Hybrid thymus, methods of making and methods of use for inducing xenograft tolerance, restoring immunocompetence and thymus function
An inducible, thymic technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, artificially induced pluripotent cells, new species of animal cells, etc., can solve problems such as inability to efficiently identify foreign antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0171] Example 1 - Generation of human / pig hybrid thymus for immune tolerance to porcine antigens and optimal immune function
[0172] Robust immune responses to xenografts are difficult to control with conventional immunosuppression without undue toxicity. Thymus transplantation is a promising approach to induce T cell tolerance to xenografts. Humanized mice generated with human hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) and porcine (SW) thymus grafts were previously shown to be tolerant to both species. However, this method still has some challenges. First, T cells selected on the SW MHC of the porcine thymus may not optimally recognize antigens presented by human MHC (HLA) in the periphery. Second, since SW thymic epithelial cells (TECs) do not display human tissue-restricted antigens (TRAs), there may be impaired negative selection and lack of Tregs against human TRAs. These problems were overcome by generating the human / pig hybrid thymus described herein.
[0173] method
[017...
Embodiment 2
[0180] Example 2 - Development of a method for producing hybrid thymus
[0181] Injection method
[0182]Cells were resuspended in Matrigel to prevent them from leaking out of the porcine thymus after injection. As a proof of principle, in this experiment, human PBMCs were used instead of human thymic epithelial cells. First, 10 million human PBMCs were stained with CFSE (2.5 μM) as a tracking dye. CFSE-stained PBMCs (8 million cells) were resuspended in 140 μl Matrigel on ice at a cell concentration of 50,000 cells / μl. Three different methods were used to inject cells into thawed porcine fetal thymus fragments:
[0183] Method A: Inject using a Hamilton syringe while placing the pellet in a well of a V-bottom 96-well plate (5-8 μl);
[0184] Method B: Injection (20 μl) using PE50 tubing;
[0185] • Method C: Injection was performed using a Hamilton syringe while holding the tablet with tweezers outside the well until the Matrigel solidified (4-6 μl).
[0186] All inje...
Embodiment 5
[0224] Example 5 - Generation of hybrid thymuses with embryonic stem cell-derived TECs (ES-TECs) and long-term persistence of human TECs in hybrid thymuses
[0225] method
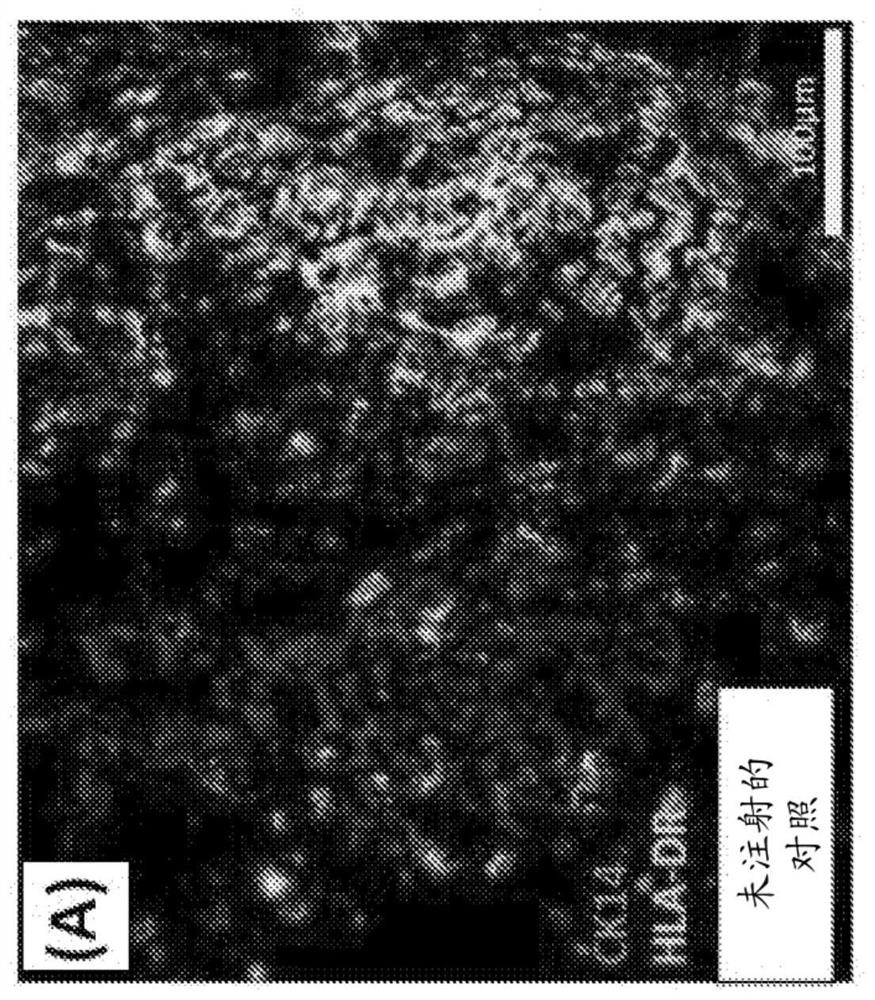
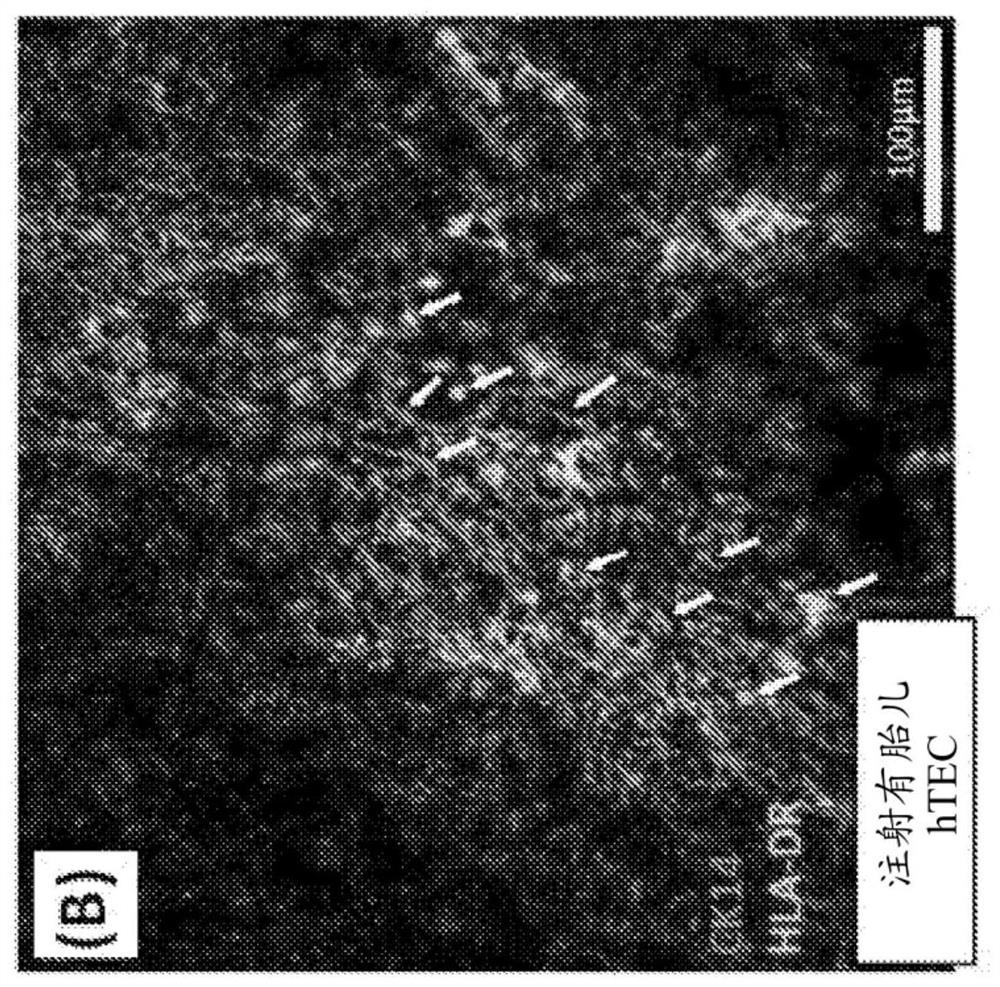
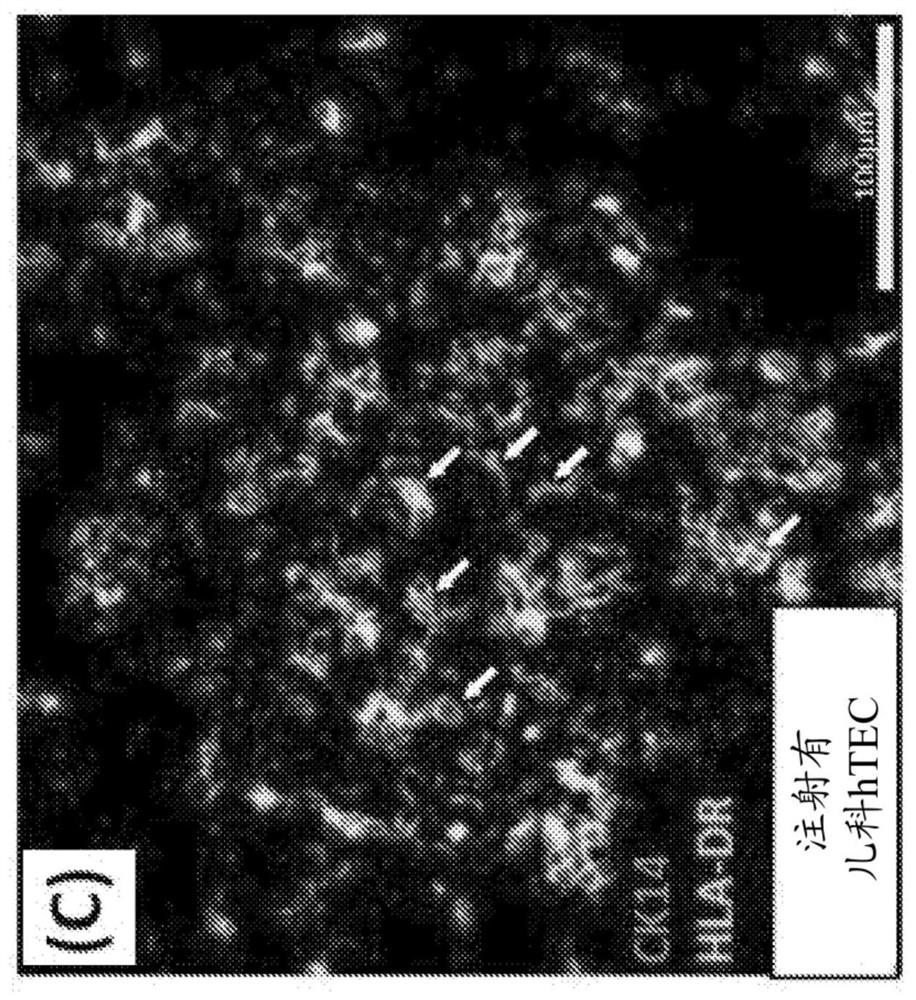
[0226] Human fetal or pediatric thymic stromal cells (hu-TEC) or hPSC-TEC progenitor cells (1-2x10 5 TECs) were injected into fetal swine thymus tissue (SW THY), which were then transplanted under the renal capsule of thymectomized immunodeficient NSG (Nod / Scid / Ilr2g- / -) mice that had been intravenously Inject 2x10 5 Individual fetal liver-derived CD34+ cells. As a control, fetal pig thymus tissue that was not injected with human TEC was implanted.
[0227] Approximately 20 weeks after transplantation, the transplanted thymus was removed, sectioned, and stained for detection of human TECs using two-photon confocal microscopy.
[0228] Cells were then released from the interstitium and cell numbers determined by flow cytometry.
[0229] result
[0230] Such as Figure 10 As shown, there is long-t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com