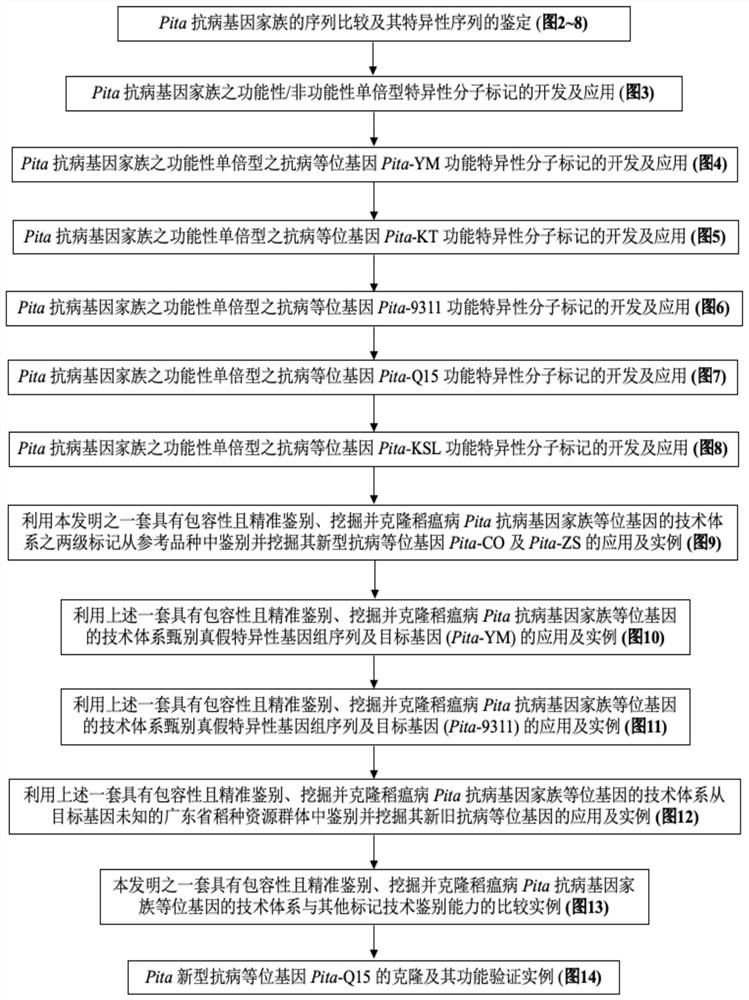
Technical system which has inclusiveness and can accurately identify, excavate and clone alleles of rice blast Pita disease-resistant gene family
An allele and disease resistance gene technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of gene family sequencing errors and difficult identification of single molecular markers, and achieve the effect of improving purpose and efficiency, rigorous inclusiveness and comparability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
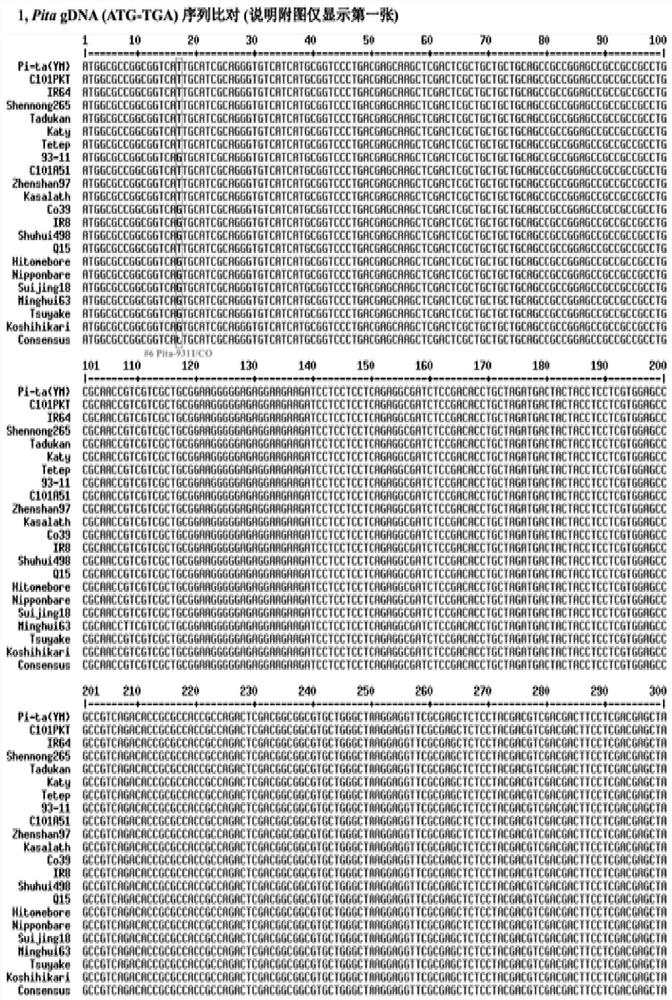
[0110] Embodiment 1: the identification of the sequence comparison of rice blast Pita disease-resistant gene family and its specific sequence ( Figure 2-8 )
[0111] 1. Experimental method
[0112] Using the genome sequence (ATG~TGA) of the cloned Pita-YM (donor variety Yashiro Mochi (YM); GenBank AF207842), retrieve and download the sequences of the other 14 presumed target gene carriers from the above public databases such as NCBI Genome sequences of reference varieties C101PKT, IR64, Shennong265, Tadukan, Katy (KT), Tetep, 9311, C101A51, Zhenshan 97 (ZS), Kasalath (KSL), CO39 (CO), IR8, Shuhui 498, Q15; for the convenience of sequence For comparative analysis, the corresponding genome sequences of 6 sequenced reference varieties Hitomebore, Nipponbare (NPB), Suijing 18, MInghui 63, Tsuyuake, and Koshihikari, which were presumed to be non-target gene carriers, were added.
[0113] The range of ATG~TAG of each gene refers to NCBI annotation.
[0114] Sequence comparison a...
Embodiment 2
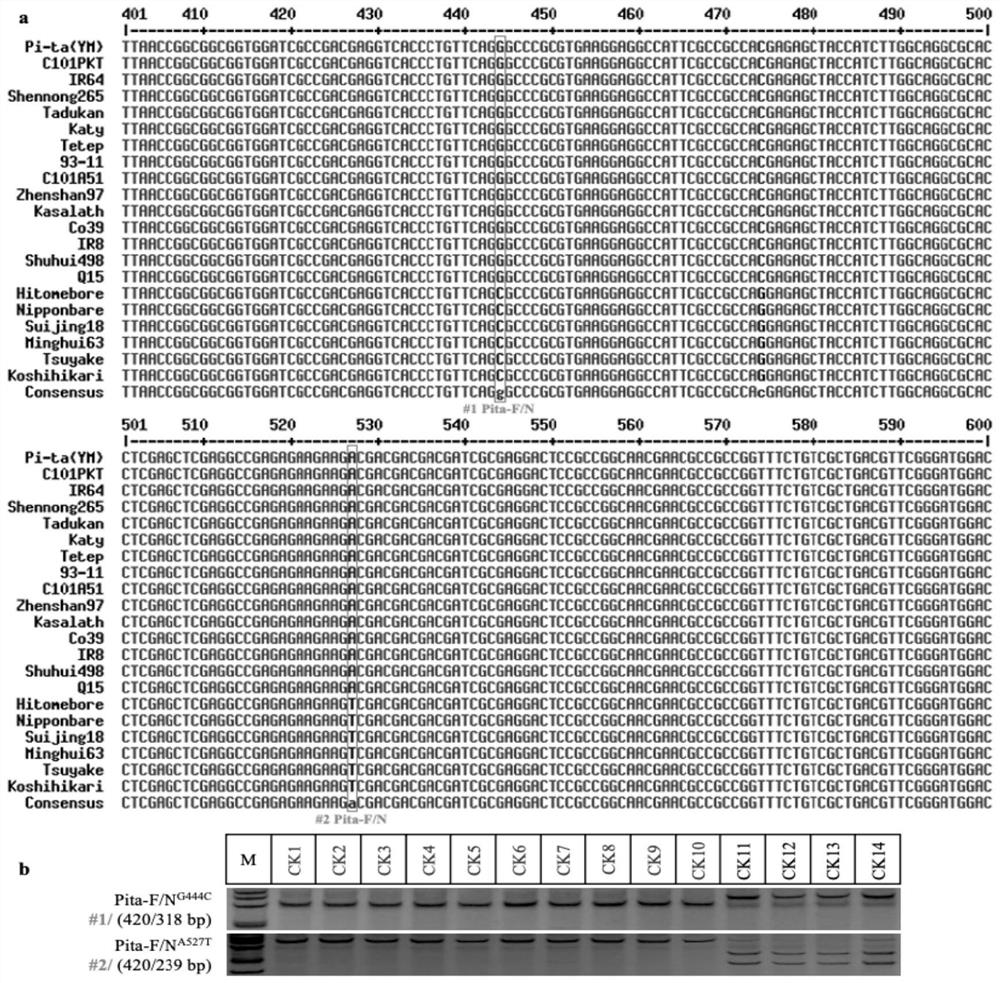
[0120] Example 2: Development and application of functional / non-functional haplotype-specific molecular markers of the Pita disease resistance gene family ( image 3 )
[0121] 1. Experimental method
[0122] The experimental method of this embodiment mainly refers to the papers published by the applicant (Yuan et al.2011, TheorAppl Genet 122:1017-1028; Zhai et al.2011, New Phytologist 189:321-334; Hua et al.2012, Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 125:1047-1055).
[0123] [The following references are the same as those mentioned above and will not be repeated here]
[0124] Briefly:
[0125] (1) Design of haplotype-specific molecular markers: According to the comparison results of the above-mentioned Pita disease resistance gene family sequences, two haplotype-specific optimal SNPs with clear functional / non-functional haplotype differentiation, According to the design principles of CAPS and dCAPS (derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences; Neff et al.2002, Trends in ...
Embodiment 3
[0157] Example 3: Development and application of the disease-resistant allele Pita-YM function-specific molecular marker of the functional haplotype of the Pita disease-resistant gene family ( Figure 4 )
[0158] 1. Experimental method
[0159] (1) Design of Pita-YM function-specific molecular markers: According to the alignment results of the above-mentioned Pita disease resistance gene family sequences, the optimal SNP was selected and designed as Pita-YM function-specific molecular markers Pita-YM T3387C (#3 marker); primer sequences are as follows:
[0160] For marker #3 (upper band, non-target gene; lower band, target gene):
[0161] SEQ ID NO.5 (Pita-YM T3387C -F; 5'-3'):
[0162] AAGTGTATGCCTTCCATTGCAGATTAT;
[0163] SEQ ID NO.6 (Pita-YM T3387C -R; 5'-3'):
[0164] ATCTTCAGATATCTCAGTTGTAACAGTTTA.
[0165] (2) Detection of Pita-YM function-specific molecular markers: Using the above pair of primers, perform PCR amplification on the 14 first set of reference vari...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com