Safflower mosaic disease pathogen detection and identification method
An identification method, mosaic disease technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve problems such as safflower yield and quality loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] dsRNA was obtained from safflower-susceptible plants showing typical mosaic leaves and necrotic spots in the safflower cultivation test field, and healthy safflower plants were used as controls.
[0037] The following steps are used for pathogen detection and identification:
[0038] (1) amplification, using primers to obtain the amplified product of recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) from the safflower sample; said primers include a first set of primers and a second set of primers, and the first set of primers includes The forward primer that NO:1 nucleotide sequence is made up and the reverse primer that is made up of SEQ ID NO:2 nucleotide sequence; The second group of primers includes the forward primer that is made up of SEQ ID NO:3 nucleotide sequence and A reverse primer consisting of the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:4;
[0039] (2) analyze the amplification product of RPA;
[0040] (3) Judgment is made on the analyzed amplification results. The occ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
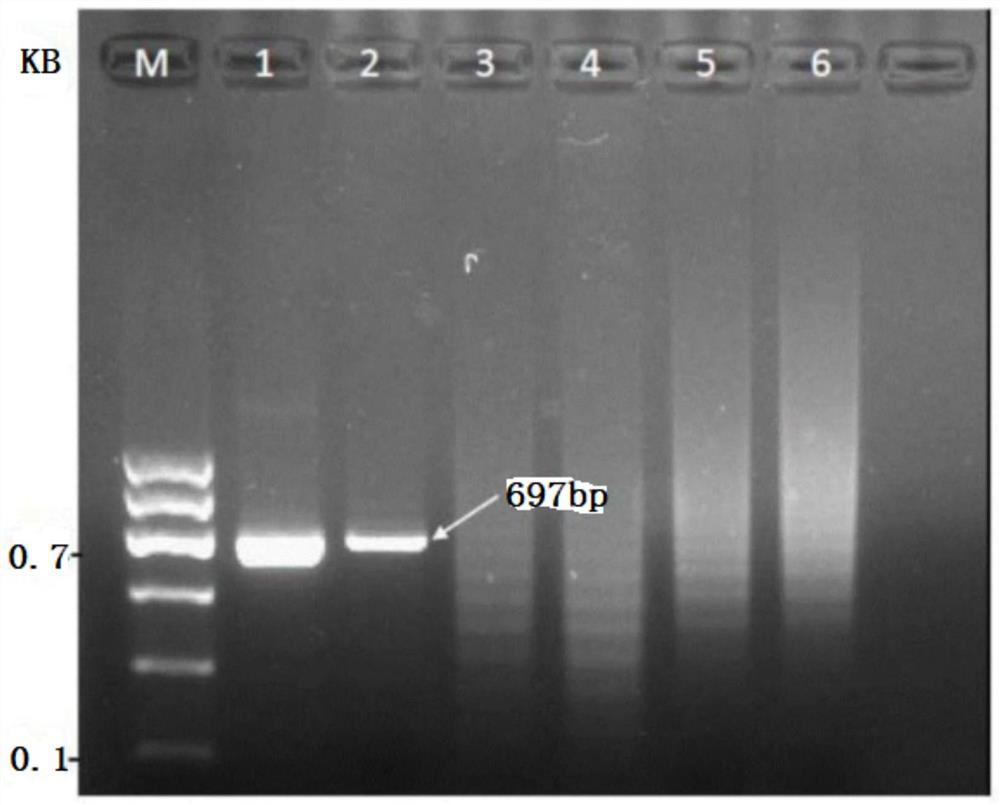
[0063] In the step (2), after the obtained RPA amplification product is recovered and purified by electrophoresis and gel slicing, healthy safflower is used as a negative control, and DL 1000 Marker is used as a standard molecular weight; electrophoresis at 120V / 90mA for 45min, and observed with an imaging system And take pictures.
[0064] When extracting dsRNA,
[0065] In step b, take the supernatant, add an equal volume of the above phenol / chloroform, centrifuge at 10,000 r / min at 4°C for 10 min, and repeat 3 times;
[0066] In step f, discard the supernatant, add 3mL binding solution, vortex mix, centrifuge at 4800r / min for 3min at 4°C; discard the supernatant and repeat 3 times.
[0067] The invention can scientifically and targetedly detect and identify pathogens, is fast and accurate, has good detection stability and strong specificity, can provide effective monitoring means for the health detection...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com