Mobile robot path planning method and system
A mobile robot and path planning technology, applied in the field of intelligent robots, can solve problems such as the minimum planned path without path time, and achieve the effect of reducing the cost of path time and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Robot path planning algorithm is one of the core contents of mobile robot research. It started in the 1970s and has produced a large number of research results so far, making great contributions to the wide application of robots. Traditional path planning algorithms can be divided into node-based methods and sampling-based methods. The representative of the node-based method is the A* algorithm. The A* algorithm is an improvement to the Dijkstra algorithm. It introduces heuristic functions and constraints, and in each round of optimization search, it is necessary to calculate the corresponding value of each feasible solution in the global scope. The value of the heuristic function, and then select the feasible solution with the minimum heuristic function value in this round of search as the optimal solution of the current round, and then continue the next round of optimization search, and finally ensure that the global optimal path can be obtained The A* algorithm finds...
Embodiment 2
[0097] This embodiment is used to provide a mobile robot path planning system, such as Figure 7 As shown, the planning system includes:
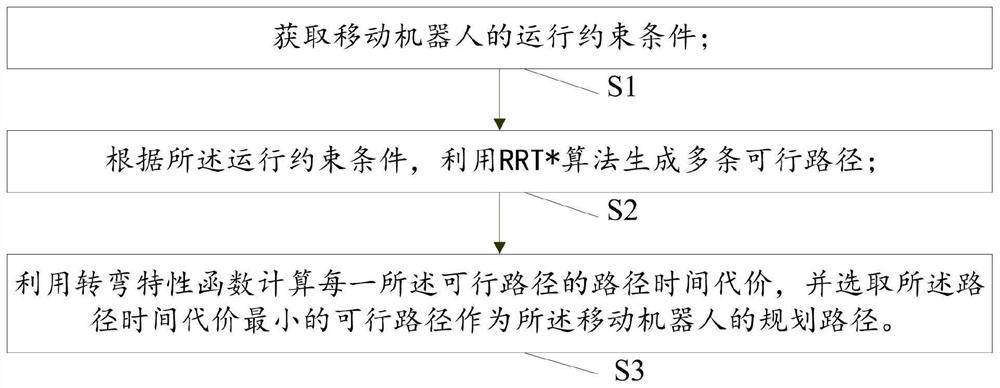
[0098] The obtaining module M1 is used to obtain the operating constraints of the mobile robot; the operating constraints include the feasible area of the mobile robot, the position of the starting point, the position of the target point, the step size, the search step size and the obstacles in the feasible area item information;
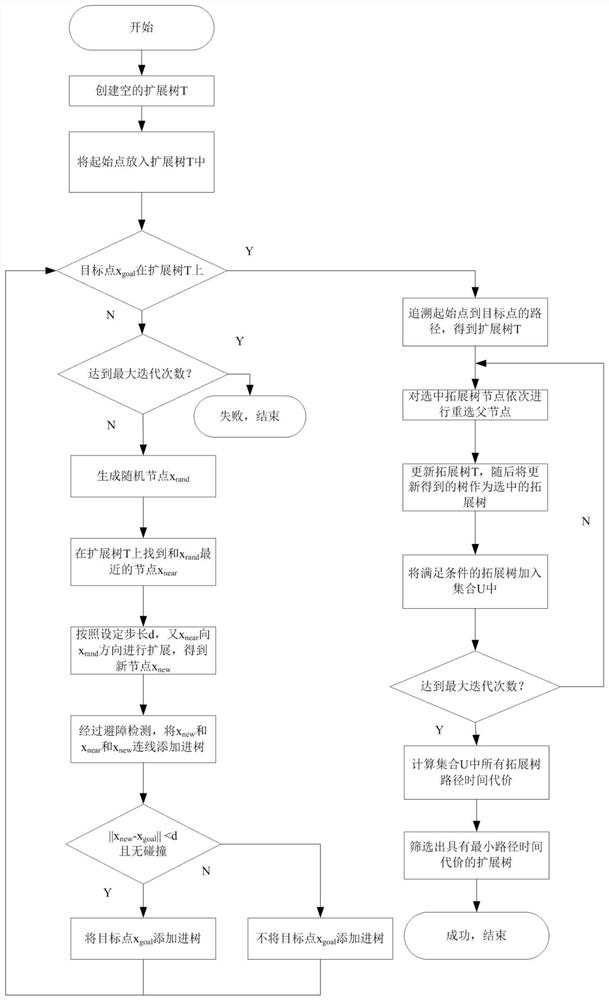
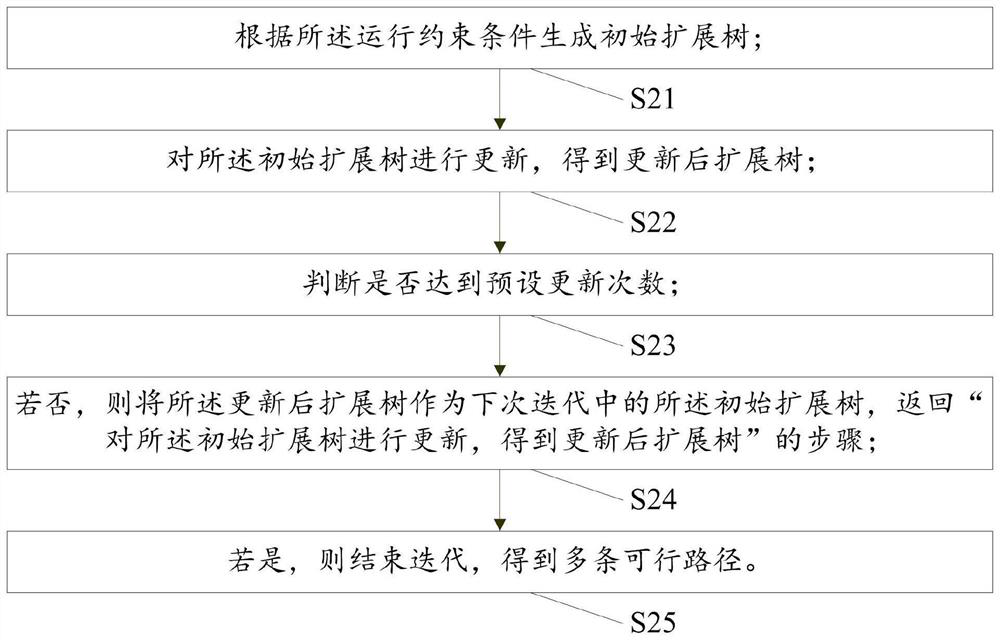
[0099] A feasible path generating module M2, configured to generate multiple feasible paths using the RRT* algorithm according to the operating constraints;
[0100] The planning module M3 is configured to calculate the path time cost of each feasible path by using the turning characteristic function, and select the feasible path with the smallest path time cost as the planned path of the mobile robot.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com