Production process method for reducing carbide mesh grade of GCr15 bearing steel bar
A production process and technology of bearing steel, which is applied in the field of production process to reduce the carbide network level of GCr15 bearing steel bar, and can solve the problems of coarse steel structure, low network uniformity, and inapplicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] In this embodiment, a production process for reducing the carbide mesh level of GCr15 bearing steel rods, the components and weight percentages of the produced bearing steel rods are: C: 0.95-1.02%, Si: 0.15-0.35% , Mn: 0.25~0.45%, Cr: 1.40~1.55%, P≤0.008%, S≤0.005%, Ni≤0.20%, Mo≤0.10%, Nb: 0.02~0.08%, Al: 0.015~0.035%, Cu ≤0.20%, Re≤0.020%, Ti≤0.0020%, O≤0.0010%, As≤0.040%, Pb≤0.0020%, Ca≤0.0010%, the rest are Fe and unavoidable impurities, including the following steps:
[0038] Step 1. Continuous casting: adopt tundish induction heating, two-stage electromagnetic stirring and light and heavy reduction process. The specification of the continuous casting slab is Φ380×450mm, which ensures the uniform composition and good surface quality of the continuous casting slab;
[0039] Step 2: Heating the continuous casting slab: put it into the furnace by hot charging process;
[0040] Step 3, continuous casting slab rolling: rolling 250mm billet;
[0041] Step 4, heating: 2...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A production process for reducing the carbide network level of GCr15 bearing steel rods in this embodiment, the basic structure is the same as that in Embodiment 1, the difference and improvement are: in the produced bearing steel rods, C, Cr, Nb The content range of Re satisfies the following formula: 1.7≤7.88(%C)+0.75(%Nb)+1.48(%Re)-4.25(%C)(%Cr)≤1.8. The content range of C, Cr, Nb, and Re is further limited by the formula, and the compound coordination effect of each element is used to promote the precipitation of secondary cementite to be finer, dispersed and uniform. Rare earth has extremely strong deoxidation, desulfurization, purification of molten steel and alloying effects, thereby improving the composition uniformity of steel; after adding trace niobium elements, the grains of bearing steel are effectively refined, increasing the grain boundary area, which is equal to increasing The nucleation point for secondary cementite precipitation is defined, and the dis...
Embodiment 3
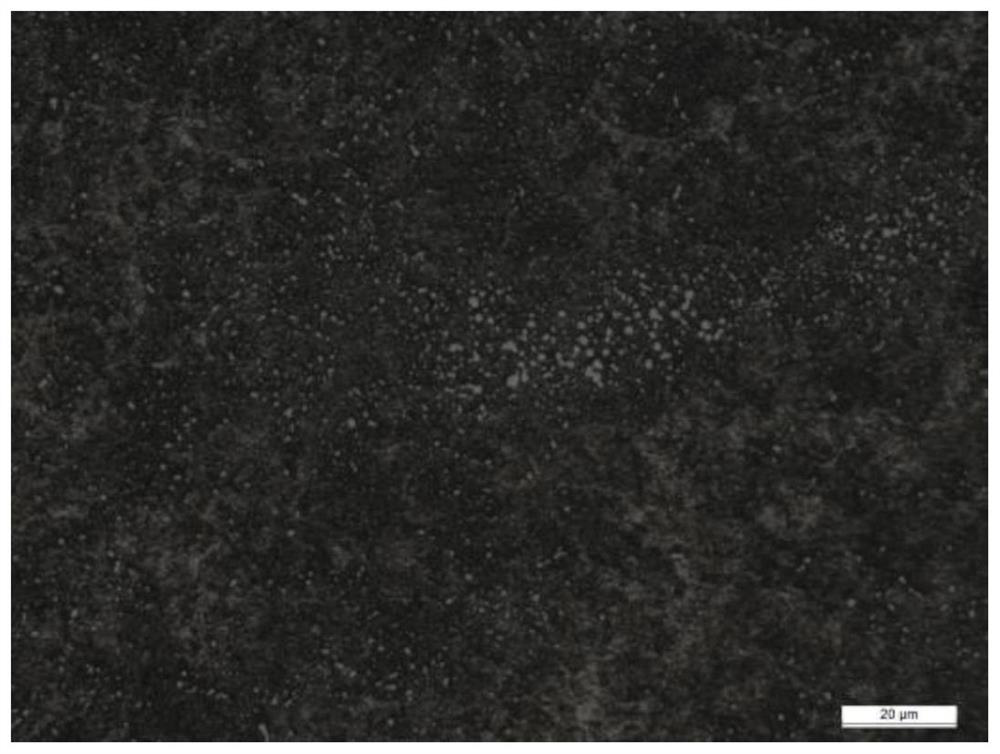
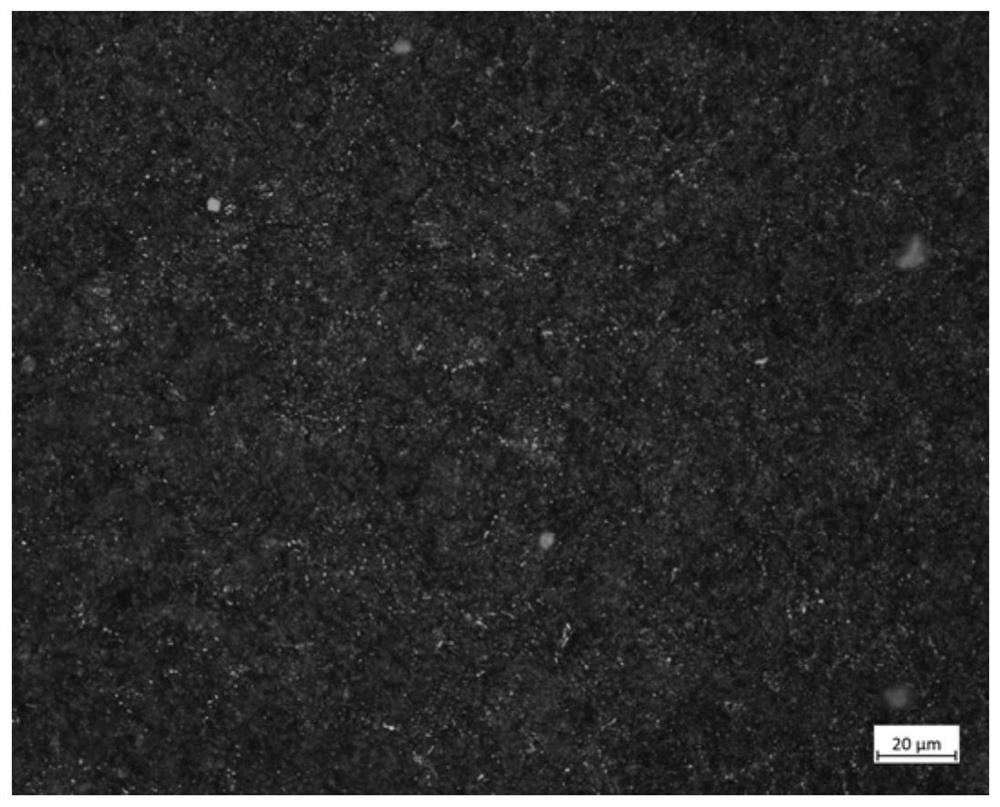
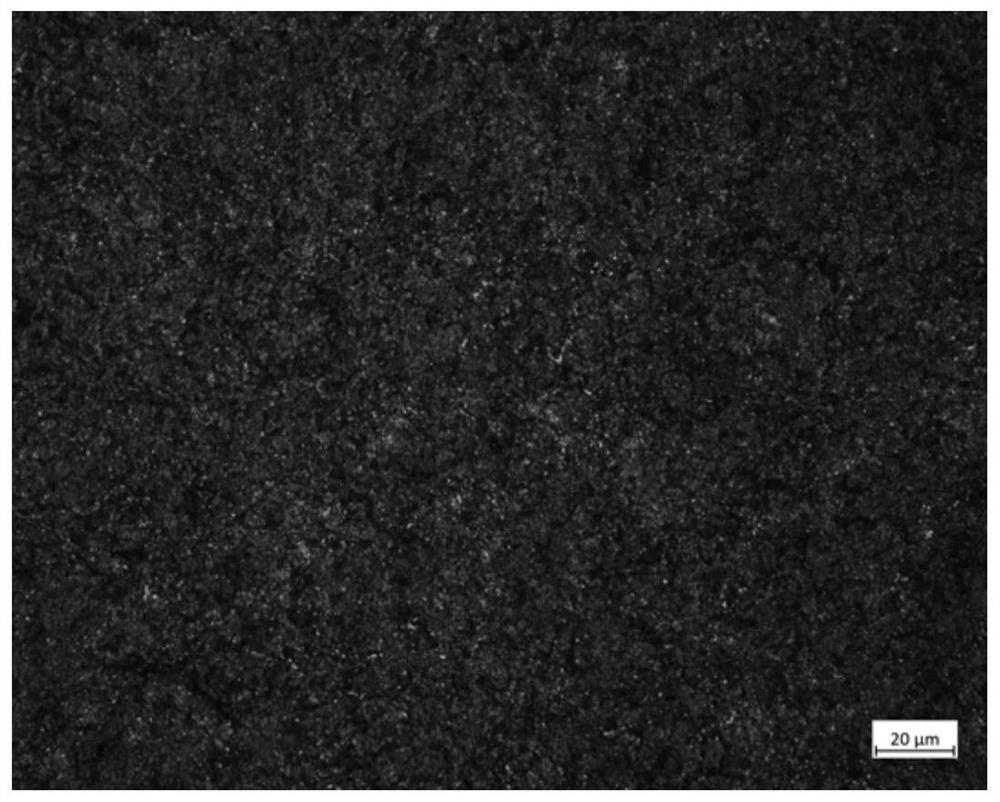
[0053] A production process for reducing the carbide network level of GCr15 bearing steel rods in this embodiment, the basic structure is the same as in Embodiment 2, the differences and improvements are as follows: figure 1 As shown, the production of hot-rolled bars with a diameter of Φ16mm:
[0054] The chemical composition of the product: C 0.97%, Si 0.22%, Mn 0.36%, Cr 1.45%, P 0.008%, S0.001%, Ni 0.02%, Mo 0.01%, Nb 0.05%, Al 0.020%, Cu 0.03%, Re 0.015%, Ti0.0010%, O 0.0005%, As 0.004%, Pb 0.0002%, Ca 0.0002%, the rest is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0055] A method for reducing the deformation of the GCr15 bearing steel carbide mesh level in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0056] The stage of continuous casting of molten steel adopts tundish induction heating with a superheat of 18°C, two-stage electromagnetic stirring and light and heavy reduction process;
[0057] The continuous casting billet is diffused at a high temperature of 1240 ℃, and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com