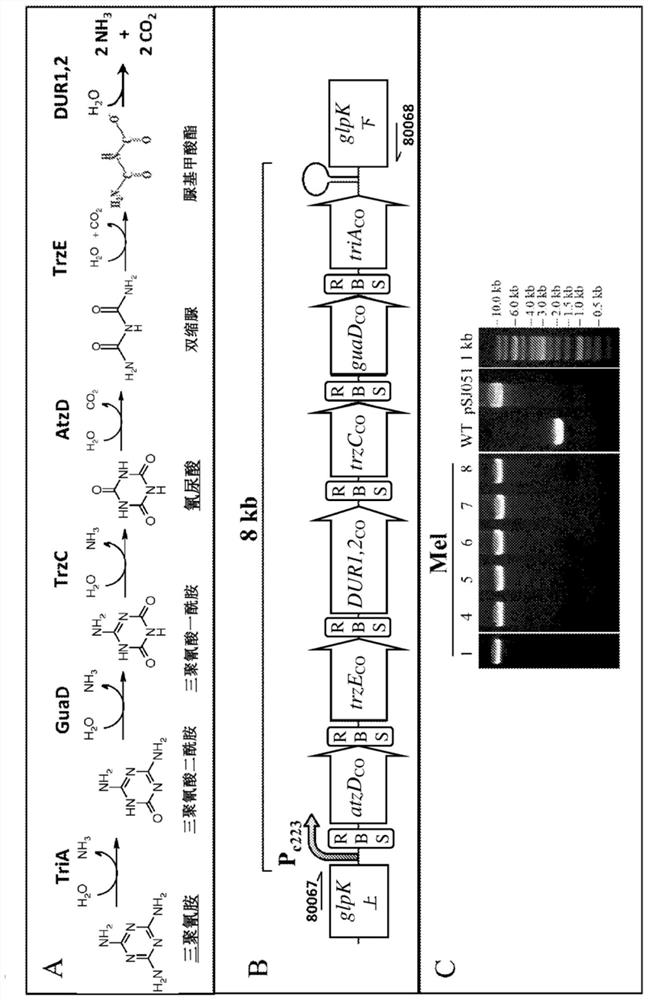
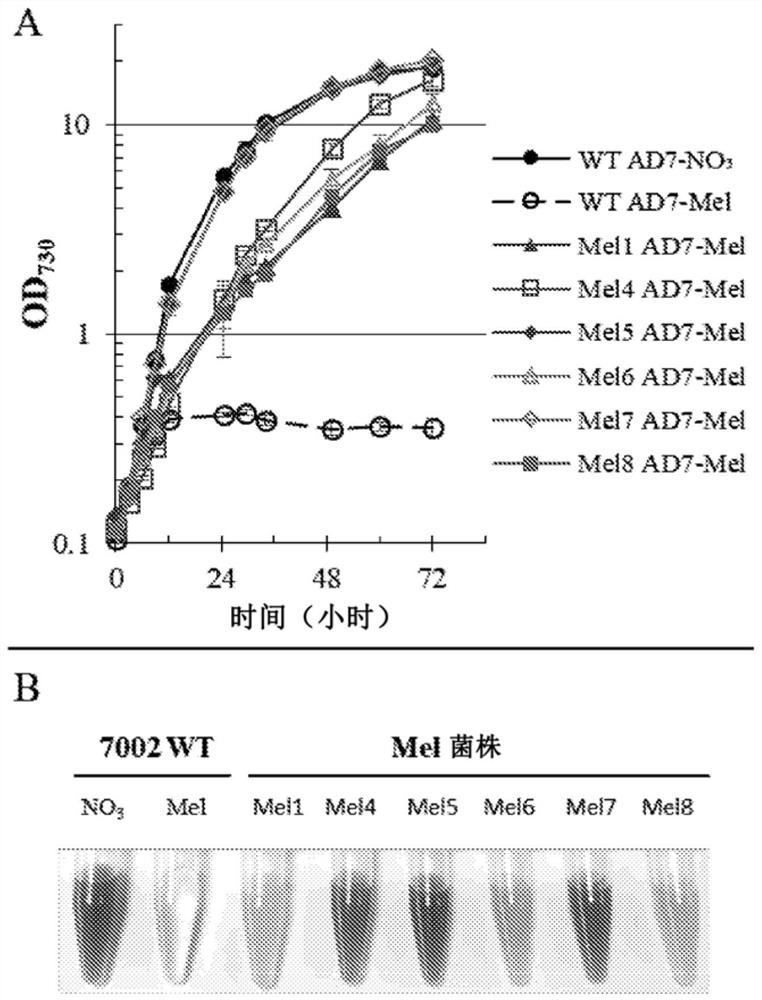
[0142] Introduction of melamine degradation pathway requires evolutionary adaptation for efficient utilization
[0143] The melamine degradation pathway utilized in this study was based on the optimal pathway reported by Shaw and colleagues (genes triA, guaD, trzC, atzD, trzE, and DUR1,2, including the R352S mutation described in the guaD gene product) [Shaw et al. People, Science.353:583-6(2016)]( figure 1 ). In our case we used codon optimized genes (triA, SEQ ID NO:70; guaD, SEQ ID NO:80; trzC, SEQ ID NO:74; atzD, SEQ ID NO:78; trzE SEQ ID NO:78; NO:72; and DUR1,2, SEQ ID NO:76), a synthetic strong cyanobacterial promoter P c223 (SEQ ID NO:82) [Markley et al., ACS Synth Biol.4:595 (2015)] and the strongest RBS sequence (AGGAGA) tested in Syn7002 [Markley et al., ACS Synth Biol.4:595 (2015) )] upstream of all 6 genes. The intergenic region (21bp in total), including the space before (7bp) and after (8bp) the RBS sequence, was generated by a random DNA sequence generator ...
Embodiment 3
[0150] Phosphite and PtxD can be used as efficient selection systems in Synechococcus sp. PCC7002
[0151] Although phosphite (Phi) was previously shown to be able to maintain Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [Polyviou et al., Environmental microbiology reports. 7:824-30 (2015)] and Synechocystis sp. PCC 7942 [Motomura et al., ACS Synth Biol. 10:1021 (2018)] Growth of modified strains of both, in both cases genetic manipulation (integration of operons containing ptxD as well as specific Phi transporters) is driven by antibiotic selection pressure . Also, neither strain (wild-type Synechocystis PCC 6803 or wild-type Synechococcus PCC 7942) appears to be unable to take up Phi without including the specific transporter, thus making the construct too large to be practical as a selection marker. use. Since no data on the ability of Syn7002 to grow on Phi as the sole P source exists in the literature, the growth of the WT strain was tested using different concentrations of Phi ( Image...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com