A biodegradable asynchronous response polymalic acid active deformation material
An active deformation, polymalic acid technology, applied in the field of polymalic acid active deformation materials, can solve problems such as difficulty in getting rid of temporary shapes or permanent shapes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
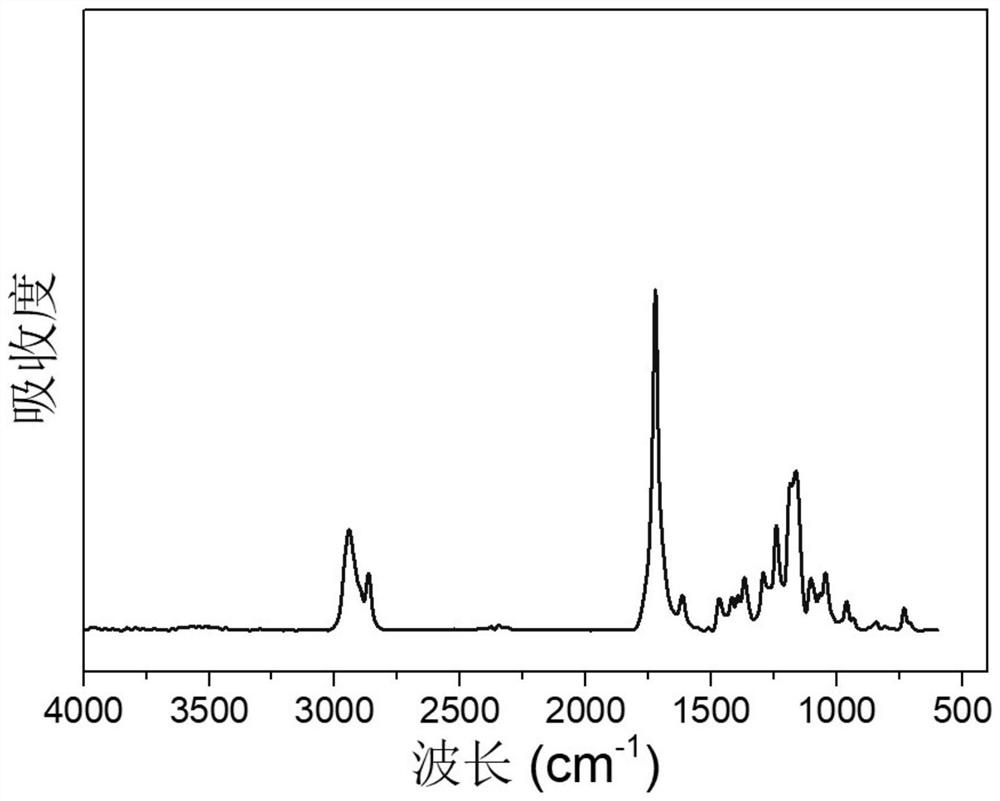
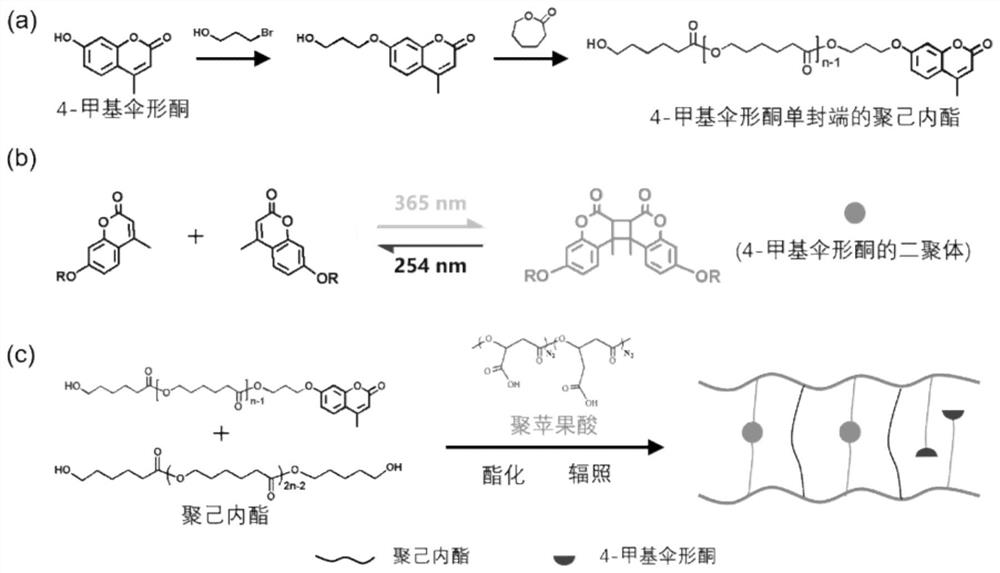
[0023] The polymalic acid with mass ratio of 0.5:1:2, polycaprolactone and 4-methylumbelliferone single-terminated polycaprolactone are ready for use, and the three are first put into the reactor, and the pressure (vacuum degree) is negative pressure: 300Pa, the temperature is 130℃, the reaction time is 24h, the preliminary sample sheet can be obtained, and its infrared spectrum is as follows figure 1 shown. It was placed in 365nm ultraviolet light at 70°C, and part of the sample sheet was exposed to ultraviolet light for irradiation, and the irradiation time of different areas was adjusted, respectively, 60min, 120min and 240min. After cooling to room temperature and maintaining a certain stretching length for 60 seconds, a temporary shape can be obtained, and then placed in an environment of 40 °C, the sample sheet can obtain asynchronous autonomous deformation ability.
Embodiment 2 to 12
[0025] The same procedure as in Example 1 was adopted, except that the mass ratio of polymalic acid, polycaprolactone and 4-methylumbelliferone mono-terminated polycaprolactone was changed, as shown in Table 1 below.
[0026] Table 1
[0027]
Embodiment 13 to 14
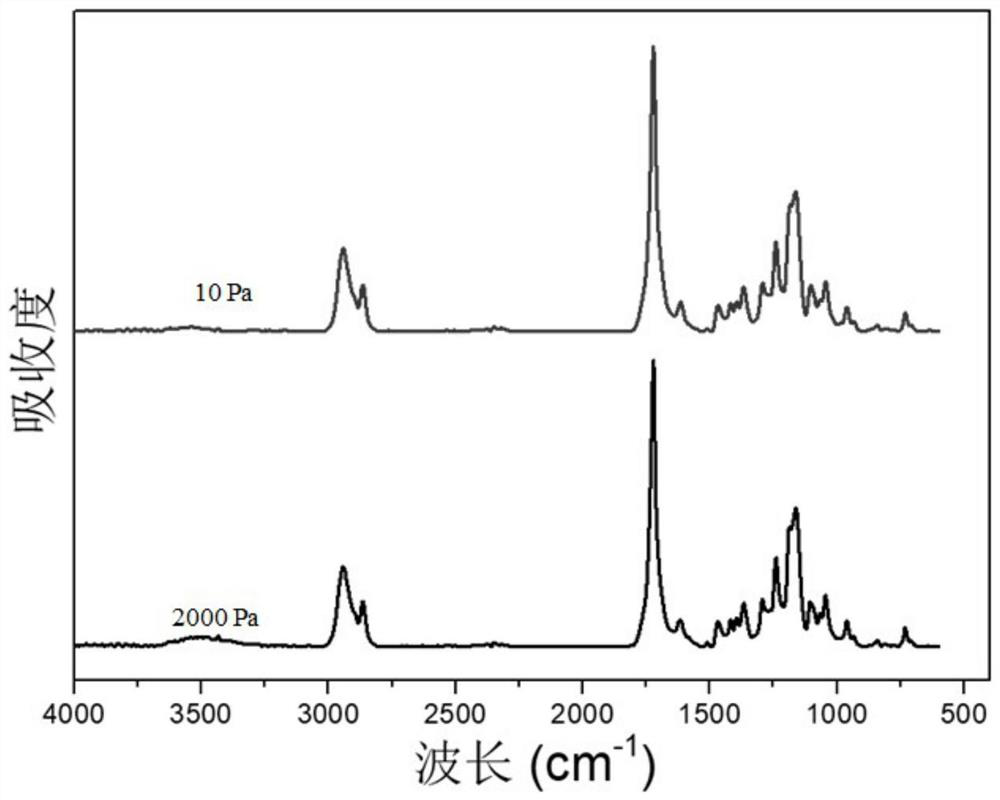
[0029] Adopt the same steps as Example 1, only change the degree of vacuum, see Table 2 below, the infrared spectrum of the obtained sample is as follows figure 2 shown, figure 2 It shows that changing the degree of vacuum does not change the structure of the polymer.
[0030] Table 2
[0031] degree of vacuum Example 13 10Pa Example 14 2000Pa
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com