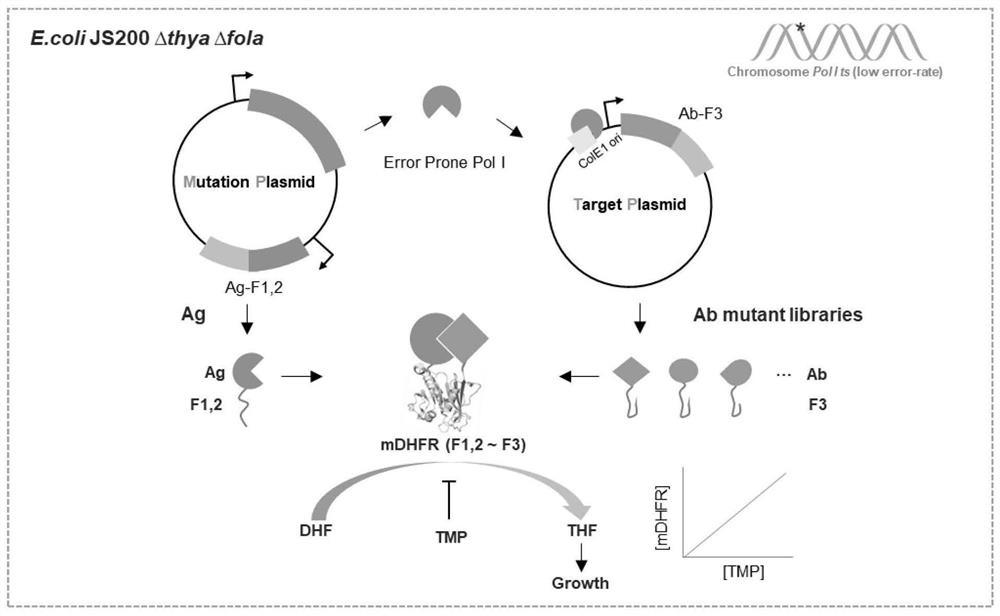
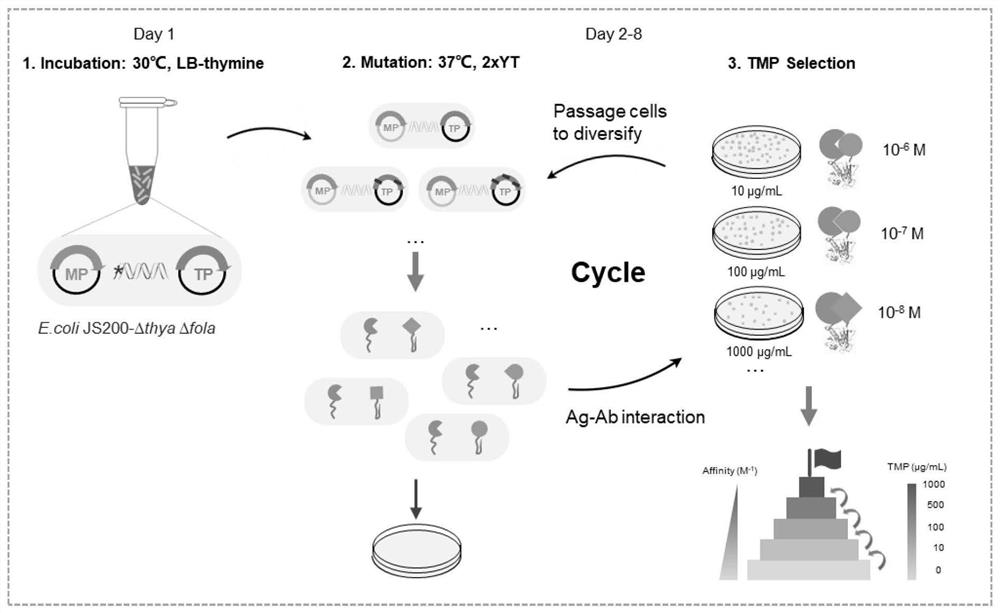
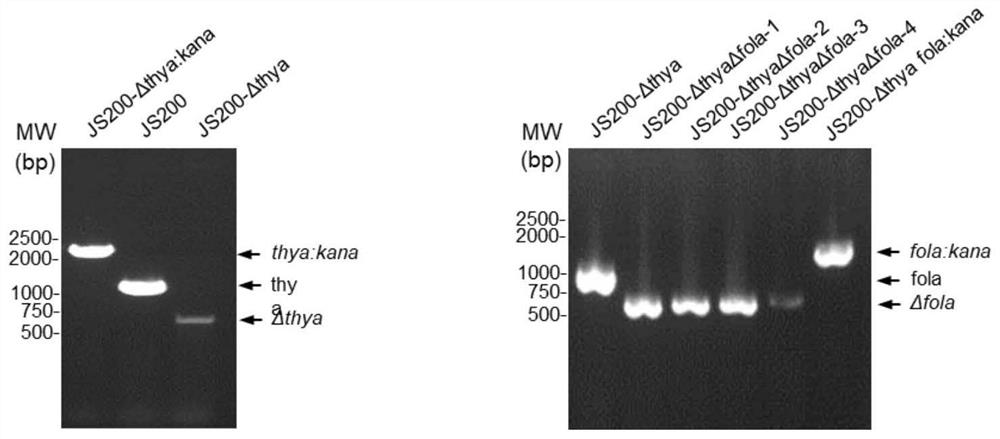
Genetic engineering strain, preparation thereof and directed evolution method for antibody affinity maturation based on genetic engineering strain
A technique of genetically engineered strains and directed evolution, applied in the field of directed evolution of antibody affinity maturation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1 Establishment of Mutation and Screening System Integration and Feasibility Exploration
[0083] 1. Plasmid construction of mutation screening system integration (using GCN4 / GCN4 3mut as an example to explore the feasibility)
[0084] 1.1 GCN4 3mut Identification of mutation sites. The literature shows that GCN4 is a yeast transcription factor, and GCN4-"Leucine-Zipper" can form a dimer. We selected this region for verification experiments, and it is still referred to as GCN4 below. Previous studies have found that mutations at L12E, N16A, and L19A of GCN4 can greatly reduce the formation of GCN4 homodimer, such as Figure 4 shown. After rational design, it was determined that the GCN4 wild type ( Figure 4 , Figure 5 GCN4 in WT ) and mutant ( Figure 4 , Figure 5 GCN4 in 3mut ) protein sequence is as follows.
[0085] GCN4 wild type: LEDKVEELLSKNYHLENEVARLKKLVGER (formerly SEQ ID NO: UniProtKB-P03069, SEQ ID NO.5)
[0086] GCN4 3mut Mutant: LEDK...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Example 2 The backbone plasmid optimization of the integration of mutation and screening system
[0118] 1. Construction of backbone plasmids pEP-mcs-(GGGGS)2-F1,2-Flag, pWT-mcs-(GGGGS)2-F1,2-Flag and pLA230-mcs-(GGGGS)2-F3-6xHis
[0119] 1.1 Thya is constructed into the mutant plasmid. According to the principle of plasmid construction in Example 1, the upstream and downstream primers F1-thya and R1-thya were designed, and the gene sequence expressing thyA was inserted into the NdeI restriction site of the mutant plasmid pEP and the control plasmid pWT described in the above Example 1 , namely pEP-thya and pWT-thya plasmids.
[0120] Upstream primer F1-thya: AAAGGGAAAACTGTCCATATGCGCGGATCATATACA (SEQ ID NO.18)
[0121] Downstream primer R1-thya: CCGTTTTCATCTGTGCATATGTTAGTGGTGGTGGTG (SEQ ID NO.19)
[0122] 1.2 Cloning of target fragments. The upstream and downstream primers F1-pEP(pWT)-2 and R1-pEP(pWT)-2, as well as F1-pLA230-2 and R1-pLA230-2 were designed accordin...
Embodiment 318A4
[0135] Example 3 18A4Hu antibody affinity maturation
[0136] 1.18A4Hu mutant plasmid, target plasmid and strain construction
[0137] Design upstream and downstream primers according to the principle of homologous recombinase construction plasmid, and PCR obtains the target fragments SEQ-AGR2 (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.21) and SEQ-18A4Hu scFv (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.22), insert the target fragment into the backbone plasmid pEP-mcs-(GGGGS)2-F1,2-Flag and pLA230-mcs-(GGGGS)2 constructed in Example 2 respectively - In F3-6xHis, the restriction sites are BamHI / NotI and MfeI / NcoI, respectively, to obtain plasmids pEP-AGR2-(GGGGS)2-F1,2-Flag (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.23) and pLA230- 18A4Hu scFv -(GGGGS)2-F3-6xHis (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 24). Then plasmid pEP-AGR2-(GGGGS)2-F1,2-Flag and pLA230-18A4Hu scFv - (GGGGS)2-F3-6xHis was constructed into the JS200-ΔthyaΔfola strain obtained in Example 1 to obtain an engineering strain of Escherichia coli containing these ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com