Method for evaluating electron loss capability of micro-plastic through trivalent arsenic oxide rate of micro-plastic
A technology for oxidizing trivalent and microplastics, which is applied in the direction of material analysis, material analysis, and material excitation analysis through optical means, which can solve problems such as susceptibility to oxygen interference, and achieve the effect of reasonable overall design and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
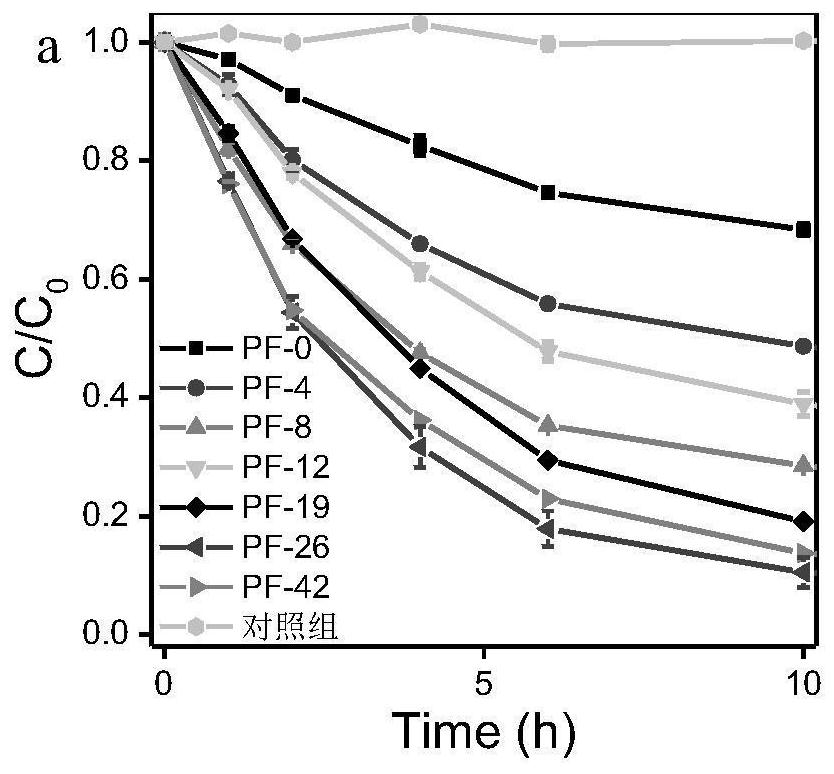
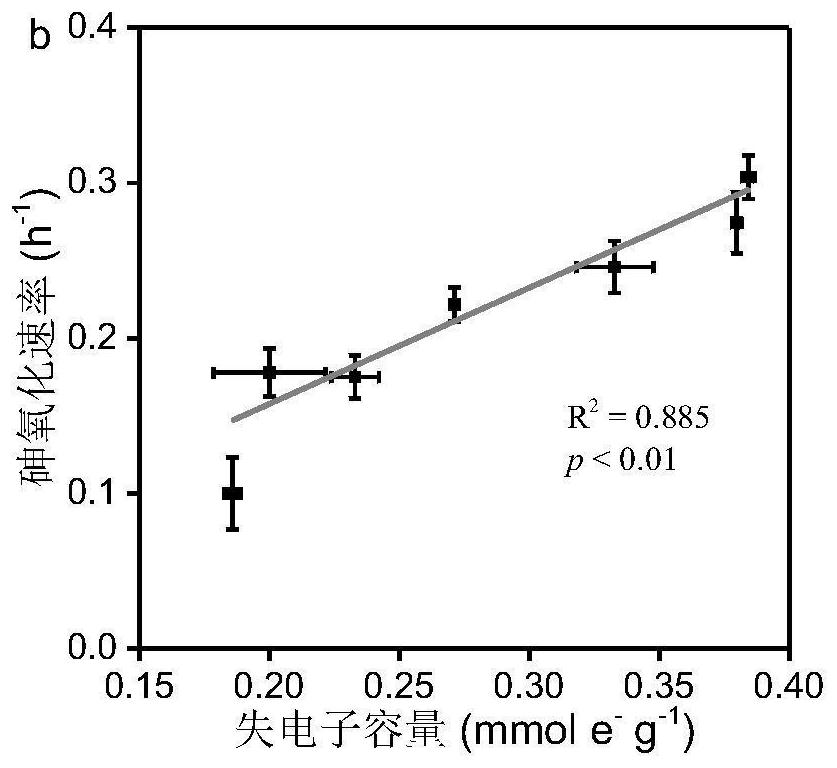
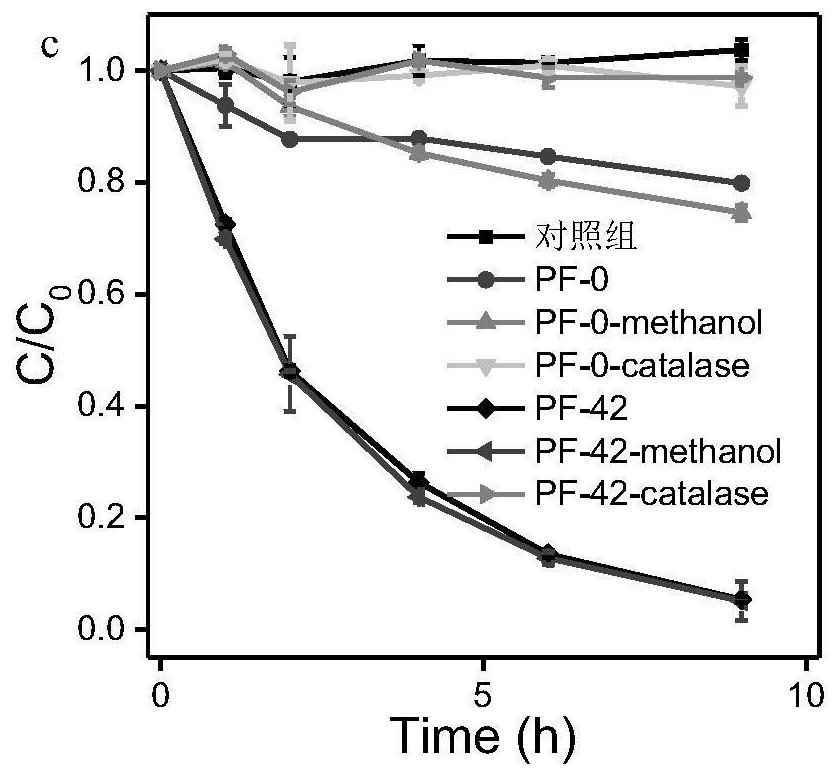
[0038] Example 1: A method for evaluating the ability of microplastics to lose electrons by the rate of oxidation of trivalent arsenic by microplastics, specifically comprising: combining microplastics with a solution containing trivalent arsenic at a concentration of 0.25 mg / L according to a mass volume ratio of 1 mg / ml Mix evenly, and then carry out shaking culture in an aerobic environment; and take samples at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 10 hours, pass through a 0.22 micron filter membrane, store the filtrate with 0.2M hydrochloric acid, and then measure it with an atomic fluorescence photometer Trivalent arsenic and total arsenic content, according to the change of trivalent arsenic concentration with reaction time, calculate the oxidation rate of arsenic, which is used to estimate the electron loss ability of microplastics.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: A method for evaluating the ability of microplastics to lose electrons by the rate of oxidation of trivalent arsenic by microplastics, specifically comprising: combining microplastics with a solution containing trivalent arsenic at a concentration of 0.5 mg / L at a mass volume ratio of 1.5 mg / L The ratio of ml was mixed evenly, and then shaken and cultured in an aerobic environment; and samples were taken at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 10 hours, passed through a 0.22 micron filter membrane, and the filtrate was preserved with 0.2M hydrochloric acid, followed by an atomic fluorescence photometer Measure the content of trivalent arsenic and total arsenic, and calculate the oxidation rate of arsenic according to the change of trivalent arsenic concentration with the reaction time, which is used to estimate the electron loss ability of microplastics.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: A method for evaluating the ability of microplastics to lose electrons by the rate of oxidation of trivalent arsenic by microplastics, specifically comprising: combining microplastics with a solution containing trivalent arsenic at a concentration of 1 mg / L according to a mass volume ratio of 2 mg / ml The ratio was mixed evenly, and then shaken and cultured in an aerobic environment; and samples were taken at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 10 hours, passed through a 0.22 micron filter membrane, and the filtrate was preserved with 0.2M hydrochloric acid, and then measured with an atomic fluorescence spectrometer. According to the change of trivalent arsenic concentration with reaction time, the oxidation rate of arsenic was calculated, which was used to estimate the electron loss ability of microplastics.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com