Bio-based nano assembled curing agent for strengthening and toughening epoxy resin and preparation method of bio-based nano assembled curing agent
A technology of toughening epoxy and nano-assembly, applied in the field of bio-based curing agent for epoxy resin, can solve the problems of low strength, few reaction sites, low crosslinking density, etc., and achieve low cost, rich surface phenolic hydroxyl groups, The effect of improving overall performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
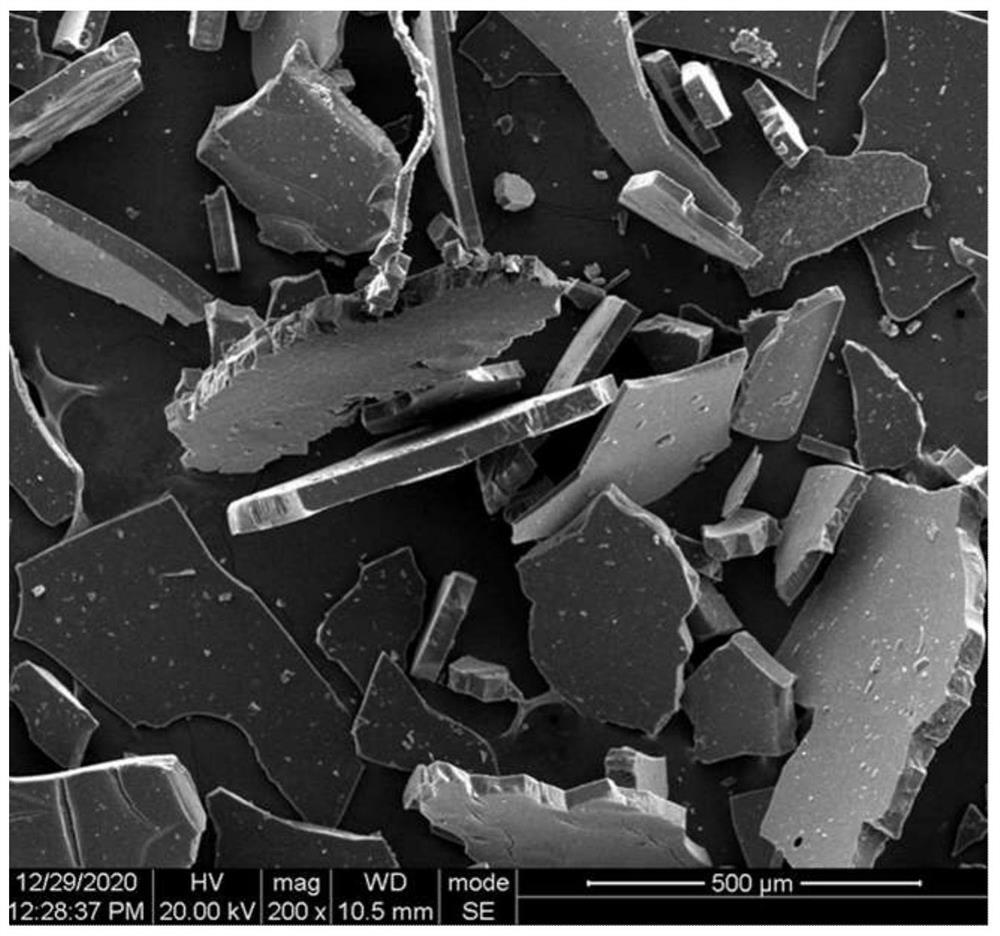
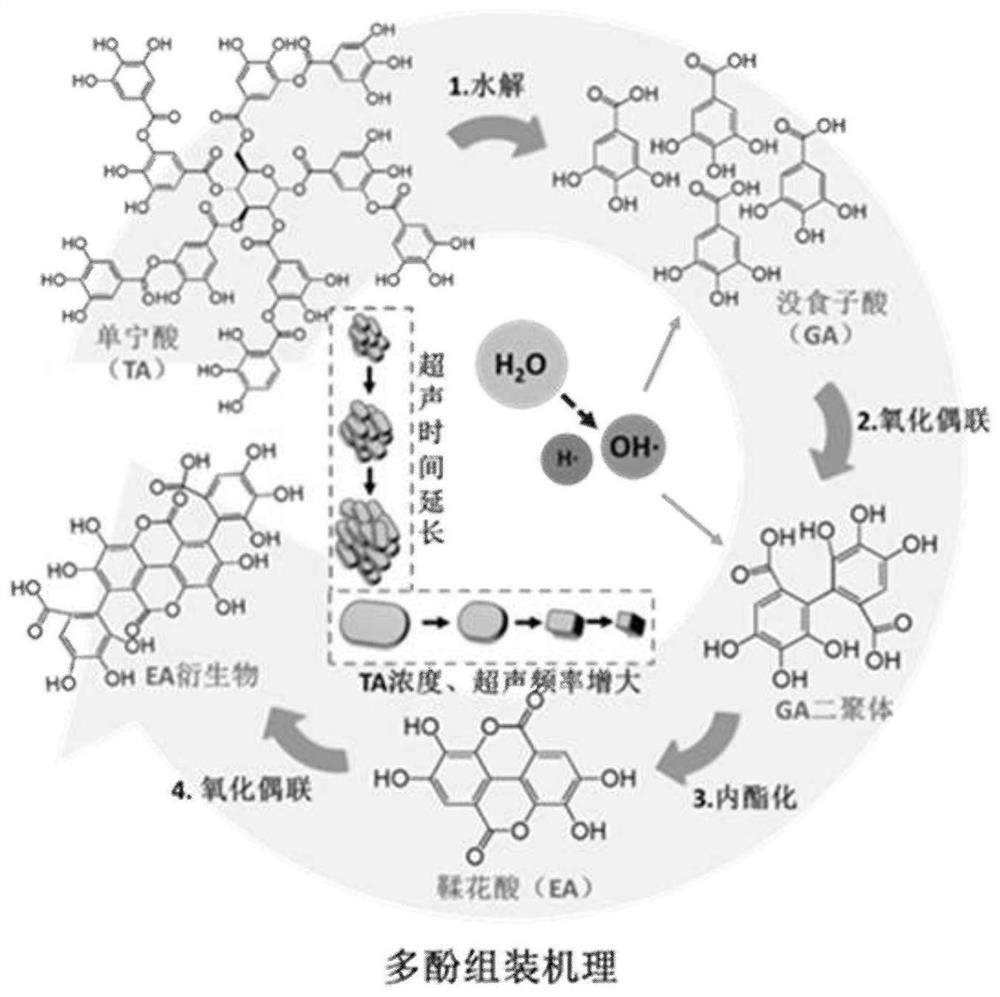
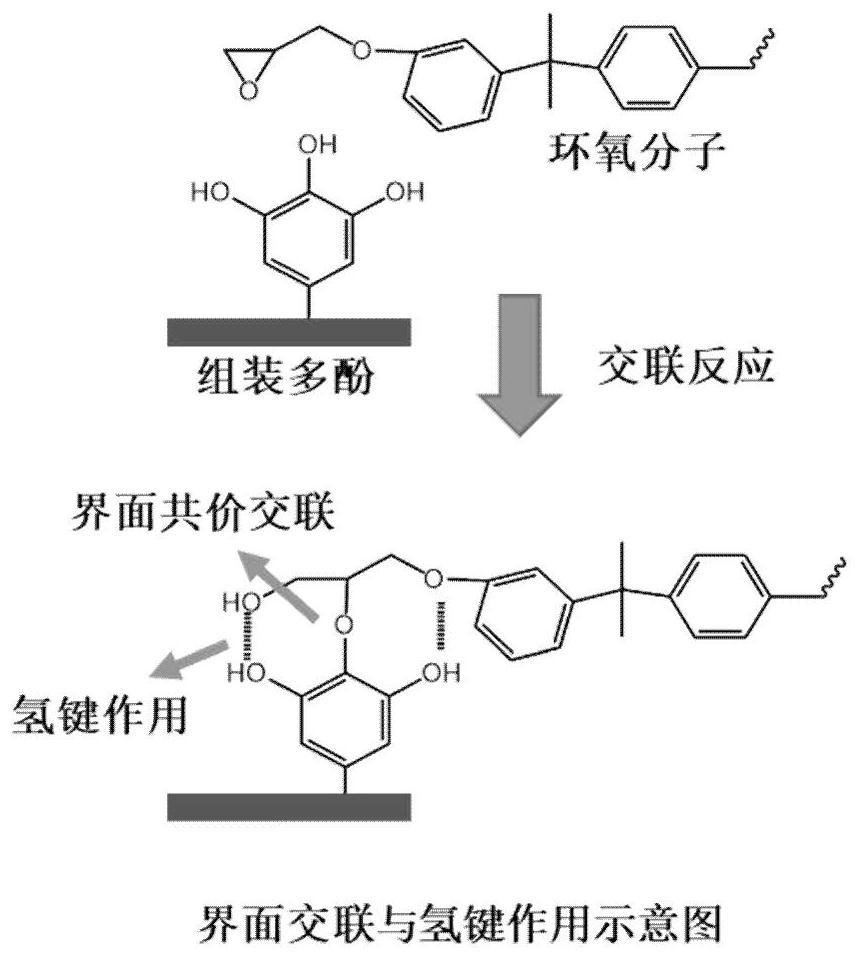
[0032] Dissolve 500g of commercial tannic acid powder in 2L of deionized water, and perform ultrasonic treatment at 400W, 25Hz for 30 minutes. Under the action of ultrasonic activation, tannic acid molecules undergo a coupling reaction and stack and assemble, forming a surface with a large number of phenolic hydroxyl groups. Micron-scale flat assemblies, such as image 3 shown. The resulting suspension was dialyzed against deionized water for 7 days to remove unreacted small molecules. The assembly suspension was taken out and freeze-dried to obtain tannic acid assembly powder. Mix 20 parts of the obtained powder with 100 parts of epoxy resin prepolymer (grade 1009F), stir well for more than 5 hours to uniformly disperse, heat up to 120°C for more than 5 hours, so that the epoxy resin material is fully cured, and bio-based Assembly of toughened epoxy resin materials modified with polyphenol curing agent.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Dissolve 500g of commercial tannic acid powder in 2L of deionized water, and perform ultrasonic treatment for 15 minutes under the conditions of 200W and 25Hz. The tannic acid molecules undergo a coupling reaction under the action of ultrasonic activation and stack and assemble, forming a surface with a large number of phenolic hydroxyl groups. nanoscale flat assemblies. The resulting suspension was dialyzed against deionized water for 7 days to remove unreacted small molecules. The assembly suspension was taken out and freeze-dried to obtain tannic acid assembly powder. Mix 20 parts of the obtained powder with 100 parts of epoxy resin prepolymer (grade 1009F), stir well for more than 5 hours to uniformly disperse, heat up to 120°C for more than 5 hours, so that the epoxy resin material is fully cured, and bio-based Assembly of toughened epoxy resin materials modified with polyphenol curing agent.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Dissolve 500g of commercial tannic acid powder in 2L of deionized water, and perform ultrasonic treatment for 15 minutes under the conditions of 200W and 25Hz. The tannic acid molecules undergo a coupling reaction under the action of ultrasonic activation and stack and assemble, forming a surface with a large number of phenolic hydroxyl groups. nanoscale flat assemblies, such as Figure 5 and Figure 6 shown. The resulting suspension was dialyzed against deionized water for 7 days to remove unreacted small molecules. The assembly suspension was taken out and freeze-dried to obtain tannic acid assembly powder. Mix 30 parts of the obtained powder with 100 parts of epoxy resin prepolymer (grade 1009F), stir well for more than 5 hours to uniformly disperse, heat up to 120°C for more than 5 hours, so that the epoxy resin material is fully cured, and bio-based Assembly of toughened epoxy resin materials modified with polyphenol curing agent.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com