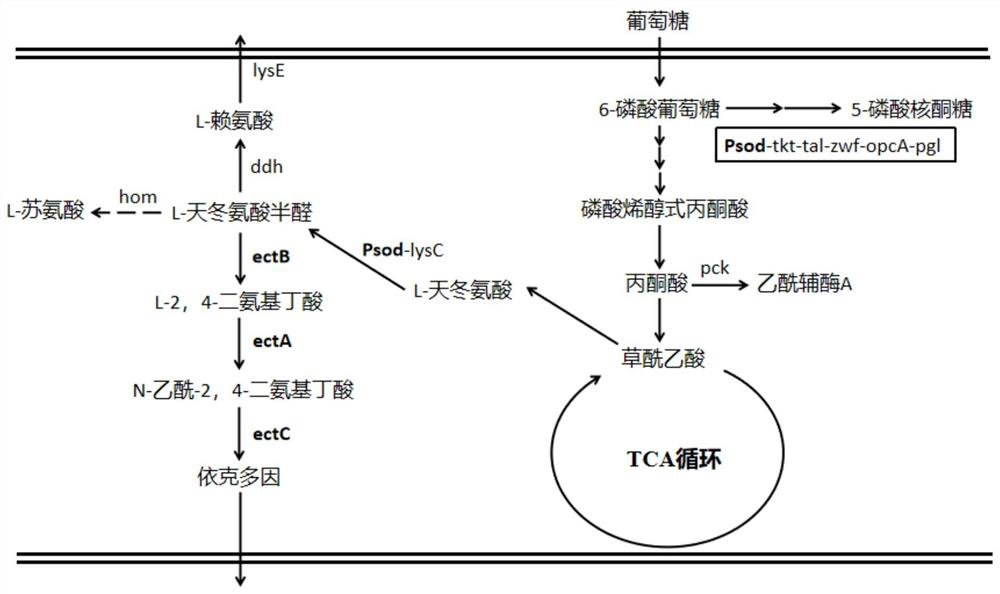
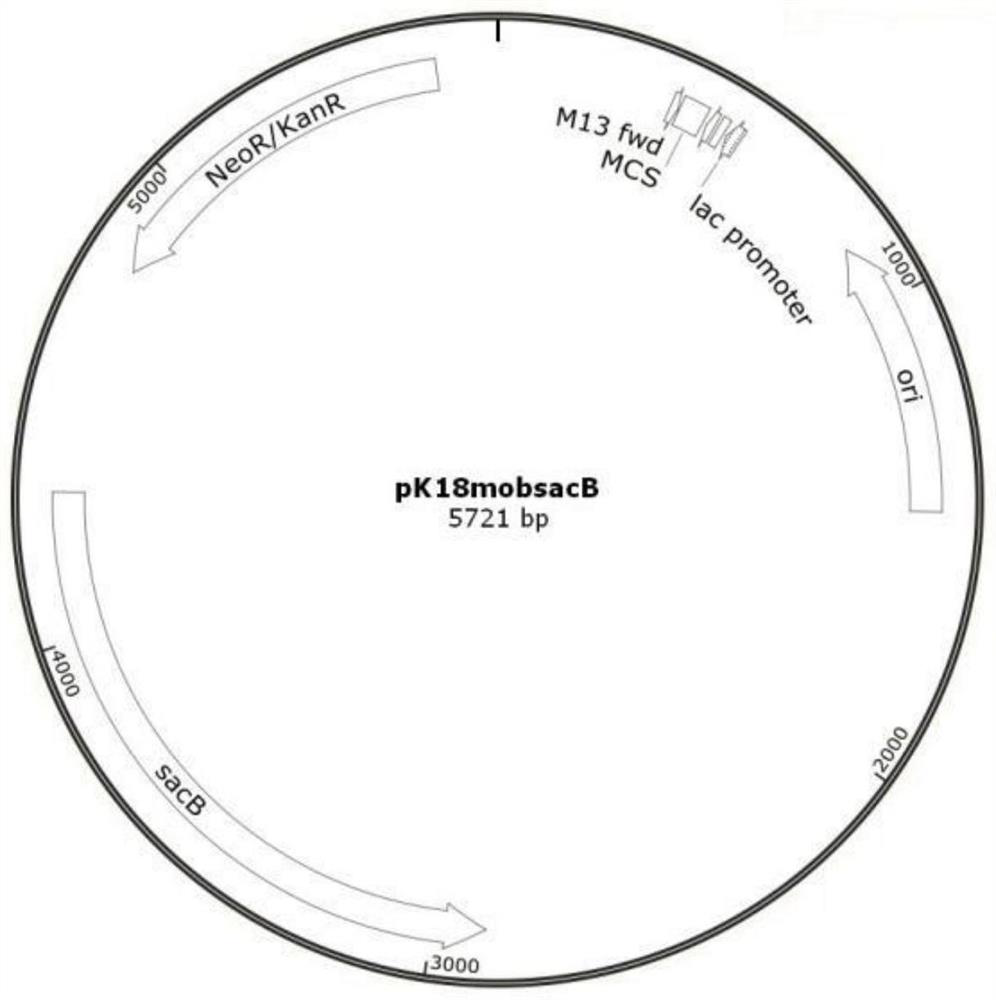
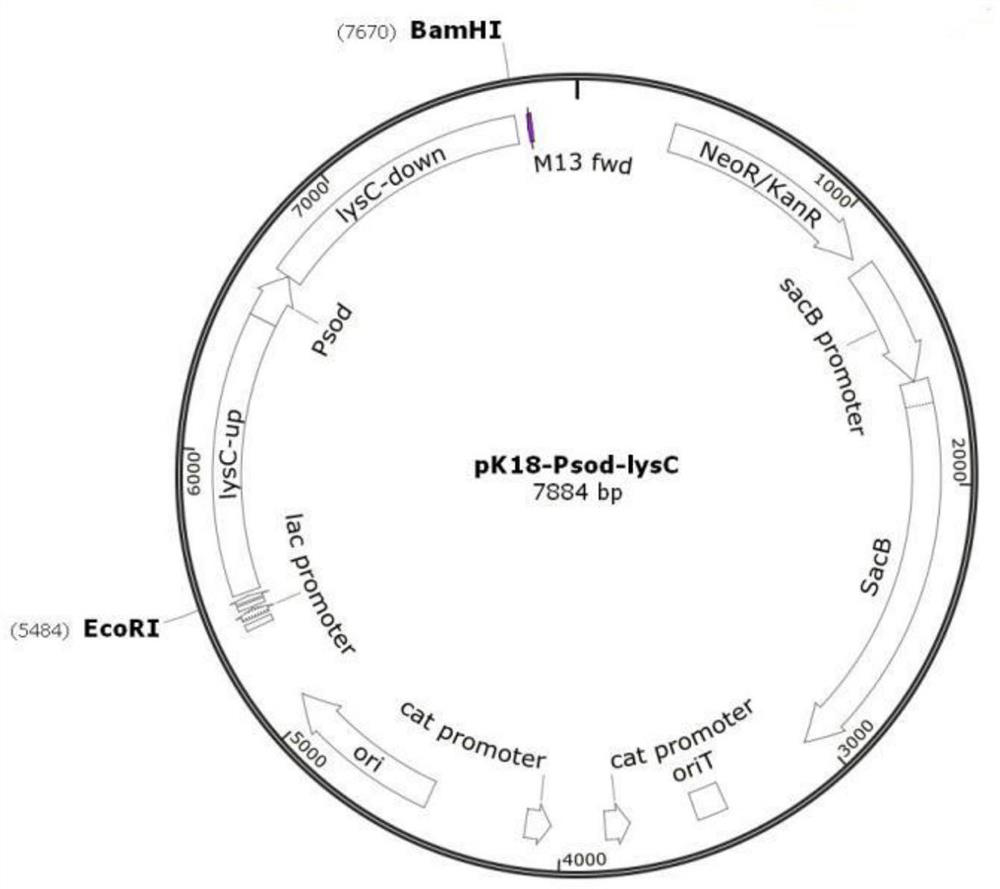
Method for constructing Ectoine producing strain
A technology for ectoine and production of bacteria, which is applied in the fields of metabolic engineering and genetic engineering, and can solve problems such as affecting the life of fermentation vessels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Example 1: Genetic modification target plasmid construction
[0079] 1.1 Construction of plasmid pK18-Psod-lysC
[0080] Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 LysC fbr The genome was used as a template, and PCR amplification was performed with Psod-lysC-up-F / Psod-lysC-up-R and Psod-lysC-down-F / Psod-lysC-down-R primer pairs, respectively. PCR amplification conditions: 95°C for 5min; 30 cycles of 92°C for 30s, 58°C for 30s, 65°C for 35s; 65°C for 10min. The Psod-lysC-up and Psod-lysC-down fragments were amplified, both of which were 1k in length, and recovered by cutting the gel.
[0081] ATCC1303 LysC fbr The genome was used as a template, and Psod-lysC-F and Psod-lysC-R were used as primers to amplify to obtain a Psod-lysC fragment with a length of 200 bp, which was recovered by cutting the gel. Using Psod-lysC-up-F and Psod-lysC-down-R as primers, the three fragments of Psod-lysC-up, Psod-lysC-down, and Psod-lysC were subjected to overlap PCR, and the product was ge...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2: Construction of genetically engineered bacterial strains
[0106] 2.1 Pipette 3 μl (more than 500ng) of pK18-Psod-lysC plasmid into Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032LysC fbr Competent cells were mixed and transferred to a 2 μm electroporation cup, and electric shock was performed at 2.5 kV for 5.3 ms. Immediately after electric shock, they were transferred to 800 μl 46°C preheated BHIS liquid medium, and incubated at 46 ℃ in a water bath for 6 minutes, and then placed in a constant temperature shaker at 30 ℃ and 220 rpm for 1 hour to revive the bacteria. After thawing, 100 μl of bacteria were spread on the BHIS plate containing kanamycin, and the plate was inverted and cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 30° C. for 48 hours. The transformant on the BHIS plate containing kanamycin was picked, inoculated into a non-resistant BHIS test tube medium, and cultured in a constant temperature shaker at 30° C. and 220 rpm for 24 hours to allow double...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Embodiment 3: the fermentation of engineering bacterium
[0111] 3.1 Shake flask fermentation: Streak the genetically engineered strains on the BHIS plate, incubator at 30°C for about 2 days, pick 2-3 single clones into the BHIS test tube; culture with shaking at 220rpm at 30°C for about 14 hours, transfer the seeds according to the ratio of 5v / v% Shake flasks, 30°C 220rpm shaking culture for about 10h; then 10v / v% inoculum amount was transferred to fermentation shaker flasks, 30°C 220rpm shaking culture for about 20h, samples were taken to detect the content of ectoine, and the fermentation results are shown in Table 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com