Capacity control valve
A capacity control and valve core technology, applied in control valve, non-electric variable control, fluid pressure control and other directions, can solve the problems of large size, unable to smoothly control the opening and closing adjustment of valve core, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 7 , the capacity control valve of Embodiment 1 will be described. Below, will be from figure 2 The left and right sides when viewed from the front side are described as the left and right sides of the capacity control valve.
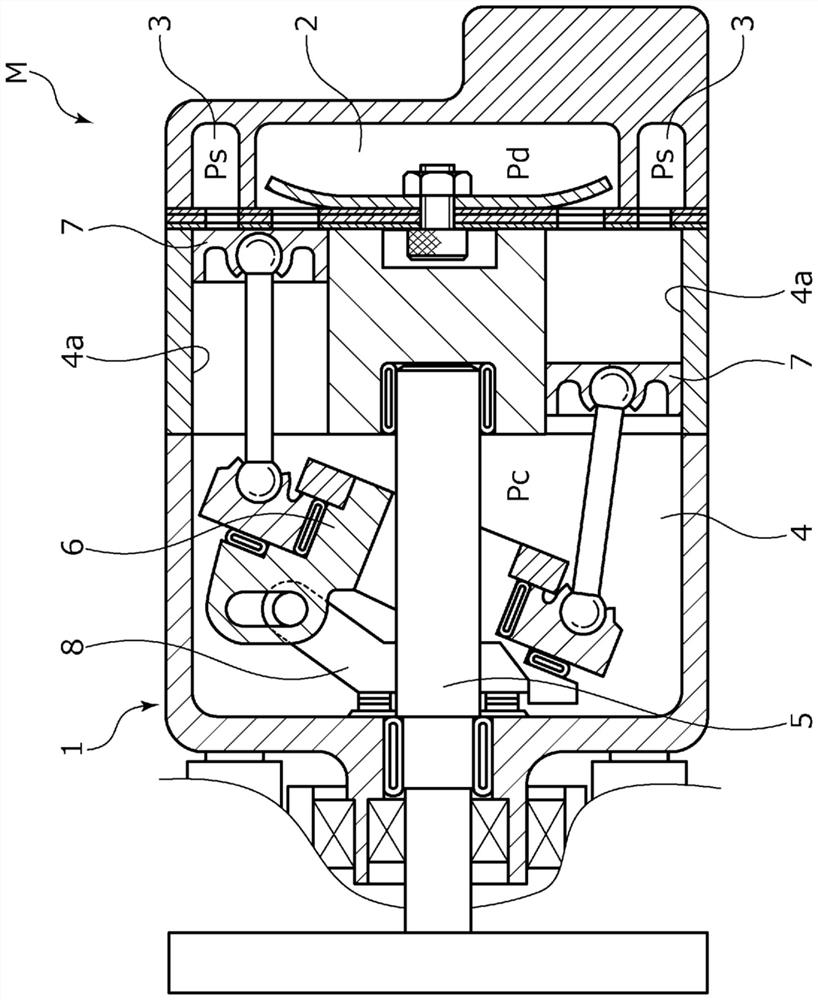
[0049] The capacity control valve V of the present invention is incorporated in a variable capacity compressor M used in an air-conditioning system such as an automobile, and controls the pressure of a working fluid (hereinafter simply referred to as "fluid"), which is a refrigerant, variably, thereby controlling a variable The displacement of the capacity compressor M adjusts the air conditioning system to the desired refrigeration capacity.
[0050] First, the variable displacement compressor M will be described. Such as figure 1 As shown, the variable displacement compressor M has a casing 1 including a discharge chamber 2, a suction chamber 3, a control chamber 4, and a plurality of cylinders 4a. In addition,...
Embodiment 2
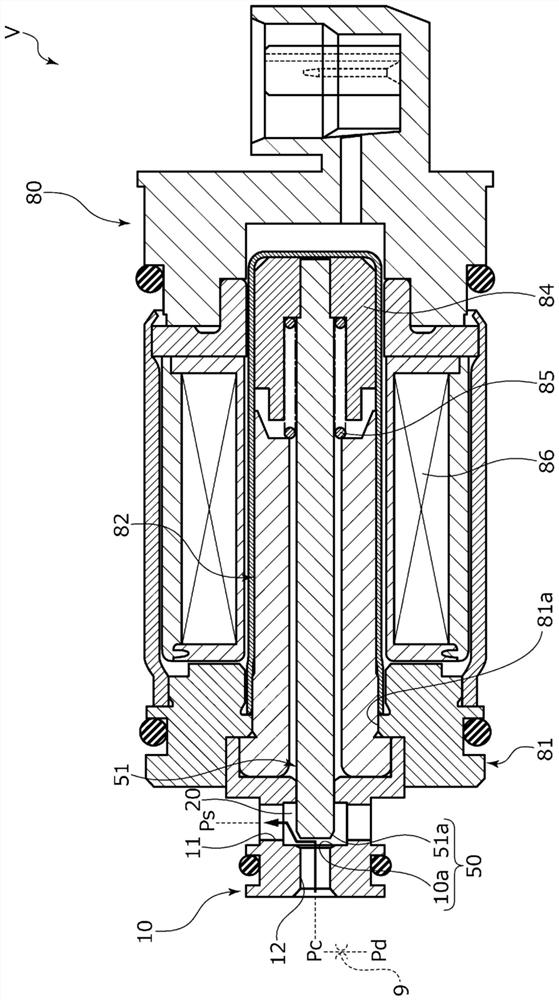
[0084] refer to Figure 8 and Figure 9 , the capacity control valve of Embodiment 2 will be described. In addition, with regard to the same structure as that of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, repeated descriptions are omitted.
[0085] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the center column 94 has a convex portion 95 formed to protrude toward the side facing the movable iron core 84 . The convex portion 95 is formed on the outer diameter side, has a tapered shape, and has an outer peripheral surface 95 b that extends over the front end surface 95 a and is inclined with respect to the axial direction of the center column 82 . The inner peripheral surface 95 c of the convex portion 95 forms a surface parallel to the axial direction of the center column 94 . In addition, on the radially inner side of the base of the convex portion 95 , an opposing surface 96 serving as the inner end of the concave portion is formed, which is perpendicular to the axial direction of the center column...
Embodiment 3
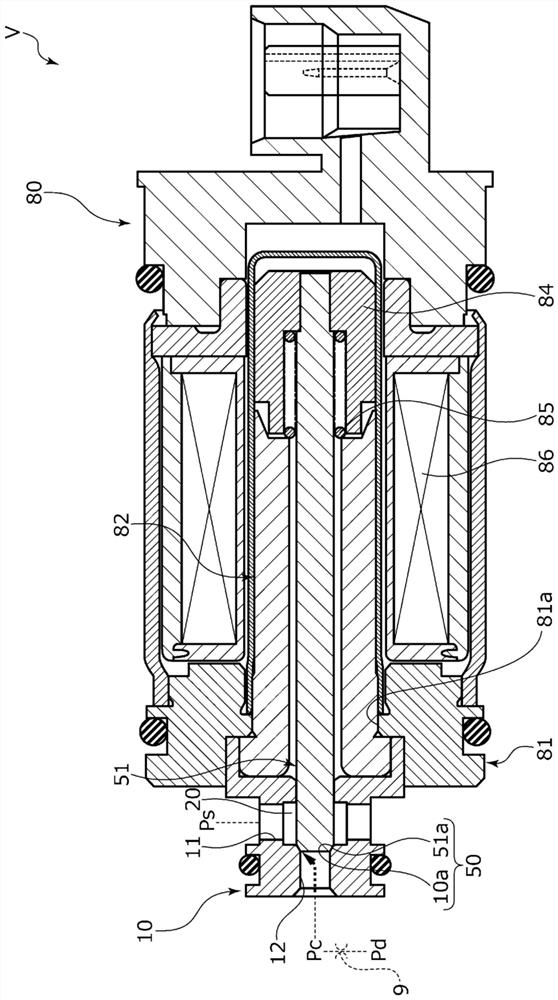
[0092] refer to Figure 10 , the capacity control valve of Embodiment 3 will be described. In addition, with regard to the same structure as that of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, repeated descriptions are omitted.
[0093] When the capacity control valve V2 is in the non-energized state, the force of the coil spring 85 presses the movable iron core 84 axially to the right, thereby, the CS spool 151 moves axially to the right, and the large diameter of the CS spool 151 The axial right side of the portion 151a is seated on the CS valve seat 110a, and the CS valve 150 is closed. And, in the energized state (i.e., during normal control, so-called duty ratio control), by applying current to the solenoid 80, the movable iron core 84 is drawn closer to the center column 82 side, that is, to the left side in the axial direction. , the CS spool 151 fixed to the movable iron core 84 moves axially leftward together, whereby the axial right side of the large-diameter portion 151a of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com