Genetically modified clostridium bacteria, preparation and uses of same
A Clostridium bacterium, genetic modification technology, applied in the field of Clostridium bacterium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
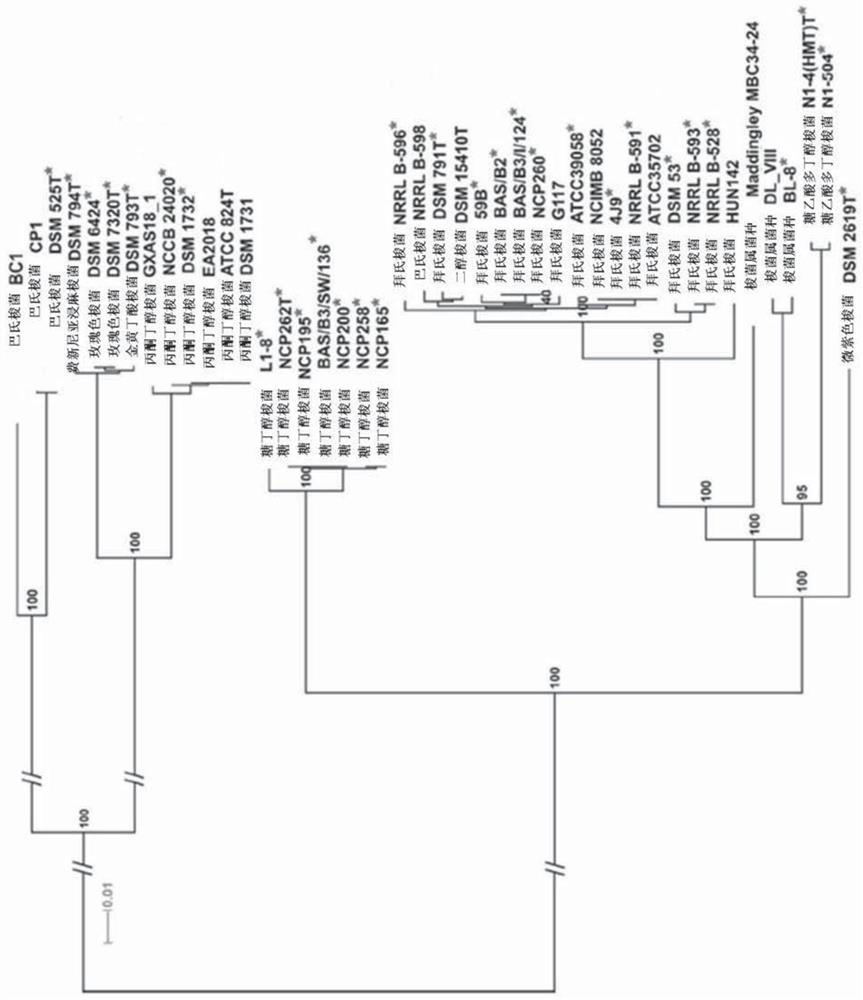
[0018] Despite being used industrially for more than a century, understanding of Clostridium bacteria is still limited by the difficulties encountered in genetically modifying them.
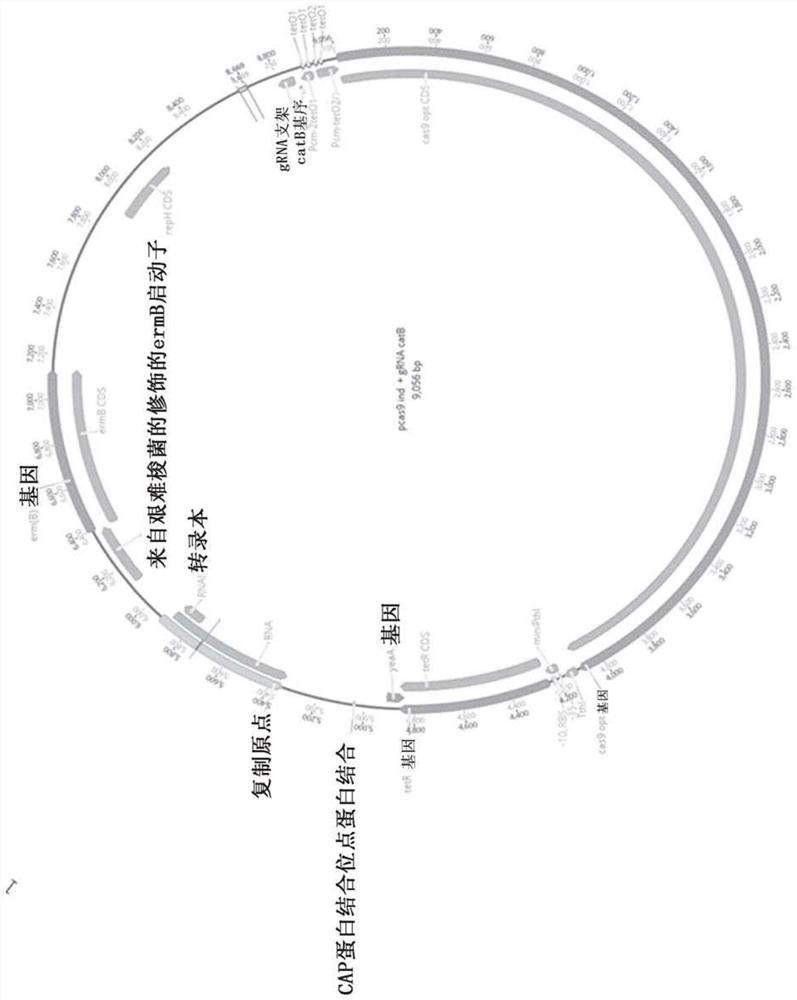
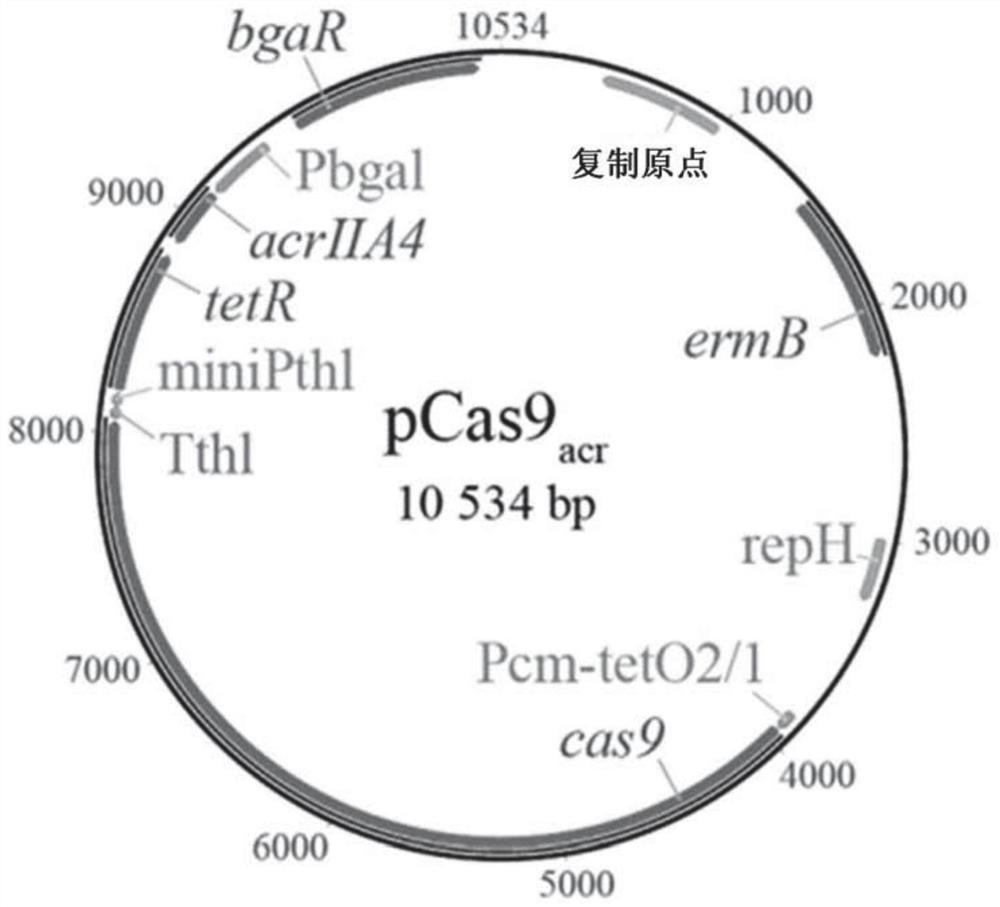
[0019] Different genetic tools have been designed in recent years to optimize strains of this genus, the latest generation being based on the use of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR) / CRISPR-Associated Protein (Cas) technology. This method is based on the use of an enzyme called a nuclease (typically a Cas-type nuclease in the case of CRISPR / Cas genetic tools, such as the Cas9 protein from Streptococcus pyogenes), which in the Double-strand cleavage in DNA molecules (target sequences of interest) is guided by RNA molecules. The sequence of the guide RNA (gRNA) determines the cleavage site of the nuclease, endowing it with extremely high specificity ( Figure 17 ).
[0020] Since double-strand cuts in essential DNA molecules are lethal to the organism, the survival...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com