Synthetic graphite material, synthetic graphite material production method, negative electrode for lithium ion secondary battery, and lithium ion secondary battery
A technology of artificial graphite and manufacturing method, applied in the direction of secondary battery, battery electrode, graphite, etc., can solve the problems of capacity deterioration, poor charging and discharging efficiency of positive electrode and negative electrode, etc., and achieve the effect that the discharge capacity is difficult to deteriorate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
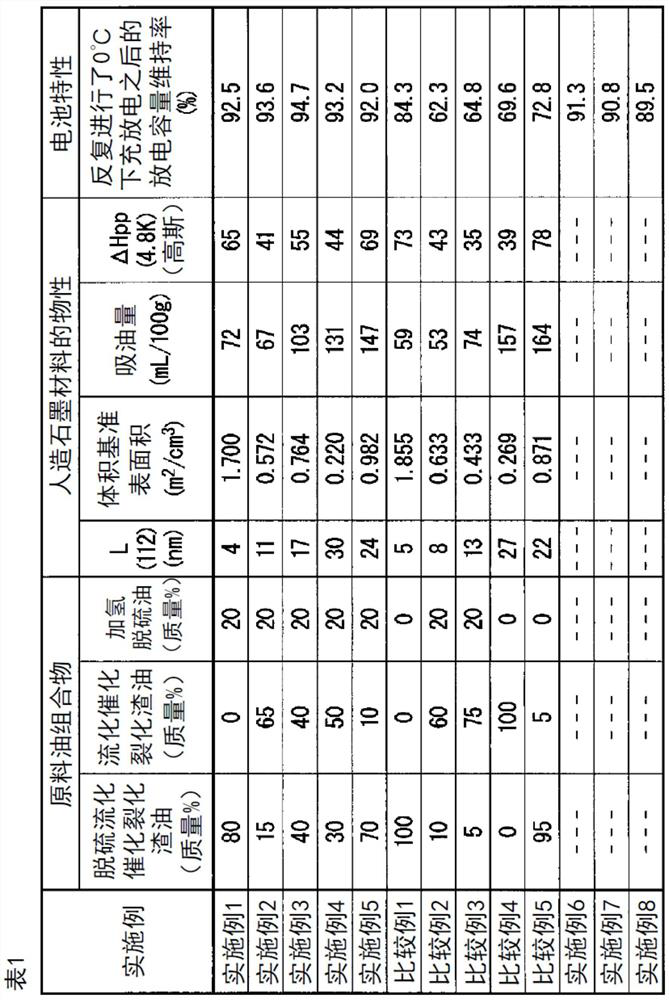
[0188] For desulfurized vacuum light oil (sulfur content 500 mass ppm, density at 15°C 0.88g / cm 3 ) was subjected to fluid catalytic cracking to obtain a fluid catalytic cracking residue (hereinafter referred to as "fluid catalytic cracking residue (A)"). The obtained fluid catalytic cracking residue (A) had an initial boiling point of 220°C, a sulfur content of 0.2% by mass, and an aromatic content of 60% by mass. In addition, hydrodesulfurization was performed on an atmospheric distillation residue with a sulfur content of 3.5% by mass in the presence of a Ni-Mo catalyst so that the hydrolysis rate became 30% or less, and a hydrodesulfurized oil (hereinafter referred to as as "hydrodesulfurized oil (A)".). The obtained hydrodesulfurized oil (A) had an initial boiling point of 260°C, a sulfur content of 0.3% by mass, an asphaltene content of 1% by mass, a saturated content of 70% by mass, and a density of 0.92 g / cm at 15°C. 3 .
[0189] Next, desulfurized vacuum light oil ...
Embodiment 2
[0203]The feed oil composition was obtained by mixing desulfurized fluid catalytic cracking residue (B-1), fluid catalytic cracking residue (A) and hydrodesulfurized oil (A) at a mass ratio of 15:65:20. This raw material oil composition was put into a test tube, and heat-treated at normal pressure and 500 degreeC for 3 hours, and coking was performed, and the raw material coke composition was obtained. This raw coke composition was pulverized by a hammer mill so that the average particle diameter measured by a laser diffraction particle size distribution analyzer was 18.8 μm. The obtained pulverized product was fired at 1000° C. under a nitrogen gas flow to obtain calcined coke. At this time, the heating time from room temperature to 1000°C is set to 4 hours, the holding time at 1000°C is set to 4 hours, and the cooling time from 1000°C to 410°C is set to 2 hours. Let cool on the air side for 4 hours. The obtained calcined coke was put into a graphite crucible, and graphitiz...
Embodiment 3
[0205] The feedstock oil composition was obtained by mixing desulfurized fluid catalytic cracking residue (B-1), fluid catalytic cracking residue (A) and hydrodesulfurized oil (A) at a mass ratio of 40:40:20. This raw material oil composition was put into a test tube, and heat-treated at normal pressure and 500 degreeC for 3 hours, and coking was performed, and the raw material coke composition was obtained. This raw coke composition was pulverized with a hammer mill so that the average particle diameter measured by a laser diffraction particle size distribution analyzer became 20.5 μm. The obtained pulverized product was fired at 1000° C. under a nitrogen gas flow to obtain calcined coke. At this time, the heating time from room temperature to 1000°C is set to 4 hours, the holding time at 1000°C is set to 4 hours, and the cooling time from 1000°C to 410°C is set to 2 hours. Let cool on the air side for 4 hours. The obtained calcined coke was put into a graphite crucible, an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com