Engine in-cylinder braking mechanism and method
A technology of engine cylinder and braking mechanism, applied in the direction of engine components, machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low braking efficiency, inability to realize secondary compression and release braking of exhaust stroke, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
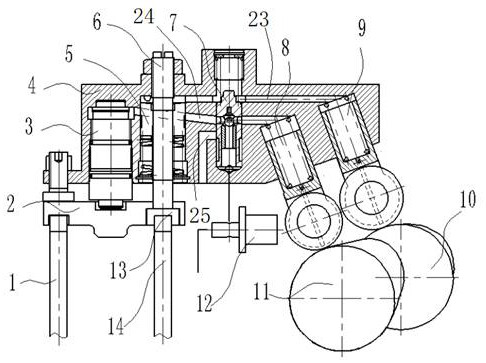
[0042] In a typical embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, an engine in-cylinder braking mechanism is proposed, including: a main part, a pressure building mechanism, an actuator, a control part, etc.
[0043] Wherein, the housing 4 constitutes the main part of the braking mechanism in the engine cylinder; the brake cam 10, the exhaust cam 11, the exhaust tappet 8, and the braking tappet 9 constitute the pressure building mechanism of the braking mechanism in the engine cylinder; Piston 3, brake piston 5, and valve bridge 2 form the actuator of the braking mechanism in the engine cylinder; the switching valve and the control solenoid valve 12 form the control part of the braking mechanism in the engine cylinder.
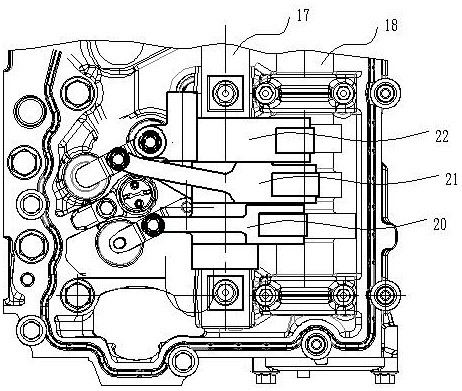
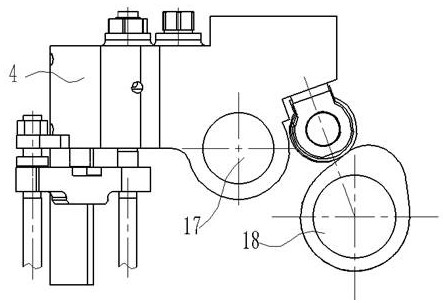
[0044] The fixing method of the housing 4 can adopt the method of being sleeved on the rocker arm shaft 17 of the traditional diesel engine and adding the auxiliary support of the housing leg 27, or can be directly fixed on the rocker arm sh...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This embodiment proposes the working method of the above-mentioned engine in-cylinder braking mechanism, comprising the following steps:
[0065] When the switching valve disconnects the brake oil circuit 23, the exhaust oil circuit 24 is conducted, and the exhaust tappet 8 generates high-pressure oil to drive the hydraulic piston 3, and then pushes the exhaust valve Ⅰ 1 and exhaust valve Ⅱ through the valve bridge 2 14 movement to achieve exhaust;
[0066] When the switching valve disconnects the exhaust oil circuit 24, the brake oil circuit 23 is connected, and the brake tappet 9 generates high-pressure oil to drive the brake piston 5, and then pushes the exhaust valve II 14 to move to realize braking.
[0067] During the braking process, after the first compression braking, the exhaust valve II 14 is further opened to perform secondary air intake during the power stroke, and then compressed and released during the exhaust stroke to achieve two in-cylinder braking;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com