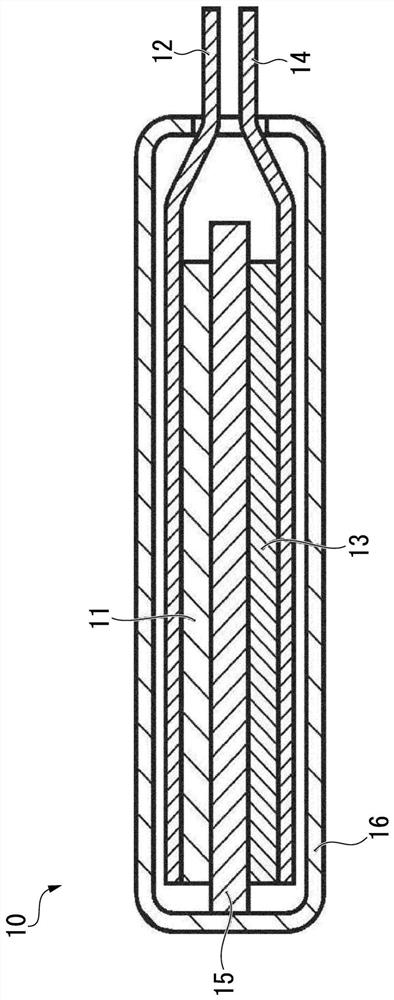
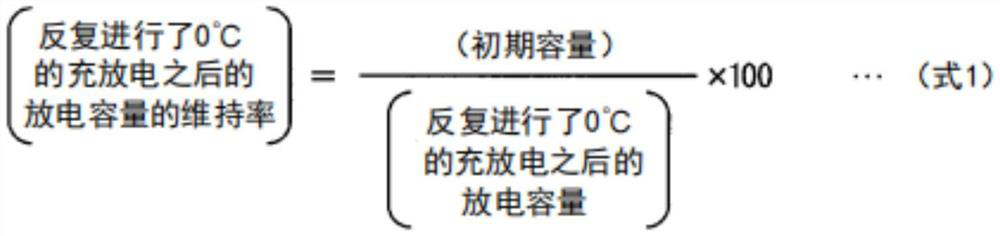
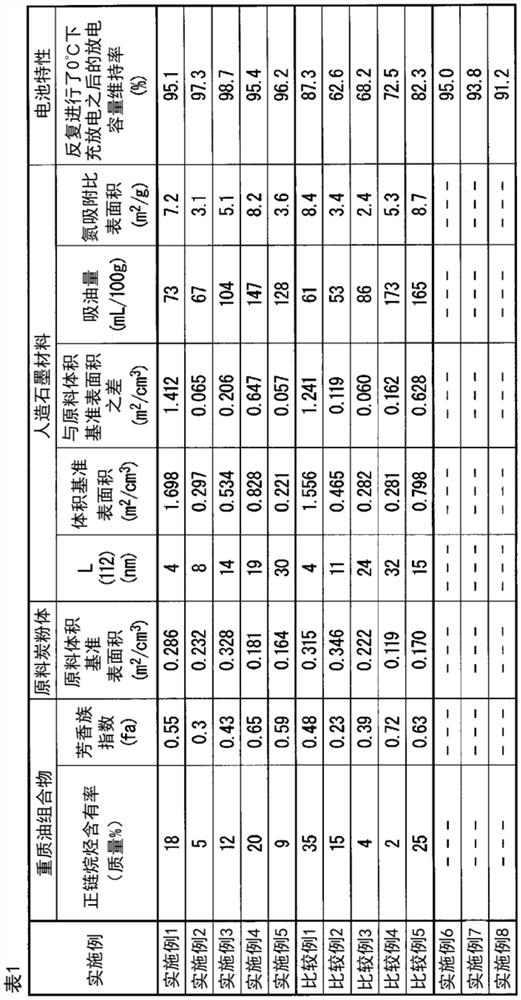
Synthetic graphite material, synthetic graphite material production method, negative electrode for lithium ion secondary battery, and lithium ion secondary battery
A technology of artificial graphite and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of secondary battery, battery electrode, negative electrode, etc., and can solve the problems of capacity degradation, poor charge and discharge efficiency of positive electrode and negative electrode, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0165] Atmospheric distillation residue with a sulfur content of 3.1% by mass was subjected to hydrodesulfurization in the presence of a catalyst so that the hydrocracking rate was 25% or less to obtain a hydrodesulfurized oil (A). The hydrodesulfurization conditions were set at a total pressure of 18 MPa, a hydrogen partial pressure of 16 MPa, and a temperature of 380°C.
[0166] In addition, under the conditions of reaction temperature 530°C, total pressure 0.23MPa, catalyst / oil ratio 13, and contact time 7 seconds, the material obtained by vacuum distillation and hydrodesulfurization of atmospheric distillation residue (sulfur component 380 mass The density at ppm and 15°C is 0.83g / cm 3 ) for fluid catalytic cracking to obtain fluid catalytic cracking residue (A). As the catalyst, a catalyst in which platinum was supported on a silica-alumina catalyst was used.
[0167] In addition, under the conditions of the heating furnace outlet temperature of 350°C and the pressure o...
Embodiment 2
[0203] After adding and mixing the same volume of n-heptane to the fluid catalytic cracking residue (A) obtained in Example 1, selective extraction was performed with dimethylformamide to separate aromatic components and saturated components. The saturated components therein were used as the stock oil composition of Example 2. The n-paraffin content and the aromatic index fa in the stock oil composition of Example 2 were determined by the same method as in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0204] The raw material oil composition of Example 2 was subjected to coking treatment in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a raw coke composition.
[0205] The obtained raw coke composition was pulverized by a hammer mill so that the average particle diameter measured by a laser diffraction particle size distribution measuring device became 30.2 μm, thereby obtaining a raw coke powder.
[0206] The volume-based surface area of the raw material coke powder (raw mater...
Embodiment 3
[0212] The hydrodesulfurized oil (A) obtained in Example 1 and the aromatic components of the fluidized catalytic cracking residue (A) obtained in Example 2 were mixed in a mass ratio of 45:55, used as The stock oil composition of embodiment 3.
[0213] The n-paraffin content and aromatic index fa in the stock oil composition of Example 3 were determined in the same manner as in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0214] In the same manner as in Example 1, the raw material oil composition of Example 3 was subjected to a coking treatment to obtain a raw coke composition.
[0215] The obtained raw coke composition was pulverized with a hammer mill so that the average particle diameter measured by a laser diffraction particle size distribution measuring device was 21.4 μm, thereby obtaining a raw coke powder.
[0216] The volume-based surface area of the raw material coke powder (raw material volume-based surface area) was obtained in the same manner as in Example ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com